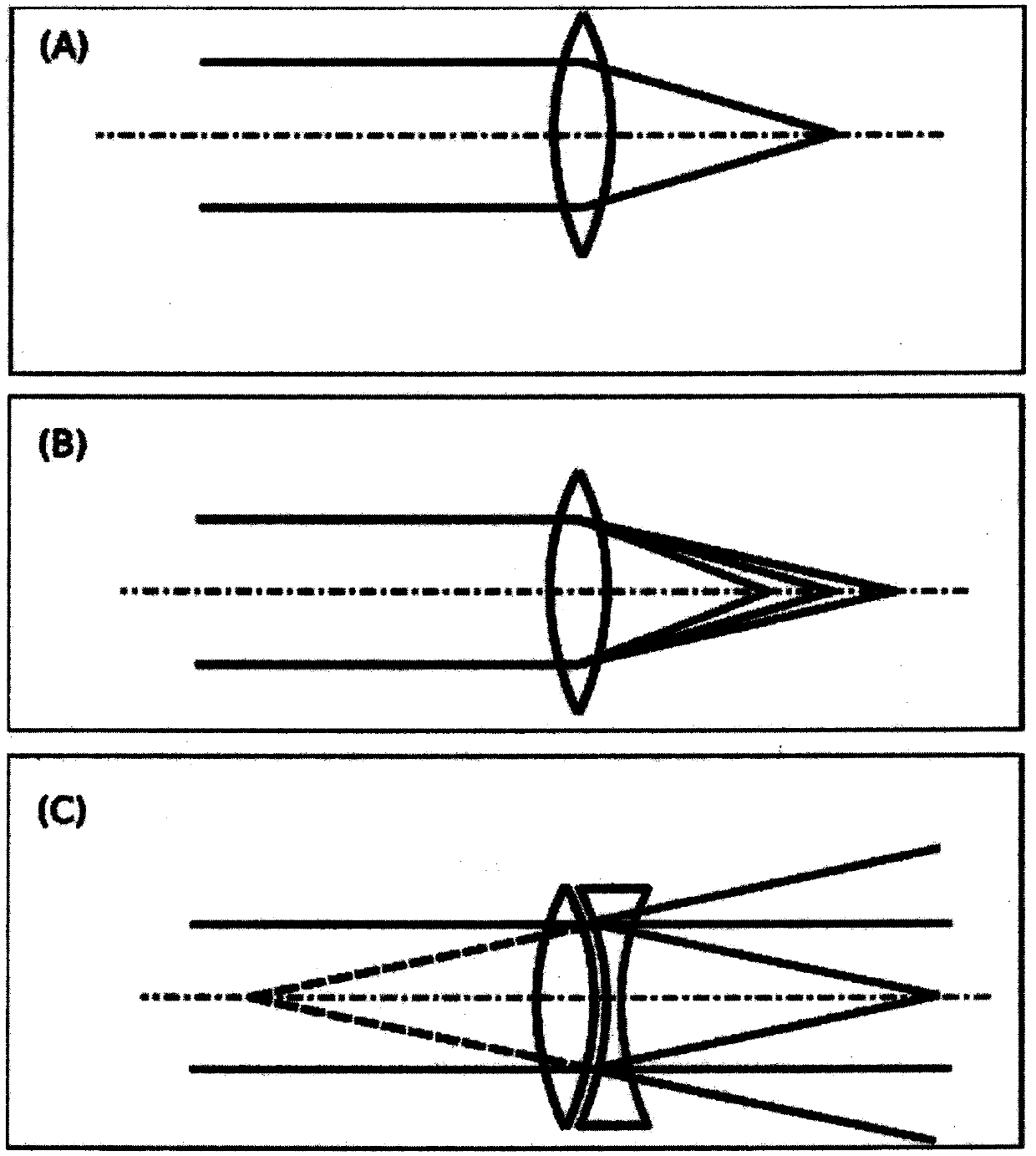
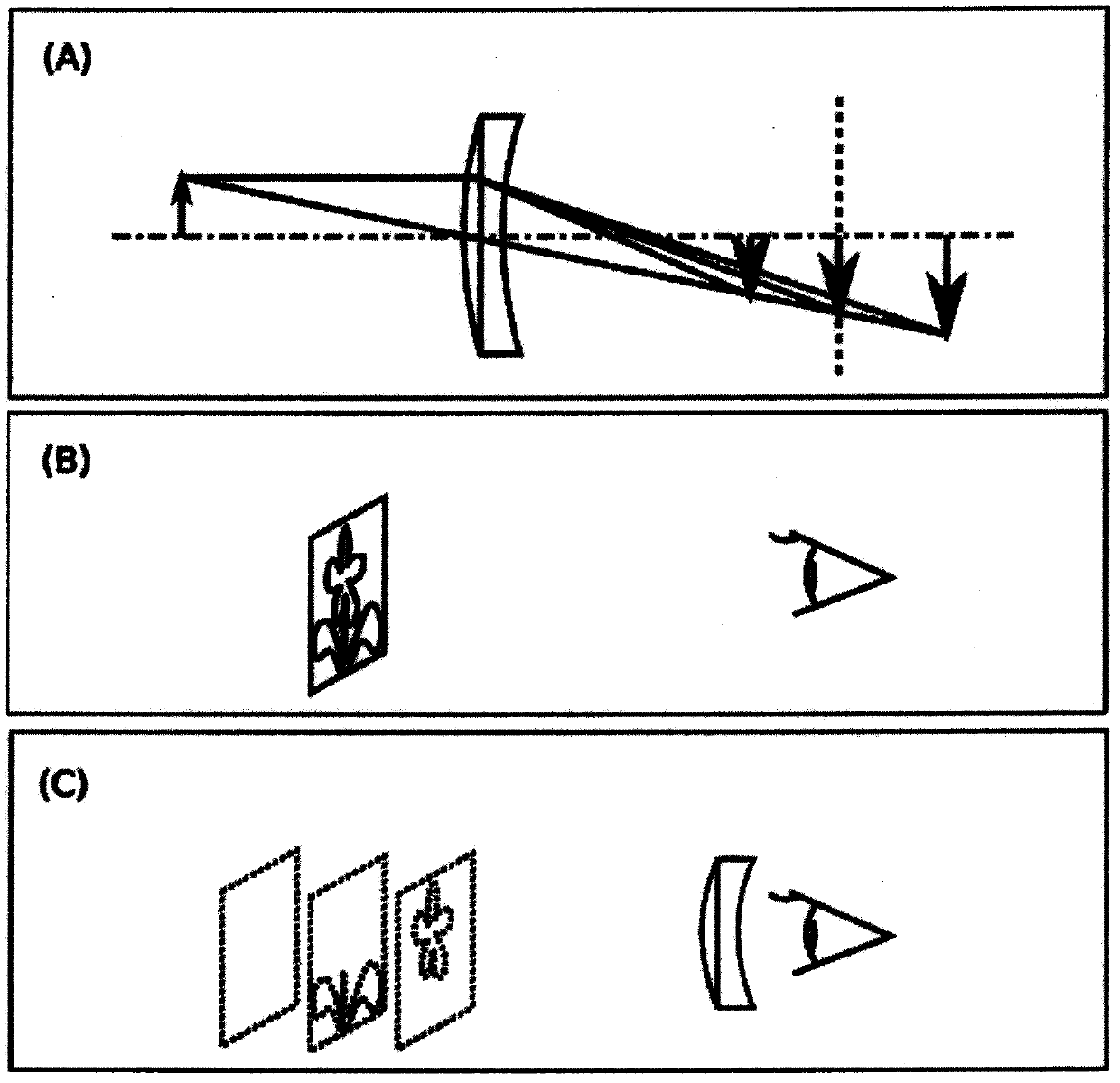
Design method for color blindness auxiliary glasses
A design method and technology of glasses design, applied in the field of visual optics, can solve the problems of confusion, color blindness, invalid color and black gray, and limited effect of color discrimination auxiliary technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Taking a user with normal eyesight (no farsightedness or nearsightedness) wearing color-blind auxiliary glasses as an example, the specific implementation method is as follows:
[0078] 1.1, the known high dispersion and low dispersion materials are heavy lanthanum flint (LaSF9) and fluorine crown (FK51A) optical glass of SCHOTT company respectively, and their refractive indices at characteristic wavelengths are:
[0079] Color, wavelength (nm) red, 650 yellow, 575 green, 530 Bi, 493 Blue 460 Refractive index of LaSF9 1.8432 1.8520 1.8594 1.8673 1.8763 FB Refractive Index 1.4849 1.4869 1.4886 1.4902 1.4920
[0080] Table 1, the refractive index of optical glass at the characteristic wavelength
[0081] 1.2. Make a high-dispersion convex lens and a low-dispersion concave lens to form a compound lens, the method is as follows. Take some D around 10 1 value, use formula (13) to get E 1 ; due to E 1 >0, we know from formula (9...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Taking a specific user with a myopia of 200 degrees wearing color-blindness auxiliary glasses as an example, the specific implementation method is as follows:
[0098] 2.1, with embodiment 1.1.
