Microscopic observation method of plant tissues
A technology for plant tissue and microscope detection, applied in the biological field, can solve problems affecting the analysis of plant cell structure and function, achieve good transparency, improve observation depth, and save costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
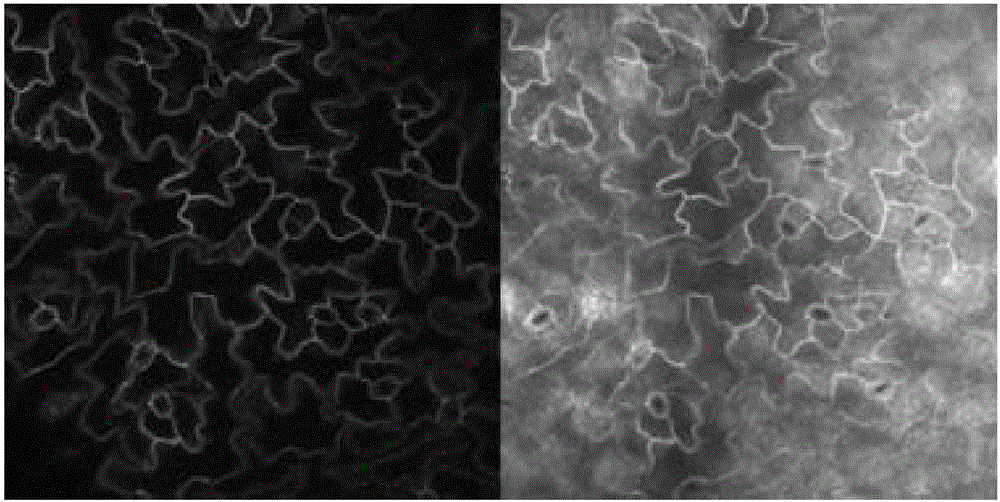
[0059] Embodiment 1, transparent treatment and microscope observation of Arabidopsis leaves
[0060] 1. Reagents required for transparent treatment of leaves
[0061] The fixative solution is composed of glutaraldehyde, paraformaldehyde and PHEM solution, wherein the volume percentage of glutaraldehyde is 4%, and the mass percentage of paraformaldehyde is 4%.
[0062] The PHEM solution was prepared with a final concentration of 40mM PIPES, 15mM HEPES, 5mM EGTA, 1mM MgCl 2 Composed of water with a pH of 6.9;
[0063] The transparent solution is composed of 4M urea, 20% glycerol (volume percentage), 0.1 volume% TritonX-100 and PHEM solution with final concentration.
[0064] 2. Transparency treatment and microscope observation of Arabidopsis leaves
[0065] 1. Transparency treatment of Arabidopsis leaves
[0066] Seeds of Arabidopsis (Columbian ecotype) were planted on 1 / 2 MS medium, vernalized at 0-4°C for two days, germinated in an incubator at 23±2°C, and moved to culture s...
Embodiment 2
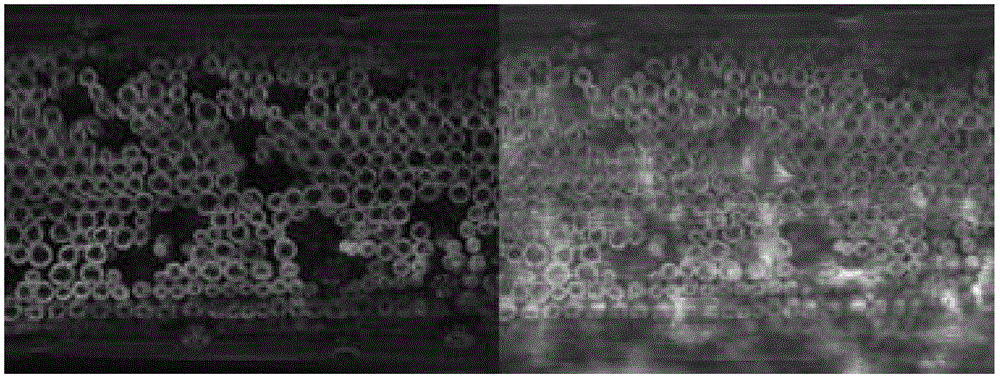
[0074] Embodiment 2, the distribution of chloroplast in the mesophyll cell of Shallot onion
[0075] 1. Reagents required for transparent treatment of leaves
[0076] The fixative solution is composed of glutaraldehyde, paraformaldehyde and PHEM solution, wherein the volume percentage of glutaraldehyde is 4%, and the mass percentage of paraformaldehyde is 8%.
