A low-abundance gene mutation enrichment method based on the removal of wild-type sequences
A wild-type, low-abundance technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as undetectable DNA mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0017] 1. Sample DNA extraction
[0018] The DNA of the sample can be extracted using the CTAB method, of course, the DNA of the sample can also be extracted using a DNA extraction kit, and the extraction steps refer to the corresponding instructions.
[0019] 2. Sample processing
[0020] The extracted sample DNA is processed according to the method of the present invention, specifically:
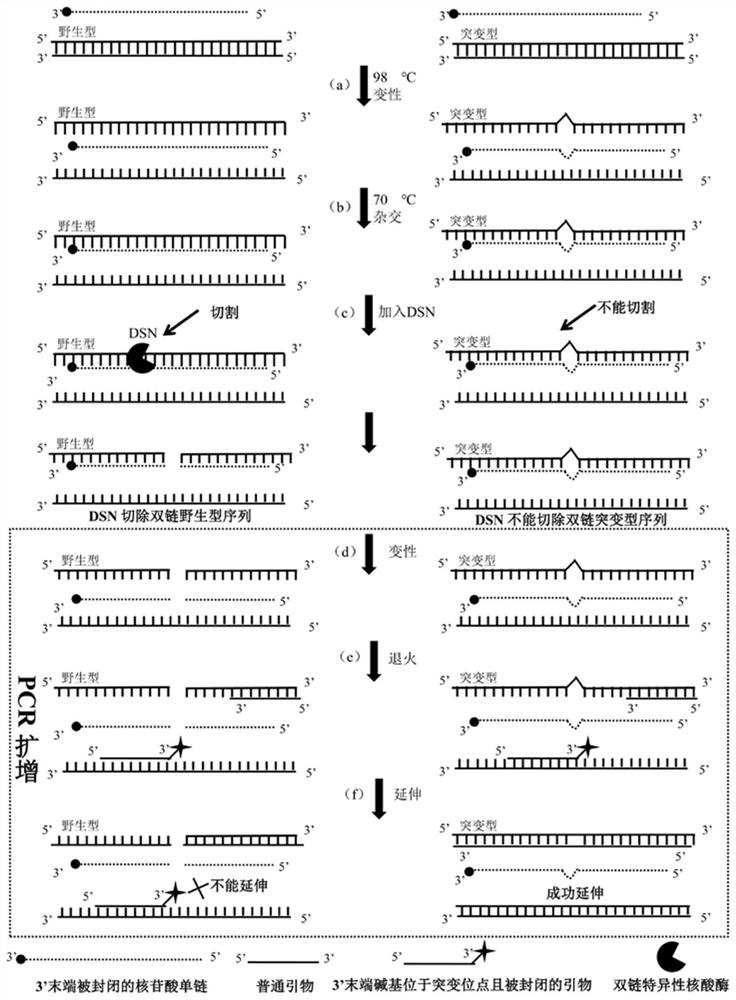
[0021] ①Hybridization: Mix the sample DNA with the hybridized strand to form a hybridization mixture, and denature it at high temperature (usually above 94 degrees Celsius for at least 2 minutes) to melt the sample DNA from double-stranded DNA to single-stranded DNA (such as figure 1 (a) in step), and then lower the temperature (usually to about 70 degrees Celsius for 1-2 minutes) to make the hybridized strand and the wild-type sequence in the melted single-stranded DNA form a completely complementary paired homologous double-stranded DNA and Non-perfectly complementary heteroduplex DNA ...
Embodiment
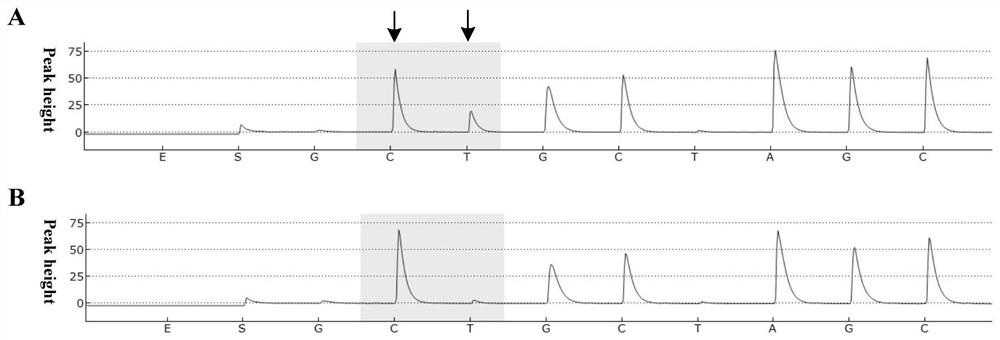
[0028] Example: Enrichment and detection of low-abundance mutation samples (5% mutation content)
[0029] In order to verify the feasibility of the method of the present invention in actual samples, a sample with a mutation content of 5% was used for identification. In this embodiment, the samples were subjected to (1) digestion with double-strand specific nuclease by the method of the present invention, followed by PCR amplification with the primers of the present invention and (2) without any treatment, and then with common primers Perform PCR amplification. The enrichment effect of the amplified products was detected and compared with a pyrosequencing platform. The specific method is:
[0030] 1. Sample preparation
[0031] A wild-type plasmid and a mutant plasmid were constructed by a biotechnology company, and the mutation sites corresponding to the two plasmids were G>A. A plasmid mixture of the mutant plasmid and the wild-type plasmid was then prepared, wherein the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com