Noise and vibration sensing
A technology for sensing signals and noise control, applied in the direction of sounding equipment, active noise control, musical instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
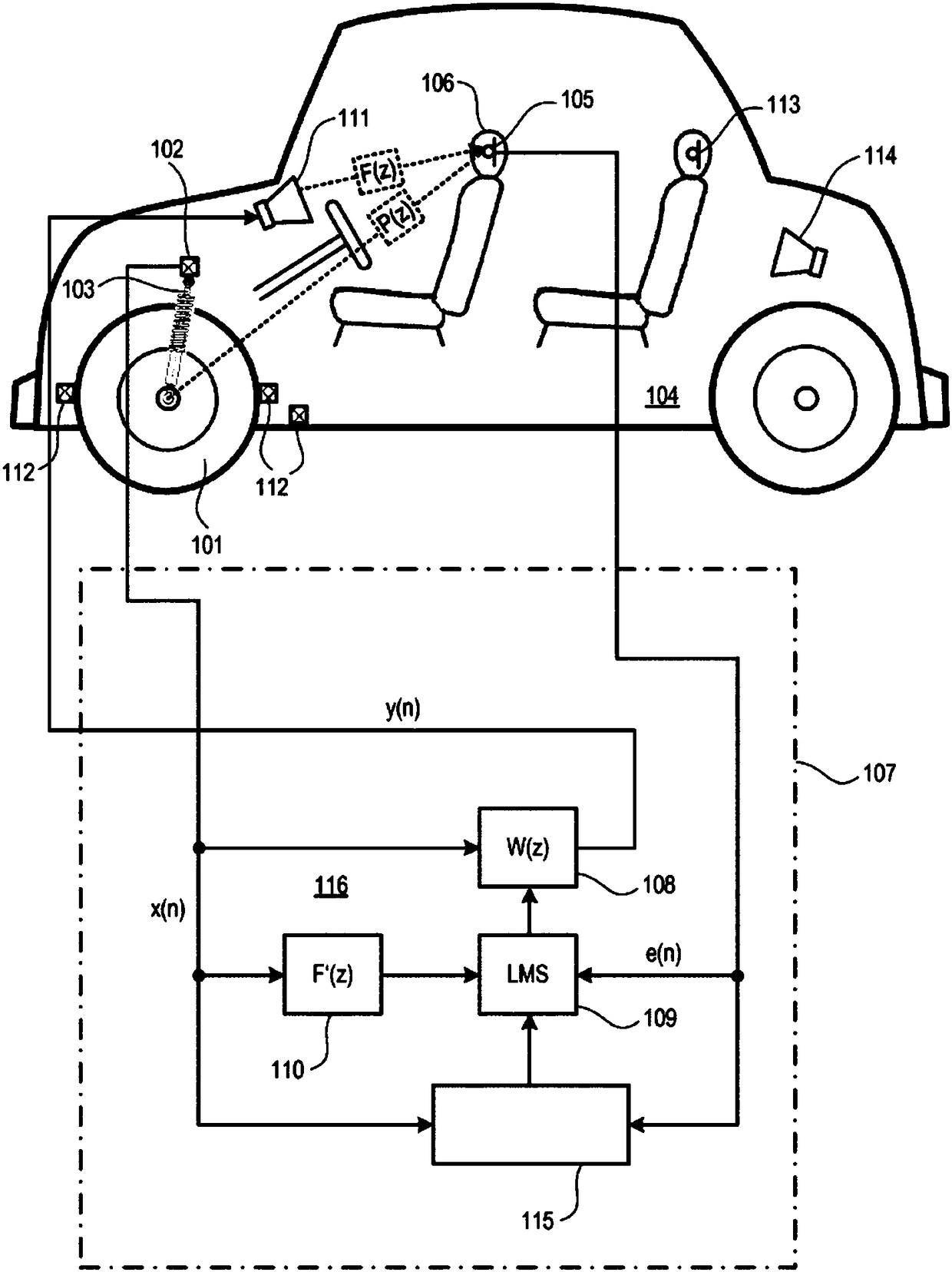
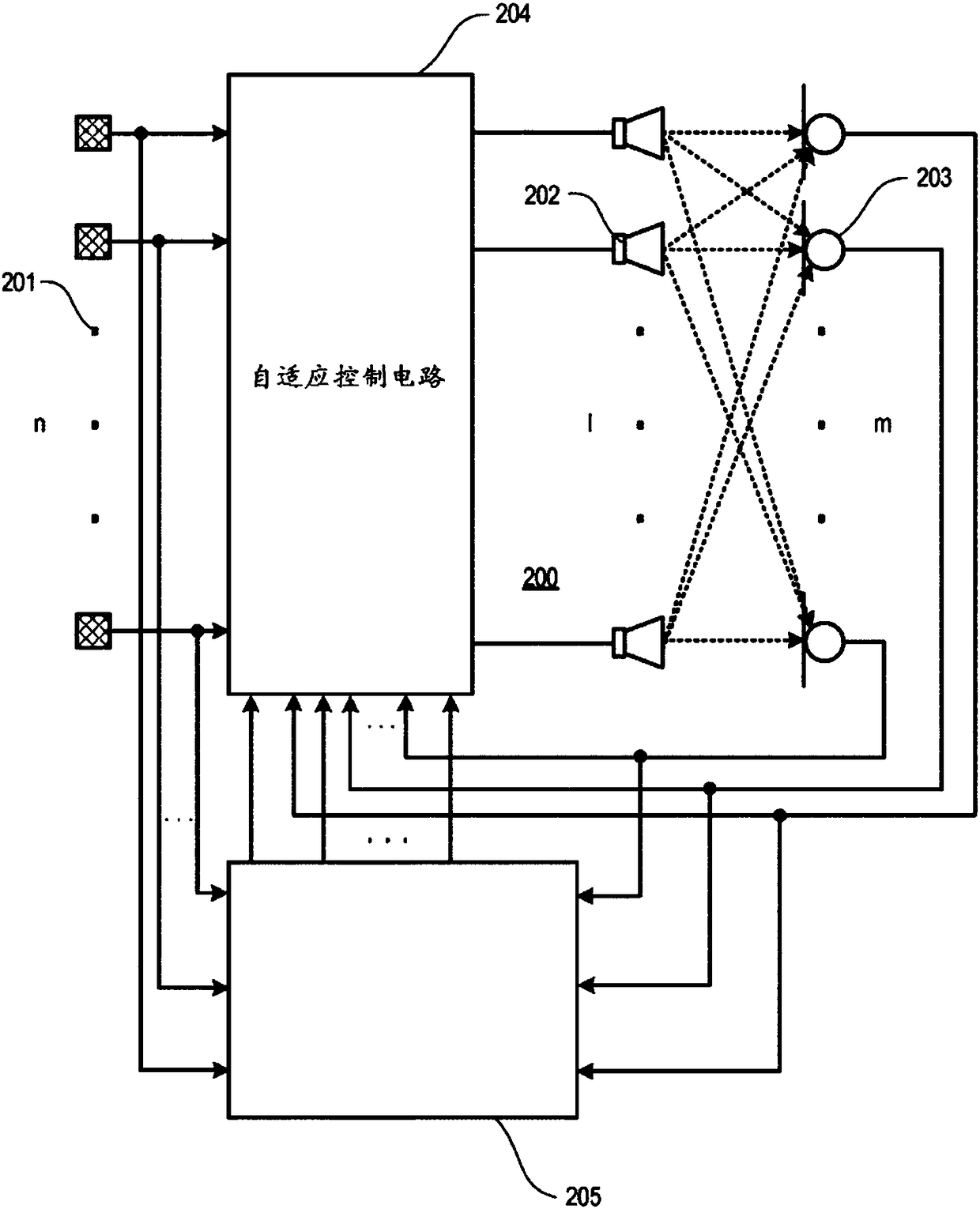
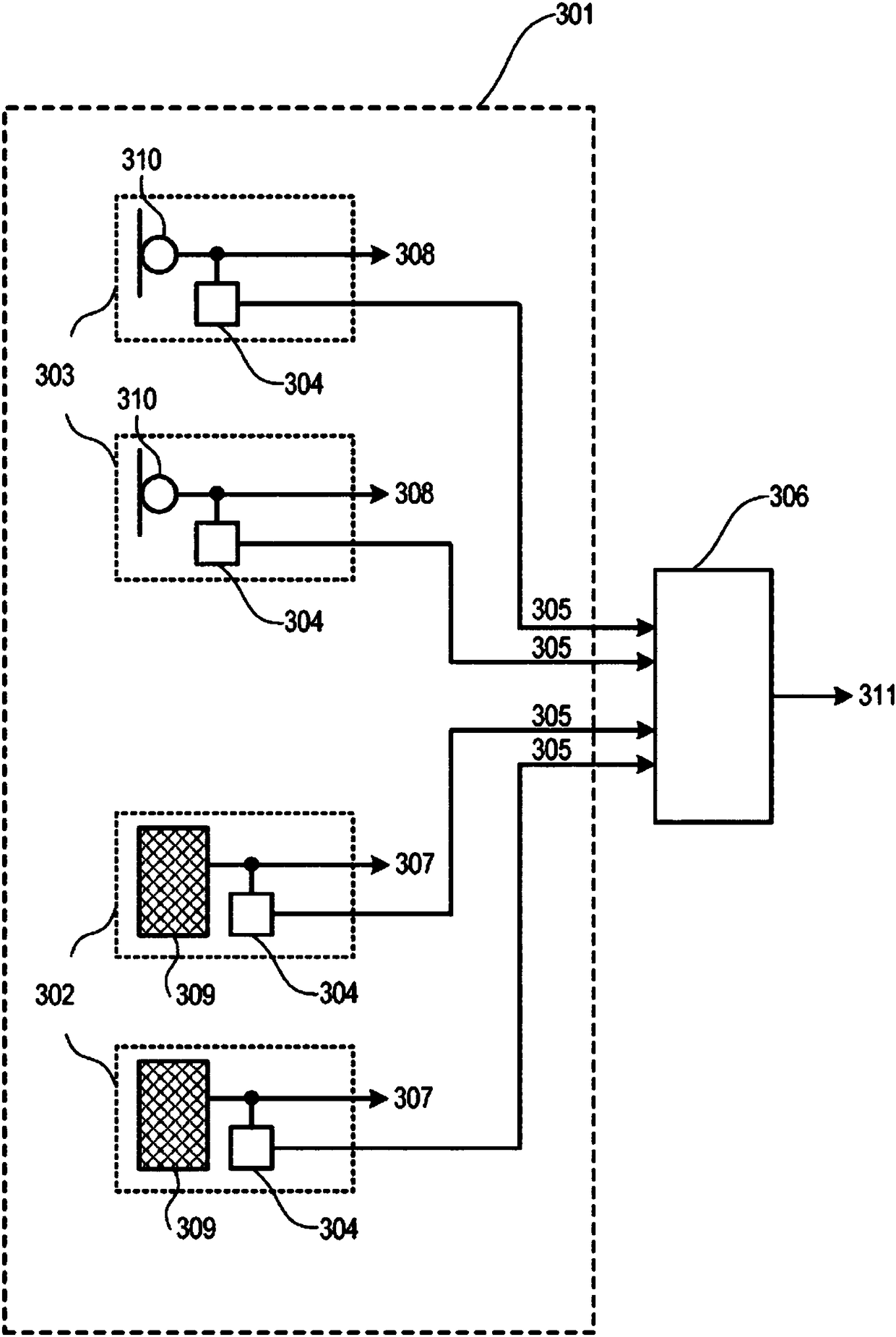
[0013] Noise and vibration sensors provide reference inputs to active road noise control (RNC) systems (eg, multi-channel feed-forward active RNC systems) as the basis for generating noise immunity that reduces or eliminates road noise. Noise and vibration sensors may include acceleration sensors such as accelerometers, force gauges, load cells, and the like. For example, an accelerometer is a device that measures intrinsic acceleration. Intrinsic acceleration and coordinate acceleration do not refer to the same concept, and coordinate acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Both single-axis and multi-axis models of accelerometers are available to detect the magnitude and direction of natural acceleration and can be used to sense orientation, coordinate acceleration, motion, vibration and shock.
[0014] Airborne and structure-borne noise sources are monitored by noise and vibration sensors to provide the highest possible road noise reduction (cancellation) performanc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com