Screening method for erythrocyte osmotic fragility and application of the same
A technology of osmotic fragility and screening methods, applied in the field of medical testing, can solve the problems of expensive operation and complexity of equipment, achieve good repeatability, fast and accurate experiments, and reduce the screening workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
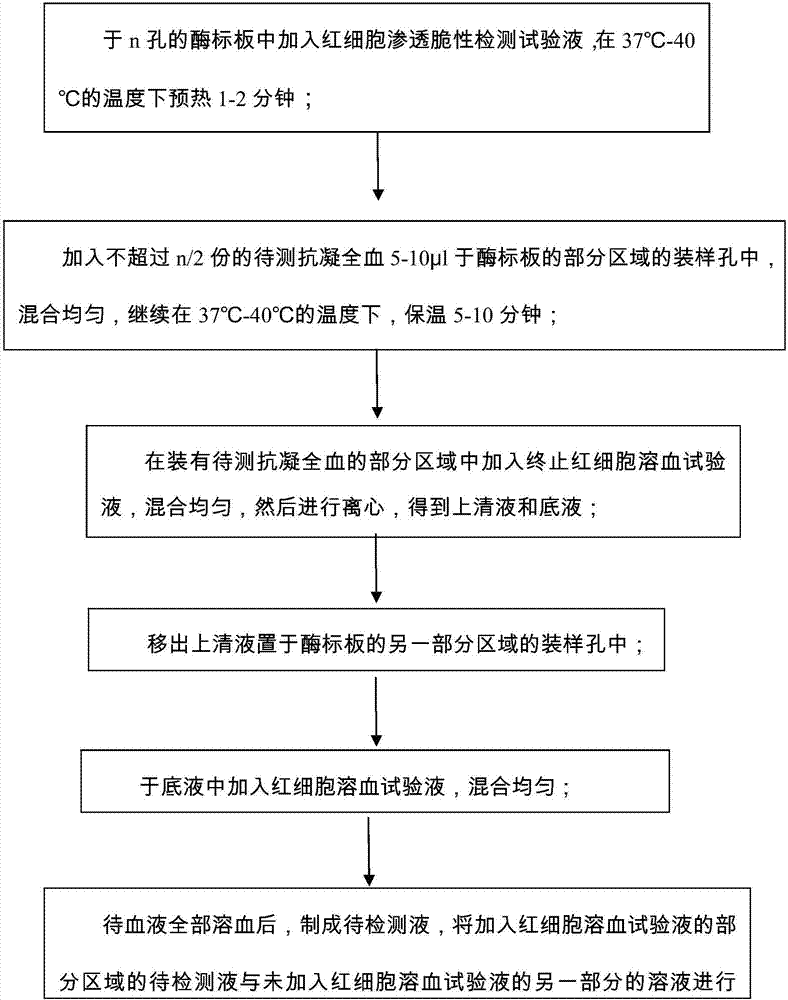
[0062] Experimental operation method:
[0063] 1. Take a 48-well ELISA plate, add 0.5ml of erythrocyte osmotic fragility test solution, and preheat at 37°C for 1 minute.
[0064] 2. Add 5 μl of anticoagulated whole blood to be tested (add up to 24 samples to be tested in each 48-well plate), mix immediately, and continue to incubate at 37°C for 5 minutes.
[0065] 3. After 5 minutes, add 0.5 ml of test solution for terminating red blood cell hemolysis, mix well, and centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes.
[0066] 4. Use a pipette gun to take 100 μl of the supernatant and add them to the other 24 wells of this plate in sequence, and add water to 200 μl / well. Then discard the remaining supernatant (do not disturb the red blood cells at the bottom of the tube).
[0067] 5. Add 200 μl / well of erythrocyte hemolysis test solution to the original wells, mix well, and after the blood is completely hemolyzed (transparent red), the enzyme-linked colorimeter is used for colorimetry on t...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Experimental operation method:
[0073] 1. Take a 48-well ELISA plate, add 0.5ml of erythrocyte osmotic fragility test solution, and preheat at 40°C for 2 minutes.
[0074] 2. Add 5 μl of anticoagulated whole blood to be tested (add up to 24 samples to be tested for each 48-well plate) and mix immediately, and continue to incubate at 40°C for 10 minutes.
[0075] 3. After 5 minutes, add 0.5 ml of test solution for terminating red blood cell hemolysis, mix well, and centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 6 minutes.
[0076] 4. Use a pipette gun to take 100 μl of the supernatant and add them to the other 24 wells of this plate in sequence, and add water to 200 μl / well. Then discard the remaining supernatant (do not disturb the red blood cells at the bottom of the tube).
[0077] 5. Add 200 μl / well of erythrocyte hemolysis test solution to the original wells, mix well, and after the blood is completely hemolyzed (transparent red), the enzyme-linked colorimeter is used for colorimetr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com