Thermally enhanced semiconductor assembly with heat spreader and integrated dual build-up circuitries and method of making the same
A technology for semiconductors and heat sinks, which is used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Figure 1-26 It is a diagram of a manufacturing method of a semiconductor component in the first embodiment of the present invention, which includes a semiconductor element 13 , a heat sink 20 , a first build-up circuit 110 and a second build-up circuit 310 .
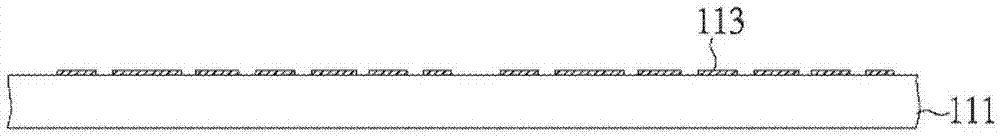
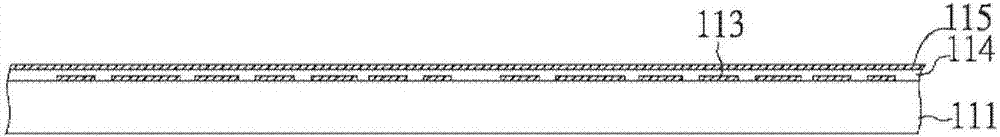
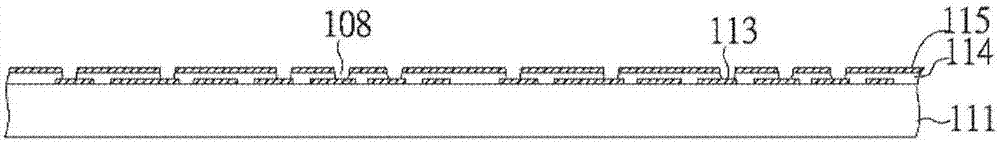
[0104] figure 1 is a cross-sectional view of the first contact pad 113 deposited on the sacrificial carrier 111 . The sacrificial carrier 111 is generally made of any conductive or non-conductive material, such as copper, nickel, aluminum, chromium, tin, iron, stainless steel, silicon, glass, graphite, plastic film, or other metals, alloys or non-metallic materials. The thickness of the sacrificial carrier 111 is preferably 0.1 to 10 mm. In this embodiment, the sacrificial carrier 111 is made of ferrous material and has a thickness of 1.0 mm. The first contact pads 113 are typically made of copper and can be patterned deposited by various techniques such as electroplating, electroless plating, evaporation, spu...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Figure 27-36 It is a diagram of another manufacturing method of a semiconductor device in the second embodiment of the present invention, wherein a positioning member is provided outside the cavity of the heat sink, and the heat sink is also electrically coupled to the second build-up circuit.
[0127] For the purpose of brief description, any descriptions in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 that can be used for the same application are incorporated here, and it is not necessary to repeat the same descriptions.
[0128] Figure 27It is a cross-sectional view of the heat sink 20 , which is provided with a positioning member 213 around the entrance of the cavity 211 . The positioning member 213 can be formed by removing a selected portion of the metal plate 21 , or by depositing a metal material or a plastic material by patterning on the metal plate 21 . The positioning member 213 is usually made by electroplating, etching, mechanical cutting or lamination steps. Acco...
Embodiment 3
[0140] Figure 37-46 It is a diagram of a manufacturing method of a semiconductor component using a laminated substrate as a heat sink in the third embodiment of the present invention.
[0141] For the purpose of brief description, any descriptions in the above embodiments that can be used for the same application are incorporated here, and the same descriptions do not need to be repeated.
[0142] Figure 37 and 38 It is a cross-sectional view of the manufacturing process of the positioning member according to an embodiment of the present invention, which is formed on the dielectric layer of the laminated substrate.
[0143] Figure 37 is a cross-sectional view of a laminated substrate, which includes a metal plate 21 , a dielectric layer 23 , and a metal layer 25 . The dielectric layer 23 is sandwiched between the metal plate 21 and the metal layer 25 . The dielectric layer 23 is generally made of epoxy, glass epoxy, polyimide, or the like, and has a thickness of 50 mic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com