Micro-plant hydrotrope allelopathic potential evaluation bioassay method
A bioassay, plant technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, horticultural methods, horticulture, etc., can solve problems such as the influence of bioassay results, the influence of the growth of recipient plants, and the vulnerability of plant water extracts to microorganisms. Ease of handling effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
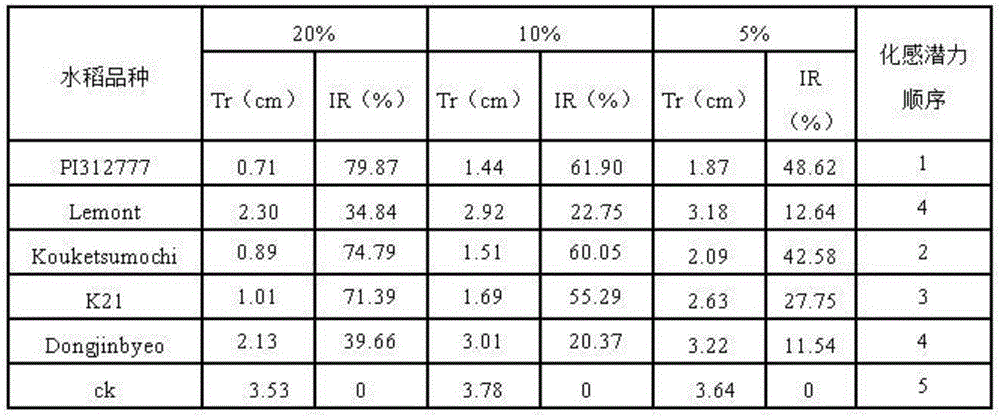
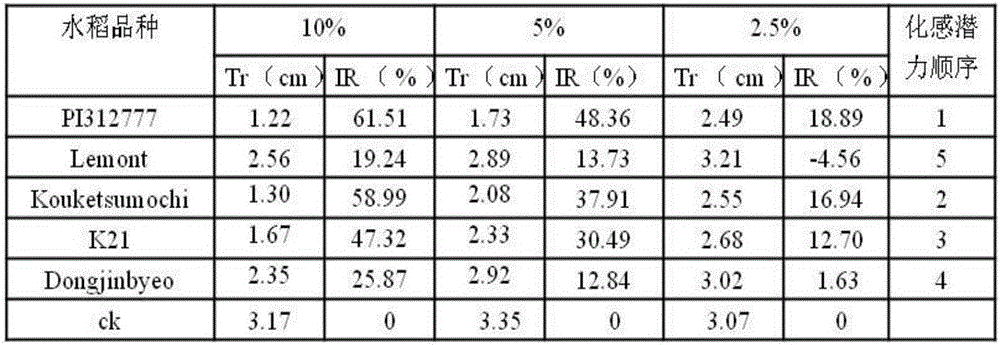
[0040] The test materials are rice and barnyardgrass, among which rice is the donor plant and the following five varieties are used: the reported non-allelopathic variety Lemont, the reported allelopathic variety PI312777, Koukesumochi, Dongjingbyeo and K21; the recipient plant is barnyardgrass . The test was repeated 3 times.
[0041] The steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0042] 1. Culture medium preparation: Prepare agar medium with a concentration of 6% in terms of mass fraction with water, sterilize at 120°C and 0.1MPa for 20 minutes, and then pour them into round and square petri dishes for use;
[0043] 2. Donor plants are the 5 kinds of rice mentioned above. After the rice seeds are fully absorbed, put them on a petri dish and place them in an incubator at 28°C for 48 hours to accelerate germination, then sow them in small pots filled with soil, and place them Plant in a greenhouse under 28°C and 12 hours of light / dark conditions for 20 days, cut the abovegro...
Embodiment 2
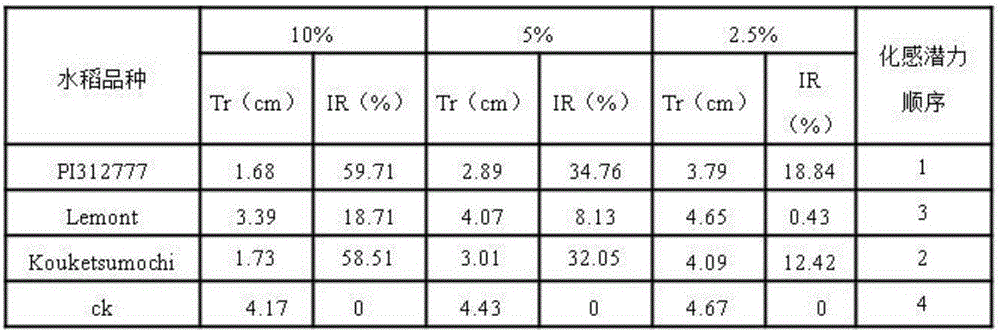
[0051] The test materials were rice and lettuce. Rice was the donor plant and the following three varieties were used: the reported non-allelopathic variety Lemont, the reported allelopathic variety PI312777 and Koukesumochi; the recipient plant was lettuce. The test was repeated 3 times.
[0052] The steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0053] 1. Preparation of culture medium: prepare agar medium with a concentration of 6% in terms of mass fraction with water, pour it into round and square petri dishes for use after ordinary high-pressure sterilization;
[0054] 2. Donor plants are the three kinds of rice mentioned above. Put the rice seeds on a petri dish after fully absorbing water and place them in an incubator at 25°C for 48 hours to germinate, then sow them in small pots filled with soil, and place them Plant in a greenhouse under 25°C and 12-hour light / dark conditions for 30 days, cut the above-ground parts of rice, and sterilize the above-ground parts of differe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com