Convex-difference-planning-based calculation method of maximum access capability of distributed power supply in distribution network
A technology of distributed power supply and access capability, applied in computing, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as the surge in computing time, the inability to meet the requirements of speed or accuracy at the same time, and the inability to guarantee the global optimality of the solution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
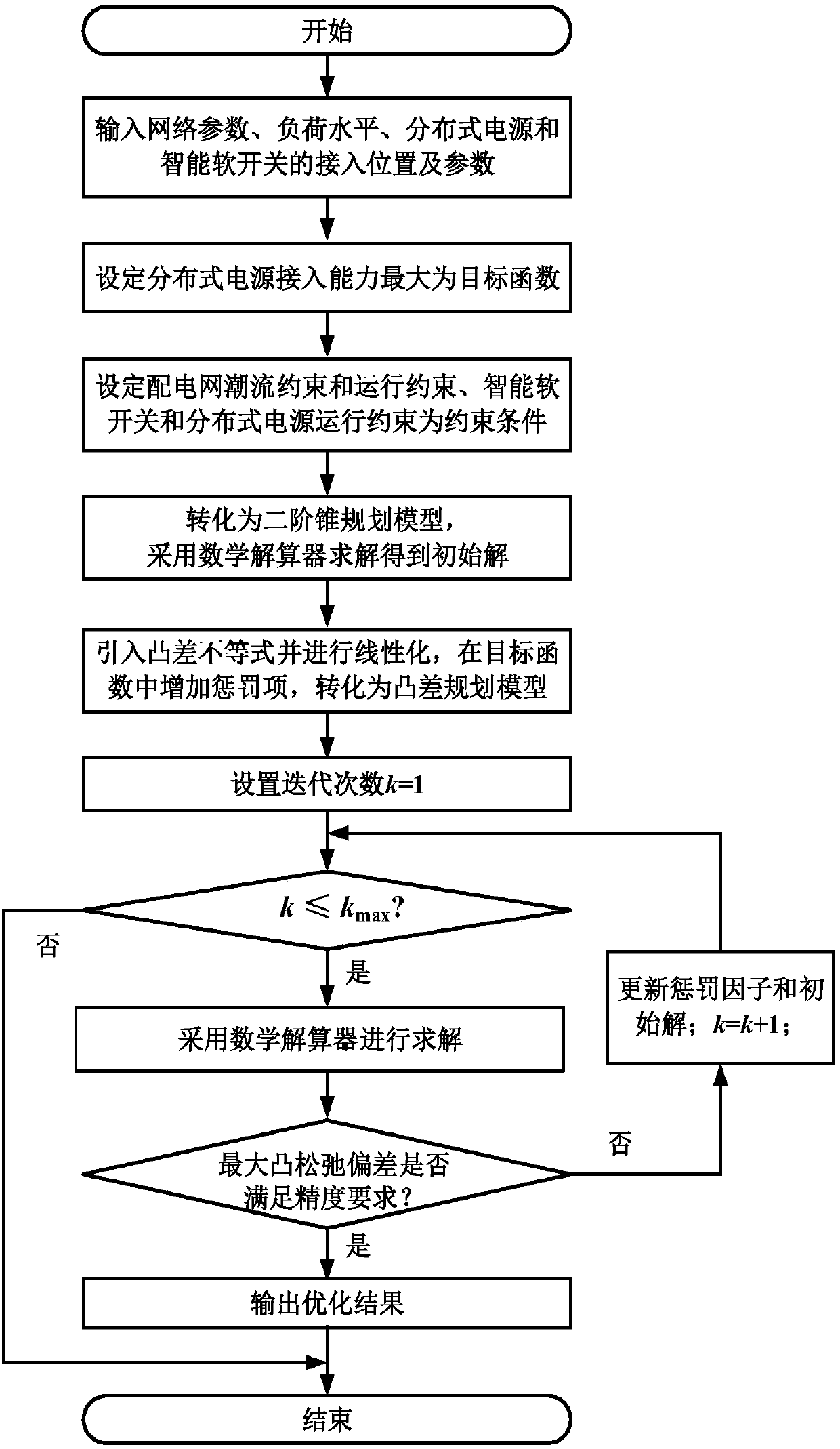
[0063] The method for calculating the maximum access capacity of a distributed power supply in a distribution network based on the convexity planning of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments and the accompanying drawings.
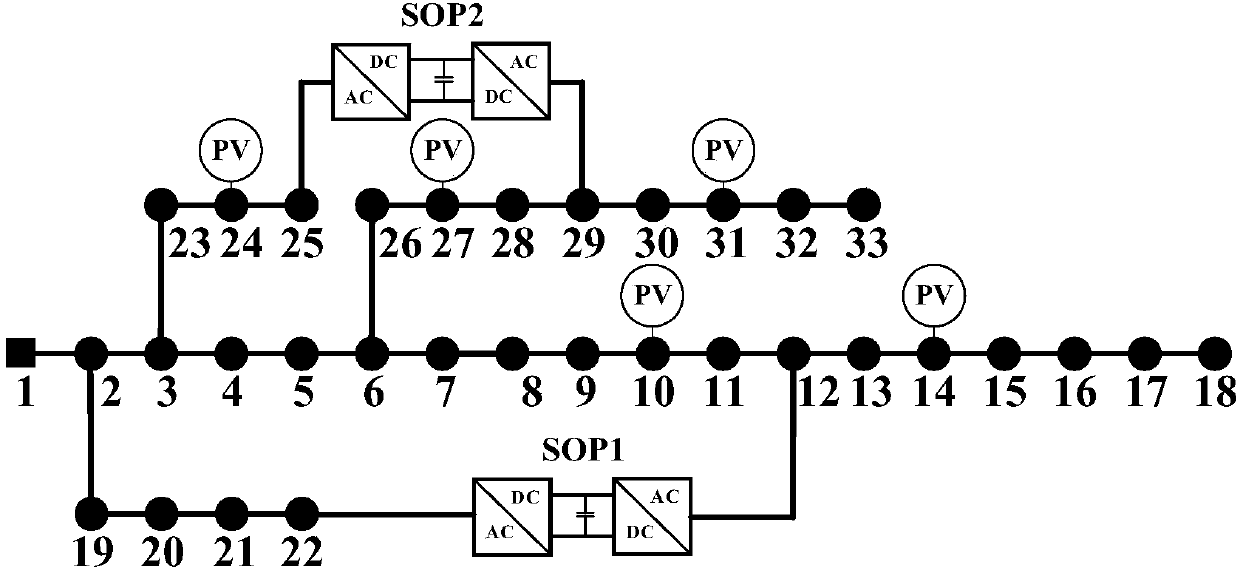
[0064] The calculation method of the maximum access capacity of distribution network distributed power supply based on convex difference planning of the present invention is used for the research on the maximum access capacity of distribution network distributed power supply, and can be solved by using MOSEK, CPLEX, GUROBI, etc. integrated on MATLAB solver. The present invention adopts CPLEX solver to solve the extended convex difference programming problem, with figure 2 The improved IEEE33 node test system shown is an example.
[0065] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for calculating the maximum access capacity of distribution network distributed power sources based on convexity planning in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com