Malicious encrypted network traffic identification using fourier transform
A technology of Fourier transform and network flow, which is applied in the detection field of malicious network transmission, and can solve problems such as the incorrect operation of the automatic malicious program detection system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] figure 1 is a block diagram of a computer system suitable for operation of embodiments of the invention. Central processing unit (CPU) 102 is communicatively connected to storage 104 and input / output (I / O) interface 106 via data bus 108 . The storage section 104 may be any read / write storage device such as a random access memory (RAM) or a non-volatile storage device. Examples of non-volatile storage devices include magnetic disk or tape storage devices. The I / O interface 106 is an interface to a device for data input or data output, or both. Examples of I / O devices connectable to I / O interface 106 include keyboards, mice, displays (such as monitors), and network connections.
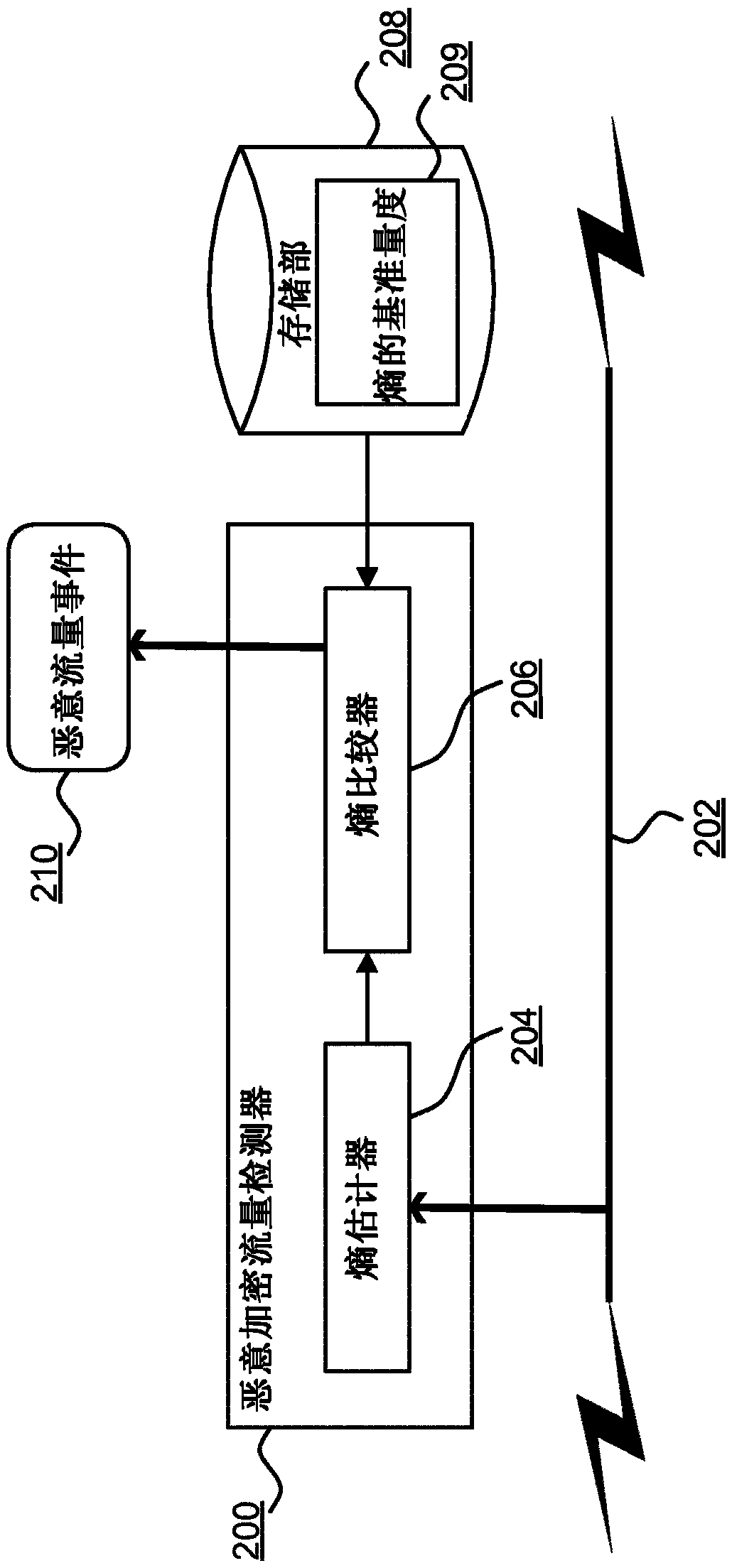
[0053] figure 2 is a component diagram of a malicious encrypted traffic detector 200 according to an embodiment of the present invention. Detector 200 is a software, hardware, or firmware component for monitoring network traffic communicated over computer network 202 and for generating mali...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com