A test method for the cold and warm feeling of textiles simulating the physiological feeling of the human body
A technology of human physiology and testing methods, applied in the direction of thermal development of materials, etc., can solve problems such as too large differences in heat dissipation laws, no turning point in the thermal power curve, and unreasonable time nodes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: cold feeling test of woolen sweater
[0052] 1. Sample information
[0053] The woolen sweater is made of 65% wool and 35% Tencel, knitted on a flat knitting machine, with a thickness of 1.81mm. It is considered to be worn in spring and autumn in the south of the Yangtze River.
[0054] 2. Sample thermal performance test and cold feeling calculation
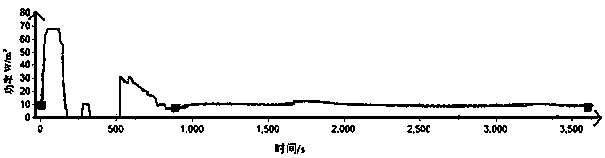
[0055] (1) The instrument used is the LD-1 clothing insulation performance tester, and the maximum heating power of the control test board is 150W / m 2 , and if the heating power is less than 20W / m 2 A warning message is issued in the event of a situation.
[0056] (2) Determination of the temperature and humidity of the test environment: according to Table 1, determine the level 3 standard environment of the test environment with a temperature of 20° C. and a relative humidity of 65%. The sample to be tested is subjected to moisture absorption equilibrium for more than 24 hours in this environment, so tha...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: cold feeling test of sweater
[0060] 1. Sample information
[0061] Sweater, made of 84.5% cotton + 15.5% polyester fiber, circular knitted fleece fabric, thickness 1.544mm, considered to be worn in Jiangnan Spring and Autumn.
[0062] 2. Sample thermal performance test and cold feeling calculation
[0063] (1) The maximum and minimum heating power controls of the instrument and the test board are the same as in Example 1.
[0064] (2) The temperature and humidity of the test environment and the pre-balanced treatment are the same as in Example 1.
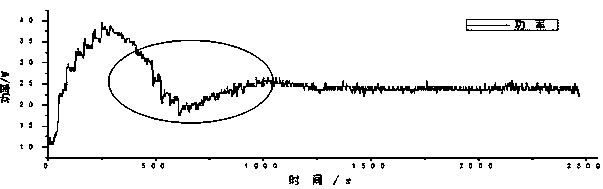
[0065] (3) Test the sweater and obtain the heating power curve of the test board as follows: Figure 7 Shown, according to this patent judgment this sample has obvious cold feeling.
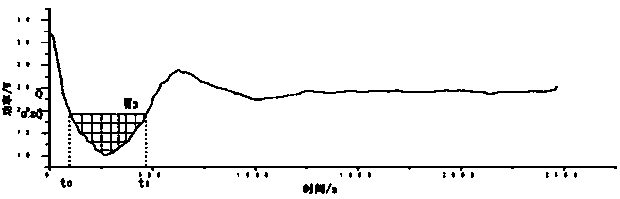
[0066] (4) Analysis and calculation of coldness index: coldness starting point t 0 and cold sensation termination point t 1 The determination method is the same as in Example 1. Calculate the average heating power in the stea...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Embodiment 3: Warming effect of hot clothing
[0068] 1. Sample information
[0069] Combination of sweater and light down jacket. The sweater is the same as in Example 2; the down jacket fabric is 100% polyester, the filler is 90% duck down, and the thickness is 3.027mm. It is considered to be worn in winter in the south of the Yangtze River.
[0070] 2. Sample thermal performance test and calculation of cold and warm feeling
[0071] (1) The maximum and minimum heating power controls of the instrument and the test board are the same as in Example 1.
[0072] (2) Determination of the temperature and humidity of the test environment: according to Table 1, determine that the test environment temperature of the sample to be tested is 10° C. and the relative humidity is 60%. Balance the sample to be tested in this environment for more than 24 hours, so that the internal and external temperature and moisture regain of the sample reach a balance, and then test.
[0073] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com