Microbial sensor based on turbidity detection and turbidity detection method
A microbial sensor and detector technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, food inspection, and biochemical analysis, can solve problems such as false positives and large test errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
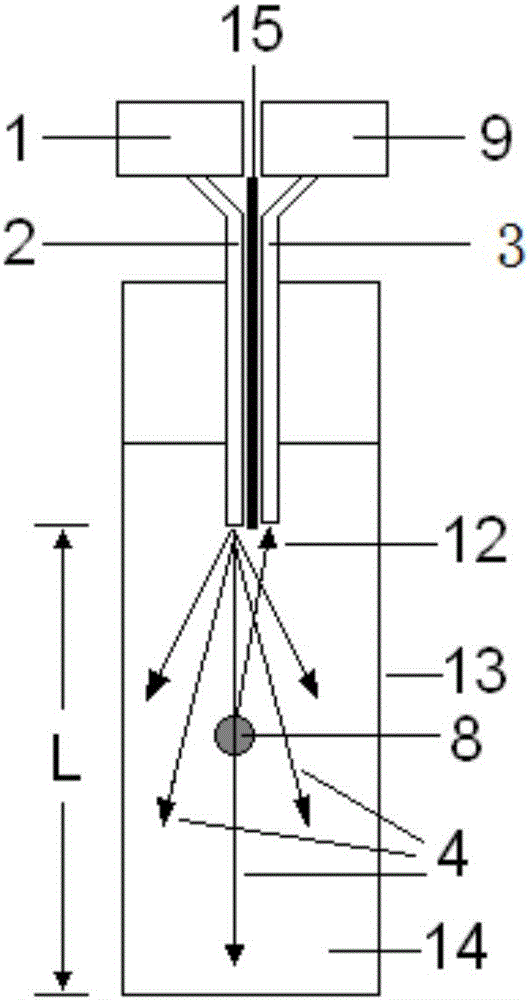
[0025] see figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a microbial sensor based on turbidity detection, comprising a light source 1, a first optical fiber 2 and a second optical fiber 3 composed of two optical fibers side by side, an optical isolation layer 15, a detector 9, and a in the cuvette 13 where the liquid medium 14 is placed. The excitation light 4 emitted by the light source passes through the first optical fiber 2 and irradiates the particles 8 in the culture medium 14 . After being scattered by the particles 8 , the scattered light 12 is received by the second optical fiber 3 and transmitted to the detector 9 .
[0026] The optical isolation layer 15 between the optical fibers can separate the light beams in the first optical fiber 2 and the second optical fiber 3 (ie, separate excitation light and scattered light) to avoid mutual interference. At the same time, since the excitation light emitted by the first fiber is divergent, the light intensity is the ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the optical fiber is replaced with a metal capillary. This embodiment only describes the structure different from the embodiment, and the same parts will not be repeated. In this embodiment, a first metal capillary tube and a second metal capillary tube are used to replace the first optical fiber 2 and the second optical fiber 3 to transmit probe light and collect scattered light. Since the light beam is transmitted inside the metal capillary, the side wall of the capillary can effectively reflect the light beam, so the side wall of the capillary can isolate the probe light and scattered light; at this time, there is no need to use an optical isolation layer between the two capillaries. The implementation of this embodiment can achieve the same technical effect as the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com