Inverter boost current-loop vector auxiliary control method
An auxiliary control and current loop technology, applied in the direction of converting AC power input to DC power output, electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problem of reducing system stability, increasing Boost inductance loss, and affecting the maximum power of the battery panel. Point tracking, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
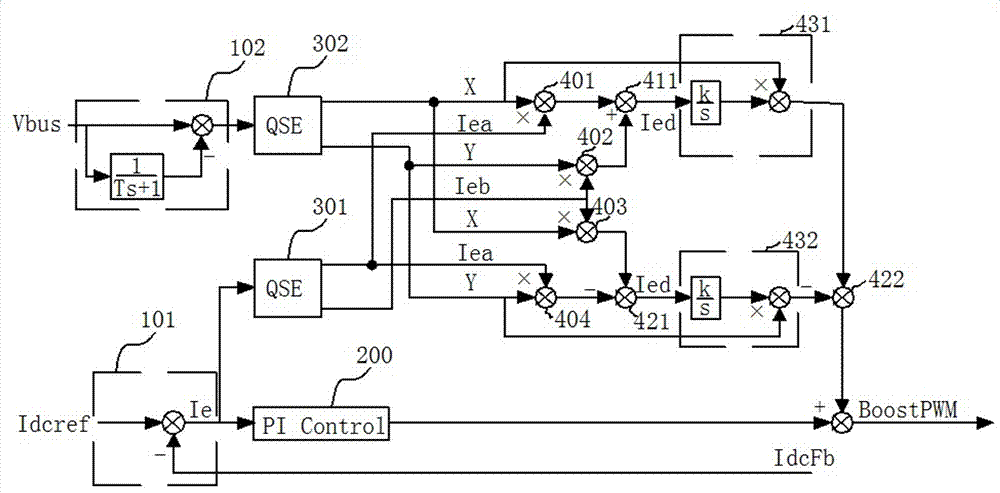
[0031] In order to make it easy to understand the technical means, creative features, goals and effects achieved by the present invention, the following examples are combined with the appended figure 1 to attach Figure 5 The technical solutions provided by the present invention are described in detail, but the following content is not intended as a limitation of the present invention.
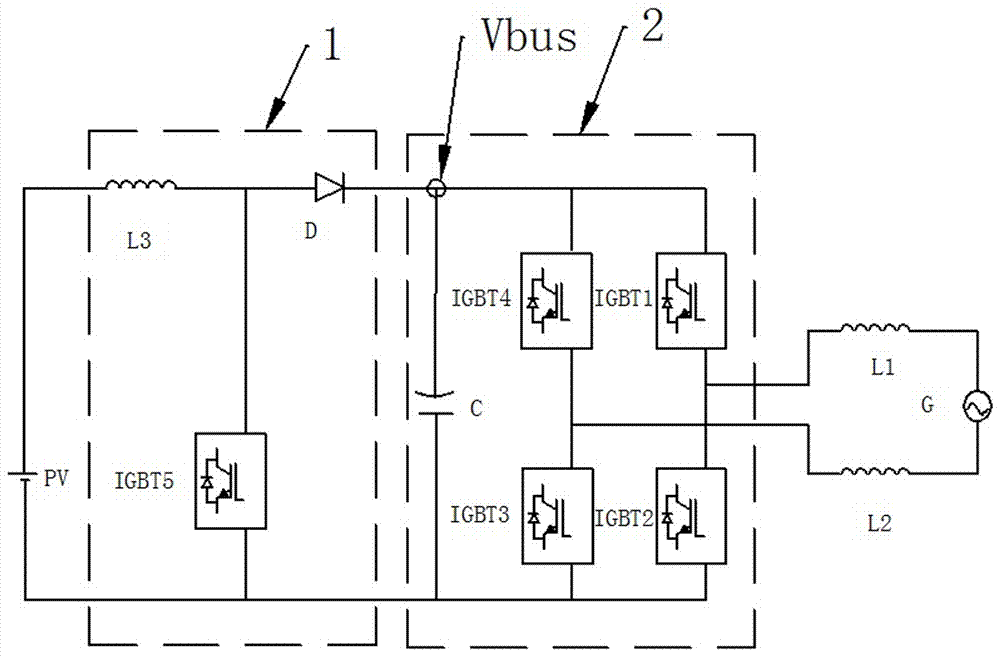
[0032] refer to figure 1 As shown, the structure of the existing photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is as follows, Vpv is defined as the Boost input voltage, Vbus is the Boost output voltage, Idc is the Boost current, L is the Boost inductance value, and Ton is the opening coefficient of BoostPwm. The value range is 0- 1. Define the Boost circuit to work in continuous current mode, and find the current increment in a single PWM cycle
[0033]
[0034] Simplifies to:
[0035]
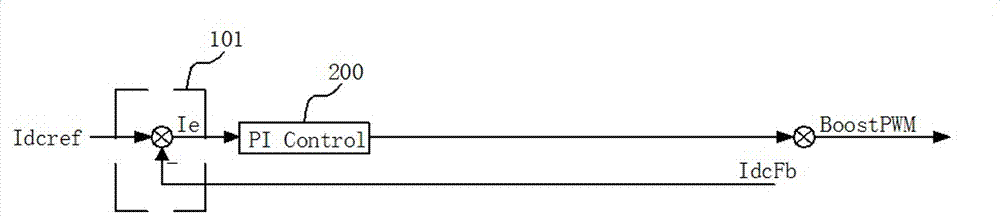
[0036] In the current loop control period, Vpv can be considered as a constant, then the control output of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com