Method for improving replacement soil to increase yield of potatoes in newly-added cultivated land of loess hilly region
A potato and soil-removing technology, applied in the fields of agriculture and land engineering, can solve problems such as the inability to effectively increase potato yield, and achieve the effects of improving soil water permeability, increasing yield, and increasing fertilizer utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
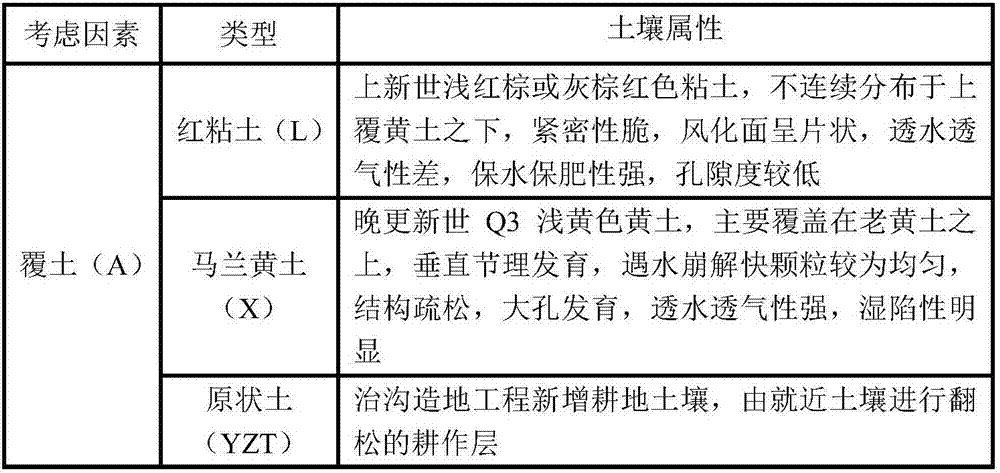
[0029] Firstly, the test field is selected, the area of the test field is measured, and the amount of foreign soil is calculated according to the area of the test field and the thickness of the prepared covering soil. In this embodiment, take Malan loess 5cm (X5), red clay (L5), and undisturbed soil (YZT) respectively, and plant 3 unit areas of each type of covering soil and thickness (that is, the standard test field size, which can be selected according to needs, such as Can be selected as 100 square meters or 1 mu), the first unit area is applied with farmyard manure, the second unit area is applied with compound fertilizer, and the third unit area is applied with a mixture of farmyard manure and compound fertilizer.
[0030] The selected potato variety is Kexin No. 1, a mid-maturity variety with a growth period of about 100 days. Strong drought resistance, suitable for cultivation in arid areas. The average output is generally 1500 kg, and the high output can reach mo...
Embodiment 2
[0039] In the present embodiment, take Malan loess 10cm (X10) respectively; Red clay 10cm (L10); Every kind of covering soil type and thickness plant 3 unit areas (that is, the size of the standard test field, which can be selected according to needs, for example, can be selected as 100 square meters or 1 mu), the first unit area is applied with farmyard manure, the second unit area is applied with compound fertilizer, and the third unit area is applied with a mixture of farmyard manure and compound fertilizer.
[0040] In order to better compare the effect of various soil amendments on potato yield, the experiments were carried out on basically homogeneous land, and the test plots were spaced at a certain distance from each other.
[0041] In this embodiment, the selection of potato varieties, sowing and harvesting time are all the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0042] table 3
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] As can be seen from this example, the effect of utilizing Malan loess ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] In the present embodiment, take Malan loess 15cm (X15) respectively; Red clay 15cm (L15); Every kind of covering soil type and thickness plant 3 unit areas (that is, the standard test field size, which can be selected according to needs, for example, can be selected as 100 square meters or 1 mu), the first unit area is applied with farmyard manure, the second unit area is applied with compound fertilizer, and the third unit area is applied with a mixture of farmyard manure and compound fertilizer.
[0048] In order to better compare the effect of various soil amendments on potato yield, the experiments were carried out on basically homogeneous land, and the test plots were spaced at a certain distance from each other.
[0049] In this embodiment, the selection of potato varieties, sowing and harvesting time are all the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0050] Table 4
[0051]
[0052]As can be seen from this example, the effect of utilizing Malan loess for soil improvement...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com