Sulfate reducing bacterium capable of achieving heavy metal settling and application of sulfate reducing bacterium
A heavy metal and sulfate technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of poor heavy metal ion treatment capacity and less than 90% removal rate, and achieve the effect of good heavy metal sedimentation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Enrichment of sulfate-reducing bacteria from soil, waste water, and paddy fields
[0037] (1) Sample collection: When collecting soil samples, first dig out the surface soil, discard the upper surface soil, collect soil samples below 5cm of the soil surface, put the collected soil samples into a ziplock bag, and remove the air in the ziplock bag , to ensure the anaerobic environment required by sulfate-reducing bacteria. When collecting samples in wastewater and paddy fields, collect samples at the bottom of the wastewater and paddy fields, it is best to collect the wastewater and the water-mud mixture at the bottom of the paddy fields together, then put them into a bottle with a cover, fill the sample to the drain The air in the bottle ensures the anaerobic state required by sulfate reducing bacteria.
[0038] (2) Enrichment of samples: After processing the collected samples, take a little and put them into SRB liquid medium to enrich the bacteria. After 7-8...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The characteristic identification of embodiment 2 sulfate-reducing bacteria
[0044] (1) Cell morphology observation and staining reaction:
[0045] After inoculation of sulfate-reducing bacteria and constant temperature culture of solid medium for a suitable time, staining and microscopic examination.
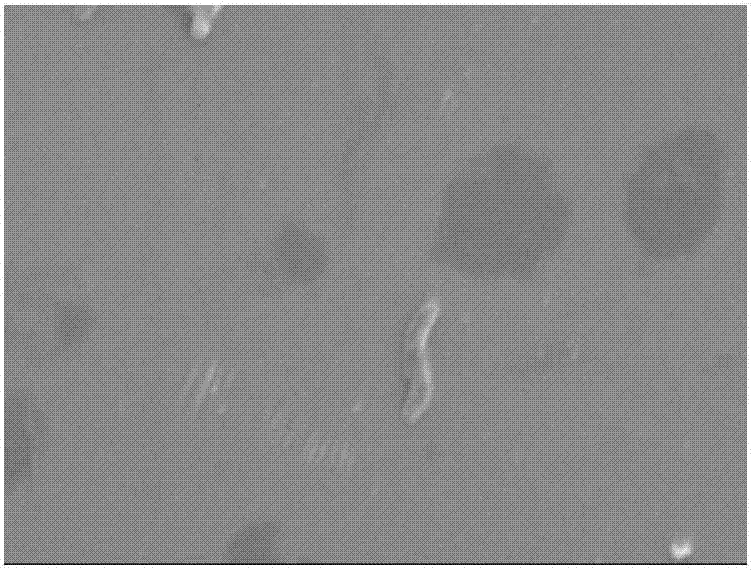
[0046] Staining and microscopic examination results: Sulphate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp.SRB-L) is an arc-shaped (rod-shaped) bacterium, Gram-negative, and the length of the bacteria is about 1.5-3.5 μm.
[0047] (2) Identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp.SRB-L) by comparative analysis of 16s rDNA:
[0048] Amplification and sequencing primers:
[0049] Forward primer: TLHJ-F 5’—AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAGA—3’
[0050] Reverse primer: TLHJ-R 5'—CAACTTCATGCAGTCGAGTTG—3'
[0051] Extract the total DNA of sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp. Sequencing was performed, and the 16s rDNA gene sequence of the strain is sho...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp.SRB-L) to the sedimentation performance of heavy metal ions (1) sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp.SRB-L) to heavy metal ions Cu 2+ Settling performance
[0054] Prepare copper sulfate mother liquor, add 10% sulfate-reducing bacteria SRB-L (Desulfovibrio sp. Atomic Absorption Determination of Cu in Supernatant 2+ content.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com