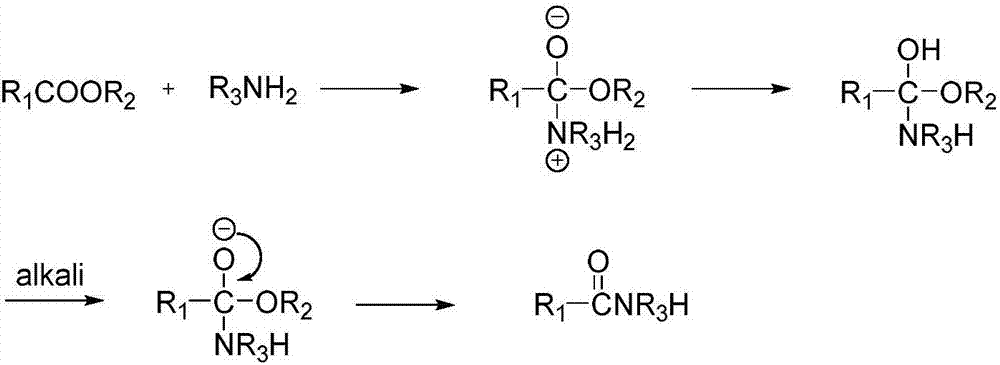
Method for preparing amide by metallic sodium catalyzed ester ammonolysis reaction
A technology for catalyzing ester and ammoniation reactions with sodium metal, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of carboxylic acid amides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult wastewater treatment, highly toxic sodium cyanide, etc. , easy separation, high conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
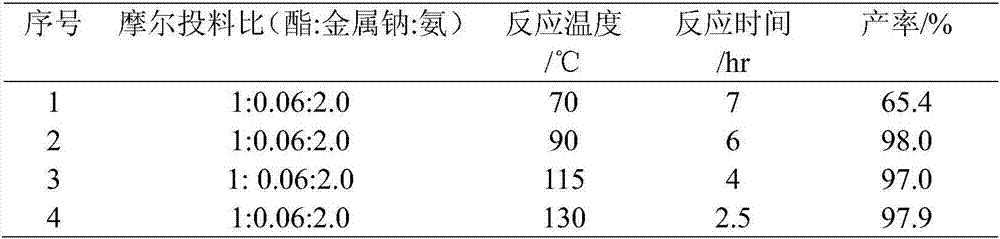
[0046] Embodiment 1, take ethyl acetate (44g) and liquefied ammonia (34g) as reaction raw material, metal sodium (0.69g) is catalyst, add 200mL belt stirring autoclave, no longer drop as reaction end point with reaction pressure, reaction time and The reaction results are shown in Table 1 below:
[0047] Table 1. Metal sodium catalyzed ester amination reaction
[0048]
[0049] When the reaction temperature is 90°C, the maximum pressure (that is, the initial pressure value) is 2.0MPa; when the reaction temperature is 70°C, the maximum pressure is 1.6Mpa; when the reaction temperature is 115°C, the maximum pressure is 3.1 Mpa; when the reaction temperature is 130°C, the maximum pressure is 4.0MPa.
[0050] From Table 1, we know that: when the reaction time of the reaction decreases as the temperature increases, the yield increases as the temperature increases. Moreover, when the reaction temperature reaches above 90° C., the reaction conversion rate reaches above 97%, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2, with ethyl acetate (44g) and liquid ammonia (quantitative) as the reaction raw materials, metal sodium (0.69g) as the catalyst, add 200mL agitated autoclave, with the reaction pressure no longer falling as the reaction end point, explore liquid ammonia Effect of dosage on response. Reaction time and reaction result are as shown in table 2 below:
[0055] Table 2. Effect of feeding ratio on reaction
[0056]
[0057] When the reaction liquid ammonia feed ratio is 2.0, continuing to increase the liquid ammonia feed has no obvious change in the reaction, and will lead to an increase in the reaction pressure. In Example 2, the initial pressure values corresponding to No. 1, No. 2, and No. 3 are 0.7 MPa, 2.0 MPa, and 3.5 MPa, respectively.
[0058] Subsequent treatment after the reaction is equal to Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3, with ethyl acetate (44g) and liquefied ammonia (34g) as reaction raw materials, metal sodium (quantitative) as catalyst, add 200mL belt stirring autoclave, take reaction pressure no longer to drop as reaction end point, explore reaction catalyst consumption effect on the response. Reaction time and reaction result are as shown in table 3 below:
[0060] Table 3, reaction temperature influence on reaction
[0061]
[0062] From table 4, it can be found that the catalyst consumption increases, and the reaction speed is greatly improved. When the catalyst consumption reaches 6% of the raw material ester consumption, the 6hr reaction conversion rate reaches 98%. If the catalyst consumption continues to increase, the reaction speed will still be increased. faster, but the conversion rate remains the same.
[0063] In this embodiment 3, the initial reaction pressure is 2.0Mpa. Subsequent treatment after the reaction is equal to Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com