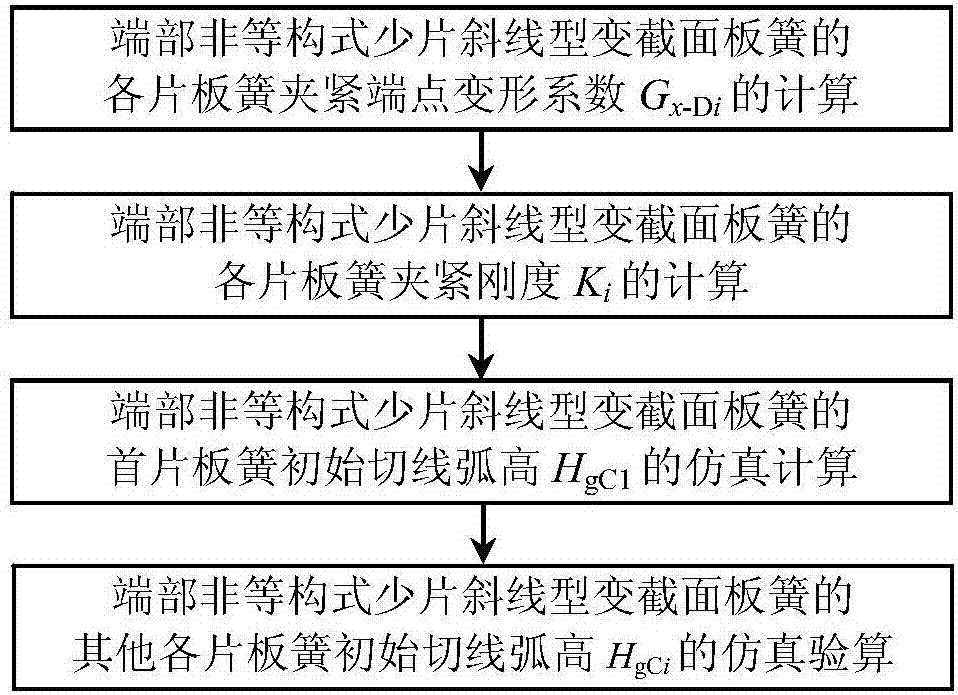
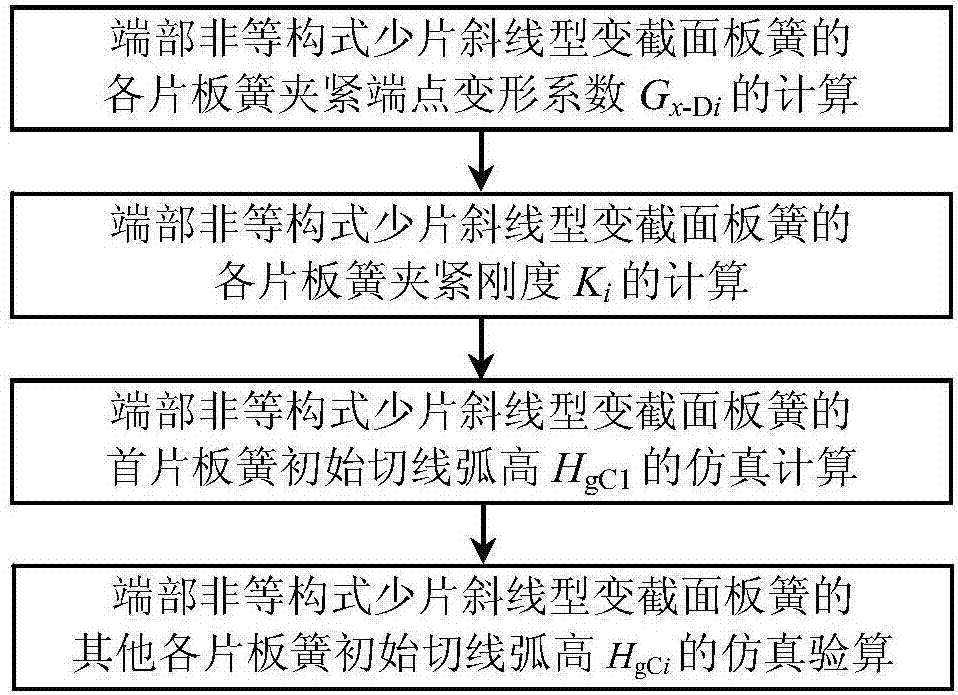
Simulation checking calculation method for original tangent camber heights of oblique-line-shaped variable-cross-section plate springs with different structural ends
A non-isostructural and oblique type technology, which is applied in the field of simulation test algorithm for the initial tangent arc height of the oblique type variable-section leaf spring, can solve the problem that the initial non-isostructural oblique type variable-section leaf spring has not been given. The simulation algorithm of tangent arc height, the calculation of the clamping stiffness of the slanted variable section leaf spring with unequal structure at the end and the complicated calculation of the clamping stiffness of the variable section leaf spring, can achieve the effect of speeding up product development, reducing design, development and test costs, and improving design level.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
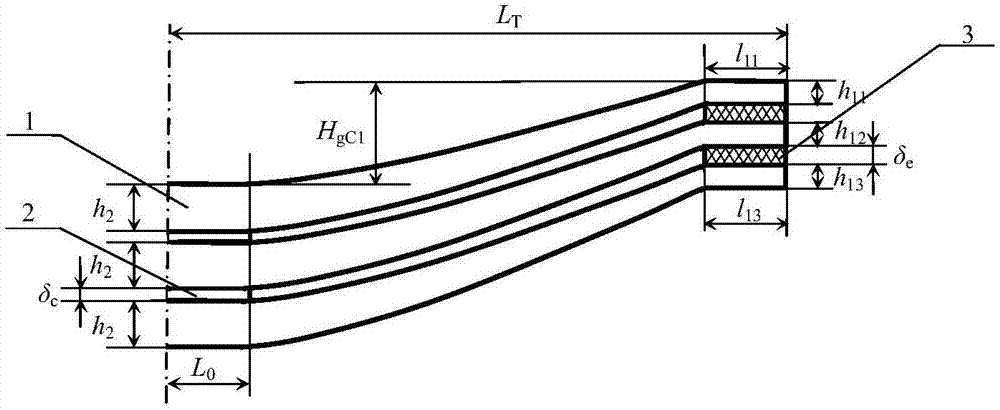
[0024] Example 1: half of the working length L of a non-equal-structured oblique-line type variable-section leaf spring at a certain end T =550mm, half the length L of the straight section of the root clamped by the saddle bolt 0 =50mm, width b=60mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa. The number of leaf springs n=3, the thickness h of the straight section at the root of each leaf spring 2 =12mm, the thickness of the straight section at the end is h 11 = 8mm, h 12 = 7mm, h 13 = 6 mm. The thickness ratios of the oblique segments