Application of nereistoxin compound in prevention of marine biofouling
A technology of marine biofouling and nereistoxins, which is applied in the fields of compounds of group 5/15 elements of the periodic table, bismuth organic compounds, paints containing biocides, etc., can solve the problems of undiscovered nereistoxins and Application and other issues, to achieve the effect of mature artificial synthesis process, good application prospects, and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
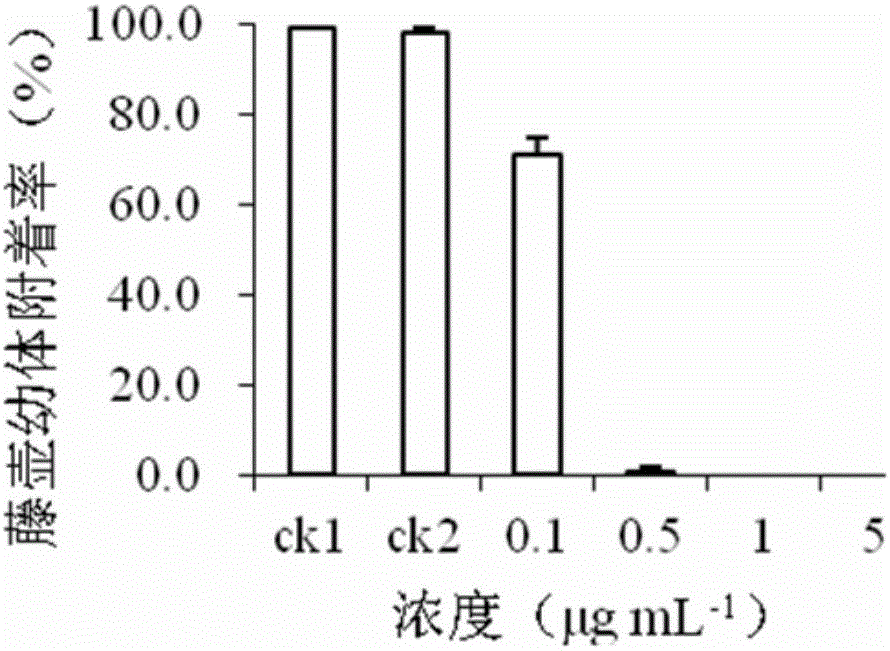
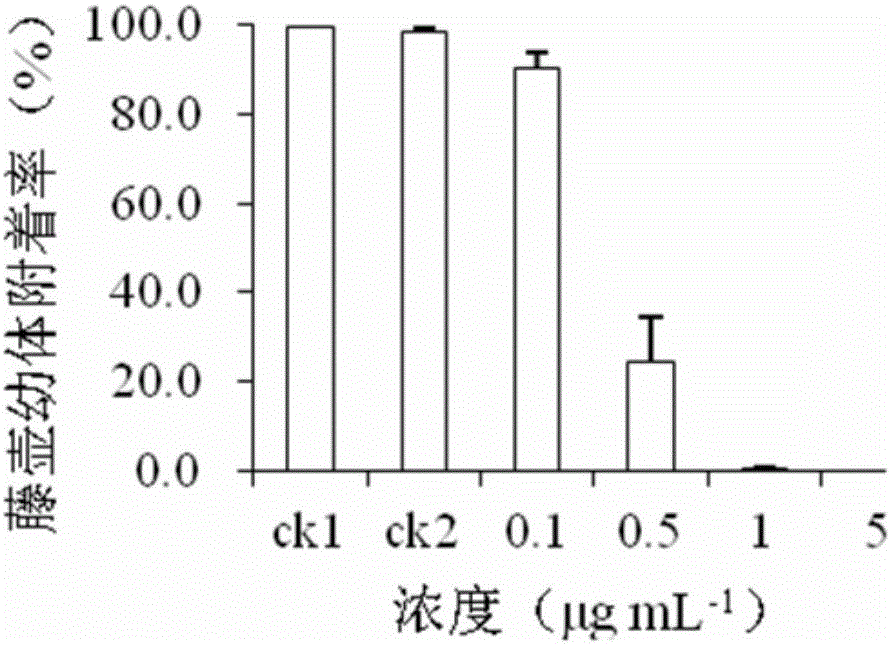
[0042] Example 1 Detection of Antifouling Activity of Nereistoxin Compounds on White Ridge Barnacle Venus Larvae
[0043] Barnacles belong to the Arthropoda phylum Crustacea Cirripedes, and are the most harmful organisms caused by fouling in the world. They mainly form juvenile barnacles through the attachment and metamorphosis of their Venus larvae, and then form fouling. At present, barnacle Venus larvae have been used as the biological model, which has become the longest, most widely used and most important antifouling detection activity model. In this embodiment, the larvae of the white-ridged barnacle Balanus albicostatus are selected as the antifouling activity detection model, and the effect of the compound on the attachment rate of the larvae is used as an indicator for evaluating the antifouling activity. Adults were collected from reefs and oyster culture racks in Wutong Sea Area, Xiamen City, and Venus larvae were cultured in a laboratory.
[0044] Using methanol a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Detection of Antifouling Activity of Nereistoxin Compounds on Mussels
[0047] Sand sieve shellfish Mytilopsis sallei is a typical alien invasive fouling shellfish, which is native to the tropical waters of Central America and belongs to the bivalve clam clamidae. It is often distributed in the inner bay waters with slow water flow. Carry out attached life, form a thicker fouling layer in marine facilities, cause huge economic losses to aquaculture and inland shipping. In this embodiment, the effect of the compound on the secretion number of sand sieve shellfish silk is used as the basis for evaluating its antifouling activity.
[0048] The shells of shellfish juveniles used in the experiment were about 10 mm long, and the surface was washed with sea water, and the original silk was cut off. Weigh nereistoxin and monosultap, and use dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as solvent to prepare a series of concentration gradient solutions respectively. Take a clean 24-well...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Toxicity detection of nereistoxins to non-target organism Artemia
[0051] Artemia salina is one of the important groups of marine zooplankton, and it is also an ideal bait for larvae and juvenile shrimp, and is often used as a detection organism for toxicity tests. In this embodiment, the 24-h acute toxicity of nereistoxin compounds on Artemia larvae is detected, and the mortality rate of the larvae is used as the basis for evaluating the toxicity. Artemia eggs were added to membrane-filtered seawater, aerated, and hatched for 24 hours at 25°C under 3000-4000 Lux light conditions. After 24 hours, stage I nauplii were collected, and the larvae were added to fresh membrane-filtered seawater, aerated, and cultured in a dark environment at 25°C for 24 hours. After 24 hours, collect II-III stage larvae as experimental materials.
[0052] Using DMSO as solvent, prepare a series of solutions of nereistoxin and monosultap with concentration gradient. Using a 24-we...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com