[0077] The PHEM solution was prepared with a final concentration of 60mM PIPES, 25mM HEPES, 10mM EGTA, 2mM MgCl 2 Composed of water with a pH of 6.9;
[0078] The transparent liquid is composed of 6M urea, 30% glycerol (volume percent), 0.1 volume percent TritonX-100 and PHEM solution with a final concentration of 6M.
[0079] 2. Transparency treatment and microscope observation of the leaves of scallion
[0080] Cultivate the scallions to a height of 20-30cm, and get the aerial parts of the seedlings;
[0081] 1) Cut the above-mentioned scallion leaves into 0.8cm long segments, wash with deionized water until the s...
Embodiment 3
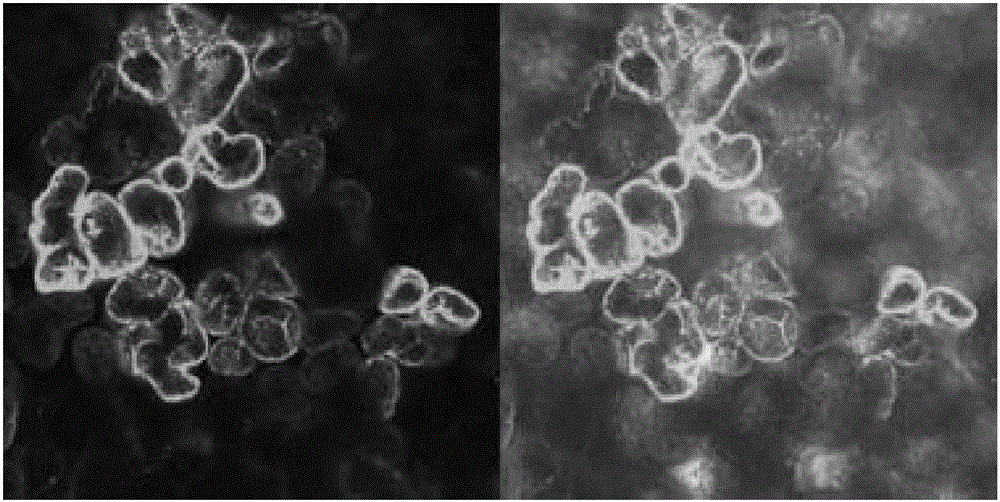
[0089] Example 3, the distribution of REMORIN protein in tobacco mesophyll cells
[0090] 1. Reagents required for transparent treatment of leaves
[0091] The fixative solution is composed of glutaraldehyde, paraformaldehyde and PHEM solution, wherein the volume percentage of glutaraldehyde is 5%, and the mass percentage of paraformaldehyde is 5%.
[0092] The PHEM solution was prepared with a final concentration of 60mM PIPES, 20mM HEPES, 10mM EGTA, 2mM MgCl 2 Composed of water with a pH of 6.9;
[0093] The transparent liquid is composed of 6M urea, 20% glycerol (volume percentage), 0.1 volume% TritonX-100 and PHEM solution with final concentration.
[0094] 2. Transparency treatment and microscope observation of tobacco leaves
[0095] Tobacco seeds are germinated at 20-25°C. After the seeds germinate, they are planted in flower soil in a greenhouse at 25±2°C, and cultivated to a plant height of 5-10cm.
[0096] 1) Shake culture the Agrobacterium strain carrying the RE...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com