Gene element for accurately controlling gene rearrangement and recombinant plasmid and application thereof
A gene rearrangement and gene element technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of unfavorable control of gene rearrangement, and achieve the effect of avoiding leakage expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1: Effects of Gene Elements of the Present Invention and pSCW11-Cre-EBD on Synthetic Yeast Chromosome Growth
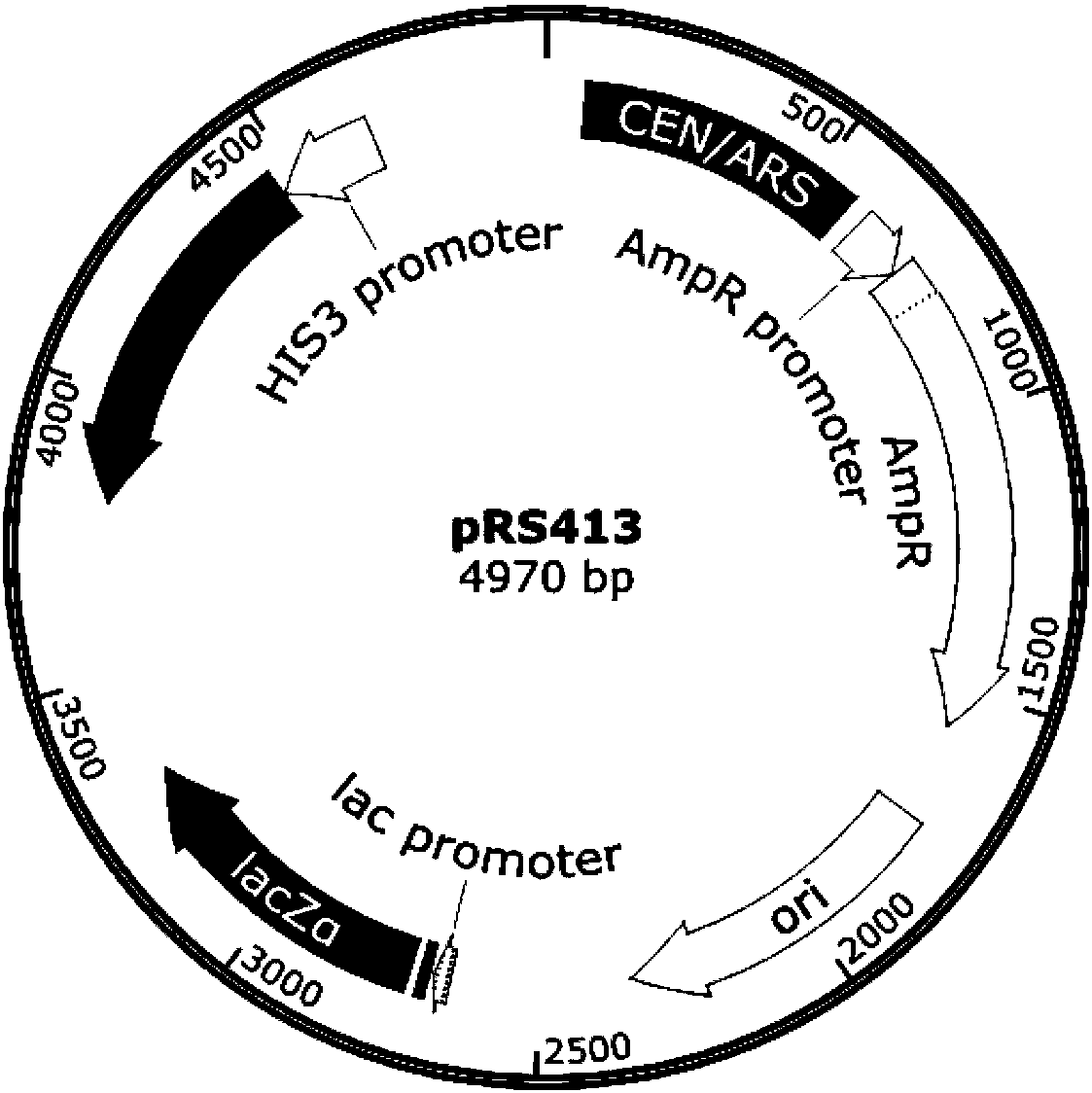
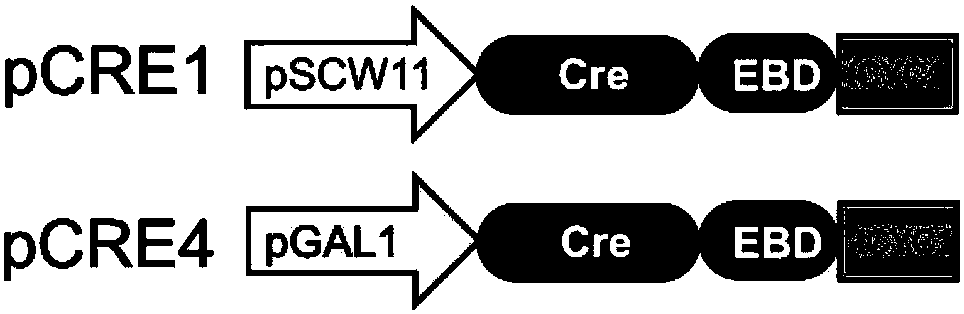
[0061] According to the gene sequences of the pGAL1 promoter, Cre-EBD fusion protein gene and tCYC1 terminator, the genetic elements of the present invention are artificially synthesized by sequential splicing (see the schematic diagram image 3), and connected to the pRS413 plasmid to obtain the recombinant plasmid pCRE4 (pGal1-Cre-EBD), see the plasmid map Figure 4 At the same time, according to the gene sequence of the pSCW11 promoter, the Cre-EBD fusion protein gene and the tCYC1 terminator, the artificially synthesized control gene elements were sequentially spliced (see the schematic diagram in image 3 ), and connected to the pRS413 plasmid to obtain the recombinant plasmid pCRE1 (pSCW11-Cre-EBD), see the plasmid map Figure 5 ;
[0062] Transform pCRE1 and pCER4 into synthetic synIII yeast and synthetic synV yeast (both synthetic chromosome...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2: Effects of Different Gene Elements on Chromosomal Gene Rearrangement in Synthetic Yeast