of each leaf spring are β 1 =h 11 / h 2 =0.6667,β 2 =h 12 / h 2 = 0.5833, β 3 =h 13 / h 2 = 0.50. The design value H of the free tangent arc height of each leaf springg10 =95.2mm,H g20 =101mm, H g30 = 107.7 mm. Root gasket thickness δ c =3mm, end gasket thickness δ e = 6 mm. According to the number of leaf springs, elastic modulus, the thickness of the root gasket and the end gasket, the structural parameters of each leaf spring and the design va...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: the width b=60mm of a non-equal few-piece slanted-line variable-section leaf spring at a certain end, and half the effective length L T =550mm, half the length L of the straight section of the root clamped by the saddle bolt 0 =50mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa. The number of leaf springs n=4, the thickness h of the straight section at the root of each leaf spring 2 = 14mm, the thickness h of the straight section at the end 11 = 9mm, h 12 = 8mm, h 13 = 7mm, h 14 = 6 mm. The thickness ratios of the oblique segments of each leaf spring are β 1 =h 11 / h 2 = 0.6429, β 2 =h 12 / h 2 = 0.5714, β 3 =h 13 / h 2 =0.50,β 4 =h 14 h 2 = 0.4286. The design value of the free tangent arc height of each leaf spring is H g10 =90.4mm, H g20 =95.4mm,H g30 =99.7mm,H g40 = 104.7mm. Root gasket thickness δ c =3mm, end gasket thickness δ e = 6 mm. According to the number of leaf springs, elastic modulus, the thickness of the root gasket and the end gasket, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Half length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com