Low-profile high-gain dual-polarized antenna
A dual-polarized antenna, high-gain technology, applied in the combination of antenna units with different polarization directions, the structural connection of the antenna grounding switch, the structural form of the radiating element, etc. The antenna is difficult to meet the needs of antenna miniaturization, destroying the excellent radiation characteristics of the patch antenna, etc., achieving significant performance advantages, facilitating mass production, and easy conformal design.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
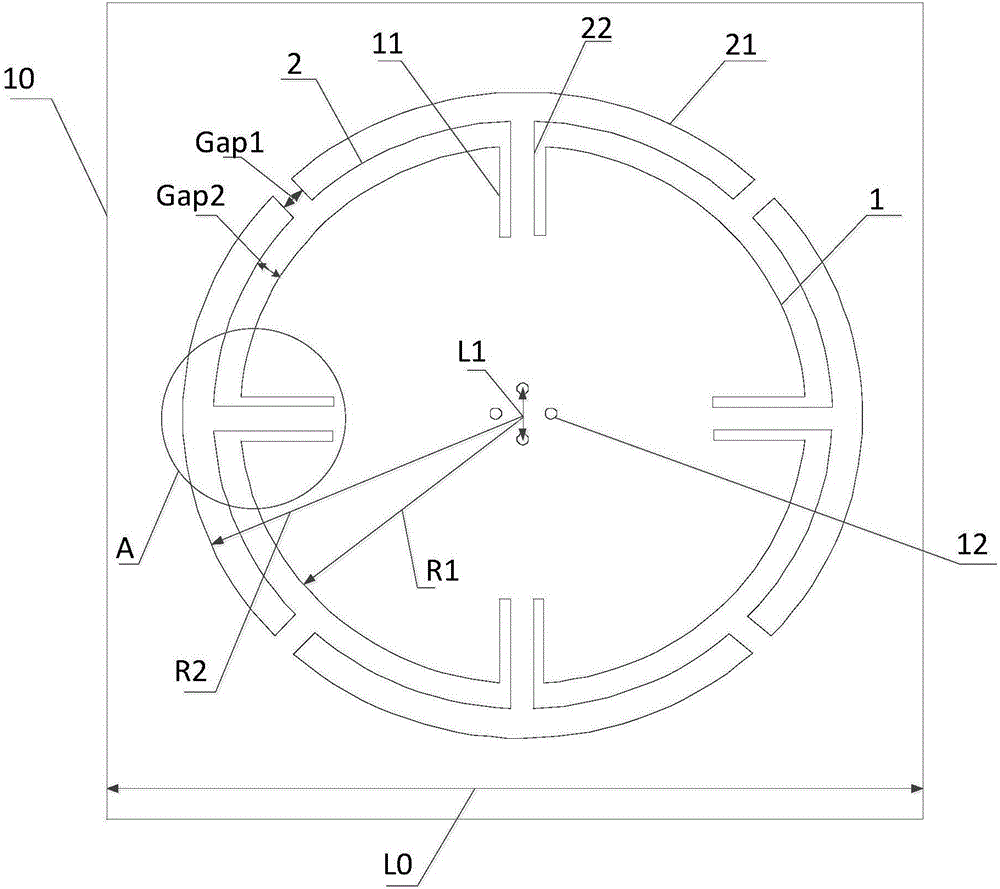
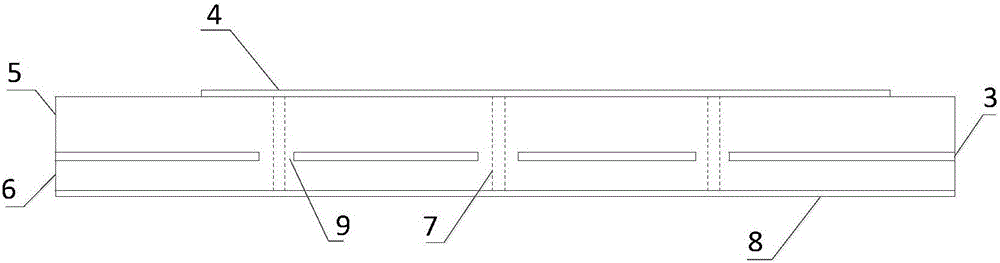
[0032] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, a low-profile high-gain dual-polarized antenna includes a feed network layer 8, a second dielectric substrate layer 6, a metal ground layer 3, a first dielectric substrate layer 5, and a radiation layer 4 stacked sequentially from bottom to top. , and four metal wires vertically passing through the feed network layer 8, the second dielectric substrate layer 6, the metal ground layer 3, the first dielectric substrate layer 5 and the radiation layer 4, and electrically connecting the radiation layer 4 and the feed network layer 8 Probe 7; when the metal probe 7 passes through the metal formation 3, four third openings 9 that are not electrically connected to the metal probe 7 are formed.
[0033] The radiation layer 4 includes a circular metal patch 1 and four "T"-shaped metal patches 2 that generate parasitic resonance; four metal probes 7 form four first openings 12 in the radiation layer 4 in a circular The center of the metal p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com