Pedestrian re-identification method based on double constraint metric learning and sample reordering
A technology of pedestrian re-identification and metric learning, applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification based on double-constrained metric learning and sample reordering, which can solve the problems of only considering cross-camera correlation information and ignoring the correlation of different pedestrian pictures.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
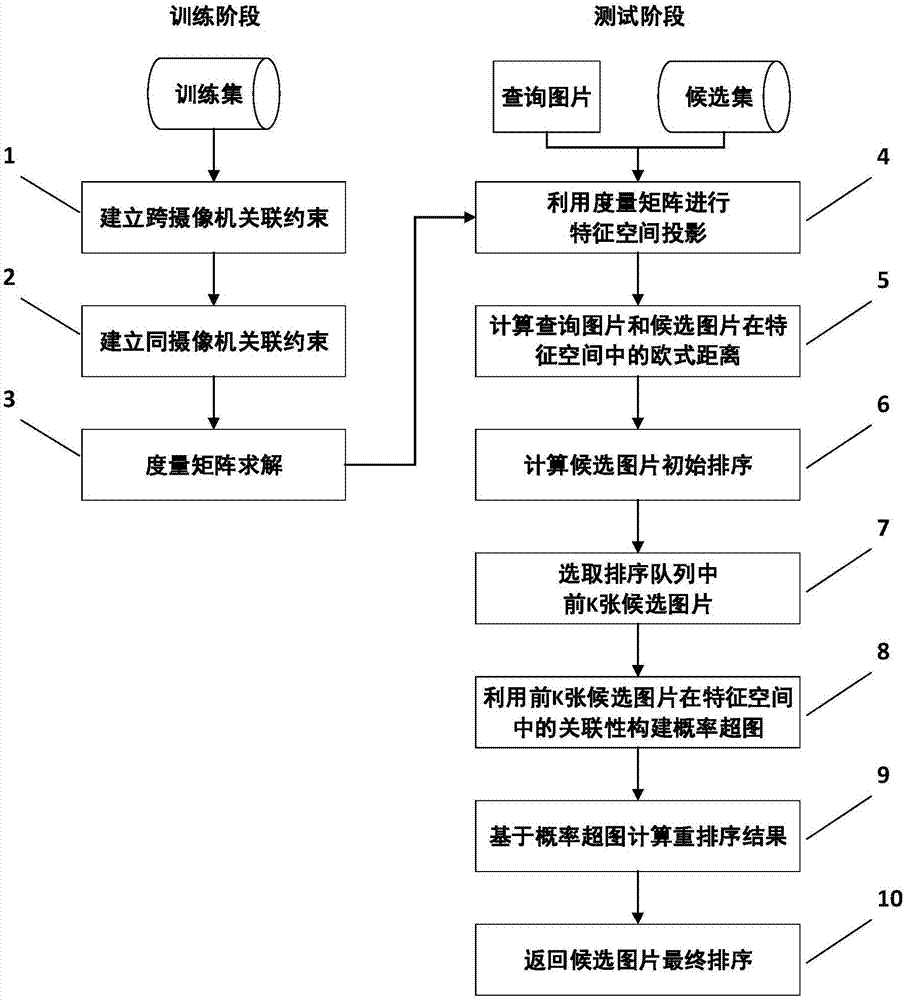
[0076] In this embodiment, pedestrian images captured by different cameras are processed, a metric matrix is learned through the training set, and a query image of a certain pedestrian target is used in the test phase to find the correct matching of pedestrian targets in the candidate sets captured by different cameras. figure 1 , in an embodiment of the present invention, including two stages of training and testing;
[0077] The training phase includes the following steps:
[0078] Step 1. Establish cross-camera association constraints: Use pedestrian images from different cameras in the training set to form cross-camera sample pairs, and establish constraints so that the feature distance between cross-camera positive sample pairs is smaller than the cross-camera negative sample pair. Feature distance between pairs , which includes the following sub-steps:
[0079] Step 1.1, define training images from different cameras as query sets and candidate set where x i and y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com