[0099] 2.2, same as embodiment 1.2, make a high-dispersion concave lens and a low-dispersion convex lens to form a compound lens, the method is as follows. Take some D around -10 1 value, use formula (13) to get E 1 ; due to E 1 Formula (19) is 200 for the degree of myopia (the focal length of myopia glasses is f 0 =-0.5m) users become
[0100]
[0101] Put (22) into the first and third lines of (18) to get and About R A , and bring the results into the critical equations (20) and (21) and obtain two R A value, and take the R that makes the high dispersion condition (6) true A ; Use formula (22) to get R from A Calculation of R B ; Obtain a new lens radian value table for 200 degrees of myopia at last, wherein positive (negative) sign represents convex (concave...
Embodiment 3
[0107] With no hyperopia, myopia (f 0 =∞) and the final optometry result is left eye dispersion D 1 =10, right eye D 1 =5 users wearing color-blindness auxiliary glasses as an example, the specific implementation method is as follows:
[0108] 3.1, with embodiment 1.1 to 1.3, obtain a batch of f 0 =∞ with different D 1 high dispersion lens.
[0109] 3.2. Cut these high dispersion lenses into appropriate sizes to make spectacle lenses. These spectacle lenses can be easily installed on spectacle frames specially used for optometry, and can also be easily disassembled for replacement.
[0110] 3.3, let the left and right lenses of the glasses have the same D 1 , and according to Example 1.5, the optimal value is 10 when the user's eyes D1 are the same.
[0111] 3.4, Keep the left lens of the glasses unchanged, and replace the D of the right lens alone 1 , make the user carry out the color discrimination test and experience feedback according to the invention step 2 (“E 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com