[0065] In order to compare the control of Cre activity by different promoters and different control methods, pCRE1 (pSCW11-Cre-EBD) and pCRE2 (pZEO1-Cre-EBD) were constructed in this example. For the plasmid map, see Figure 7 ), pCRE3 (pGAL1-Cre, see the plasmid map Figure 8 ) and pCRE4 (pGal1-Cre-EBD) four "switch" plasmids ( Figure 9 ), where pZEO1 is a constitutively expressed weak promoter, which is a comparative setting considering whether pSCW11 is too strong to cause leaky expression; the EBD junction domain of pCRE3 is removed. The above four "switch" plasmids and the control plasmid pRS413 were respectively transformed into the synthetic synV Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the recombinant strains pRS413-synV, pCRE1-synV, pCRE2-synV, pCRE3-synV and pCRE4-synV were cultured in glucose medium After culturing for 32 hours, samples were taken at intervals of 2 ho...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3: Effects of Gene Elements According to the Present Invention on Gene Rearrangement of Synthetic Yeast Chromosome in Different Induction Modes
[0068] In order to evaluate the performance of the gene elements of the present invention, pRS413-synV (control) and pCRE4-synV were cultivated under 4 different conditions in Example 2: (1) SC-His glucose medium; (2) with 1 μ M estradiol (3) SGal-His galactose medium; (4) SGal-His galactose medium supplemented with 1 μM estradiol. The growth curve was recorded by a microplate reader, and the doubling time of the yeast was calculated according to the formula.
[0069] Such as Figure 11 As shown, when the cells were cultured with SC-His glucose medium, there was no significant difference in passage time between pCRE4-synV and the control group. When 1 μM estradiol was added to the glucose medium, the generation time of pCRE4-synV was prolonged compared with the control group, which indicated that the pGAL1 promoter a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com