Depth pedestrian re-identification method based on positive sample balance constraint
A technology of balanced constraints and positive samples, applied in the field of deep learning and pedestrian re-identification, can solve the problems of fewer hidden layers and not deep networks, etc., achieve the effects of simple network structure, improved structural loss, and enhanced feature expression ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
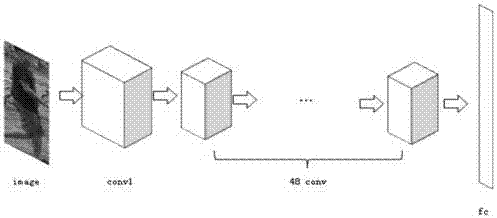
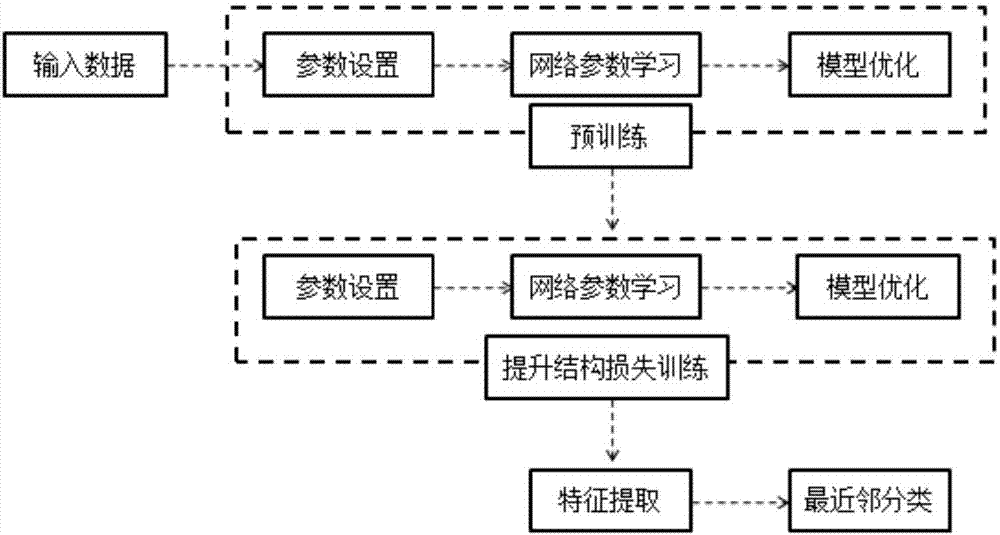
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, a deep pedestrian re-identification method based on positive sample balance constraints includes the following steps:
[0042] S1: Input Data Training Dataset in, N is the number of samples, d is the image pixel, c is the number of different pedestrians in the training set, x i is a d-dimensional column vector, y i =[y i1 ,y i2 ,y i3 ,...,y ic ] T is a c-dimensional column vector with elements equal to 1 or 0, and X=[x 1 ,x 2 ,x 3 ,...,x N ], X is a matrix of d rows and N columns;
[0043] S2: Use the softmax classification model to pre-train the network;
[0044] S3: Train the network using the lifting structure loss;
[0045] S4: performing feature extraction on the test sample image;
[0046] S5: Use the obtained features to perform nearest neighbor KNN classification on the test samples to obtain re-identification results.
[0047] The concrete process of step S2 is:
[0048] Set the training learning rate η and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com