Interference detection
A technology that interferes with devices and wireless access points. It is applied in the field of wireless communication and can solve problems such as Wi-Fi link damage, Wi-Fi transmitters being unable to perceive channels, and Wi-Fi range reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
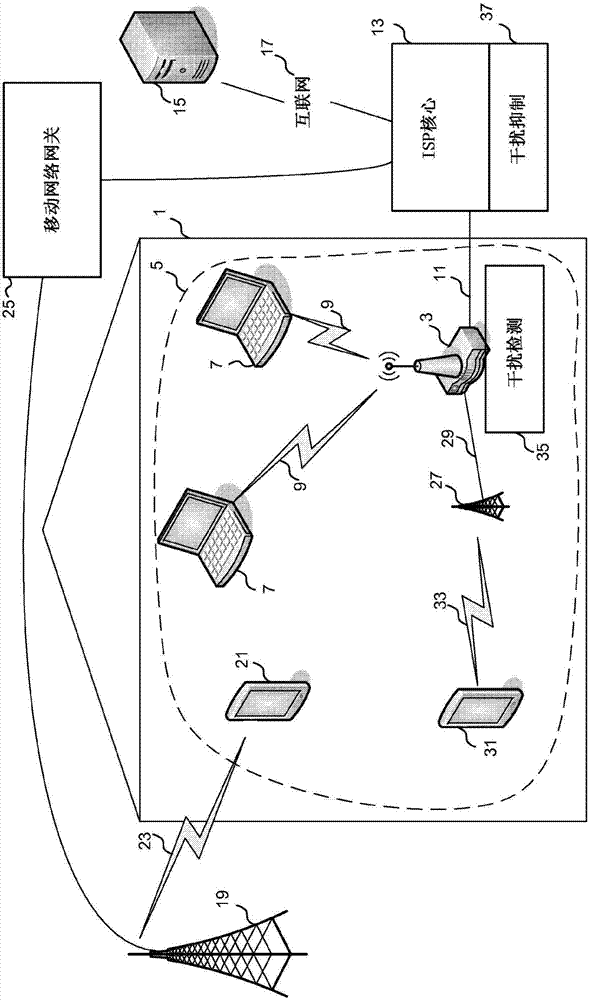
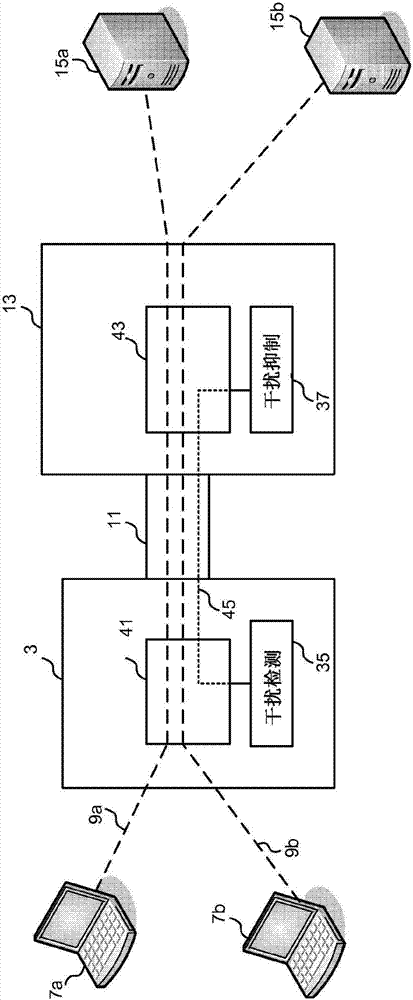
[0064] According to a first embodiment, the interference detection function 35 is configured to monitor the devices connected to the hub 3 and in particular to monitor the data flow carried by the hub 3 between the devices.
[0065] Such as Figure 5 As shown in , with the addition of an LTE femtocell 27 connected to the mobile network gateway 25, the interference detection component 35 will determine that there is a new data stream 47 carried by the hub.
[0066] Interference detection component 35 then compares the list of all flows to the matching criteria. Examples of matching criteria may include the MAC address of a known LTE femto cell or the IP address of a known mobile network gateway.
[0067] exist Figure 5 , the flow attributes of flow 47 match, and thus interference detection component 35 can identify LTE femtocell 27 (which is the device corresponding to the local IP address of flow 47) as a target for a Wi-Fi device also connected to hub 3 potential source o...
no. 2 approach
[0168] In a first embodiment, the interference detection component is configured to detect the presence of any potentially interfering devices connected to the hub, and the interference suppression component determines an appropriate response to suppress the interference. In the event that the hub is not connected to any interfering devices, the hub will not report any interfering devices to the interference management component.
[0169] Figure 12 An example network system in the second embodiment is shown.
[0170] exist Figure 12 In a network of , several hubs 201a - 201f are shown with wireless access points 203 to create a wireless LAN 205 . Some of the hubs 201a, 201b, 201e also have small cells 207 attached to them. For example, a first hub 201a has a femtocell 207a, a second hub 201b has a femtocell 207b, and a third hub 201e has a picocell 207c.
[0171] Each hub 201 performs processing according to the first embodiment to inform the interference suppression com...
no. 3 approach
[0216] In a third embodiment, the interference mitigation component is located within the network core and is configured to perform hub processing on connected hubs as in the first embodiment, but also operates to detect hubs that may be affected by small cells of neighboring hubs . The interference suppression component includes additional processing to determine the geographic location of the connected hubs, and applies aggregation processing of the connected hub interference information so that suppression information can be sent to a cluster of neighboring hubs.
[0217] Figure 15 The outline of the network system in the third embodiment is shown.
[0218] exist Figure 15 in the network (with Figure 12 Similar to the network of the second embodiment shown in ), multiple hubs 301a-301f are shown with wireless access points 303 to create a wireless LAN 305. Some of the hubs 301a, 301b, 301e also have small cells 307 attached to them. For example, a first hub 301a has...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com