Rotating motor, elevator tractor with same, and elevator
A technology for rotating electrical machines and traction machines, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced motor performance, reduced heat dissipation area, magnet demagnetization, etc., and achieves the effect of improving cooling performance and reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
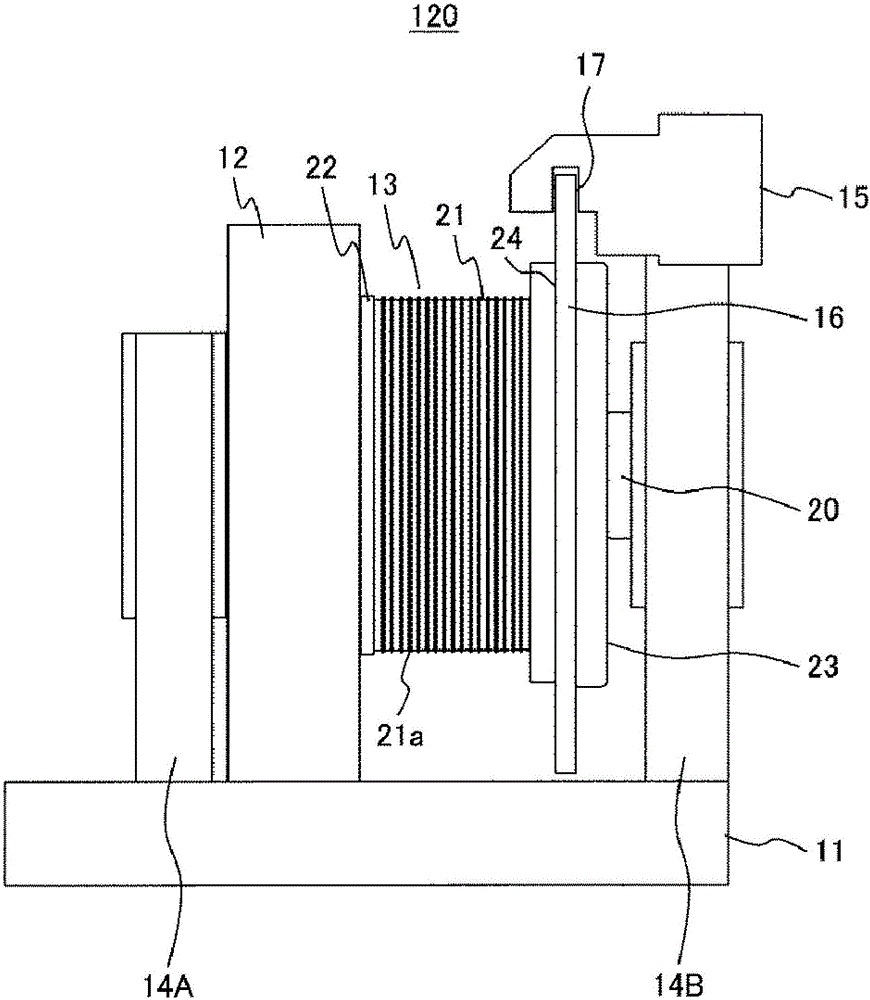
[0040] figure 1 An outline of the overall structure of the elevator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is shown.
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, a machine room 110 is provided on the top of a hoistway 100 installed in a building, and a traction machine 120 is placed in the machine room 110 and fixed on the floor of the machine room by a fixing mechanism. The traction machine 120 has a plurality of sheaves for suspending a plurality of main ropes 130 . One end of the main rope 130 extending from the sheave is connected to the upper end of the counterweight 150 via the guide pulley 140 , and the other end is connected to the upper end of the car 160 . The car 160 and the counterweight 150 are hoisted in the hoistway 100 by the main rope 130 wound on the sheave.
[0042] When the traction machine 120 works to rotate the sheave, the main rope 130 is driven along the rotation direction of the sheave due to the friction between the main rope 130 and the sheave...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Next, use Figure 11 and Figure 12 Example 2 of the present invention will be described. The differences from Embodiment 1 will be mainly described below.
[0081] Figure 11 It is an external perspective view of the traction machine of Example 2. and Figure 5 Likewise, a state in which the stator 31 and the rotor 30 are spaced apart from each other in the axial direction is shown. Figure 12 express Figure 11 A truncated section along A-A in the middle.
[0082] This embodiment 2 is different from embodiment 1 in that no opening is provided on the end frame 33 ( Figure 5 35A, 35B). That is, the partial space in which the blower vane 41 is located is completely closed on the side opposite to the connection portion side of the rotor 30 connected to the sheave 13 . Therefore, in addition to the partial space where the stator core including the field coil 37 and the permanent magnet 40 are located is substantially sealed, the partial space where the blower van...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Next, use Figure 13 and Figure 14 Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. The differences from Embodiment 1 will be mainly described below.
[0089] Figure 13 It is a perspective view showing the appearance and axial cross-section of the hoisting machine according to the third embodiment. and Figure 5 Likewise, a state in which the stator 31 and the rotor 30 are spaced apart from each other in the axial direction is shown. in, Figure 13 together expressed Figure 7 and Figure 9 Airflows AF3 and AF4 are shown in respectively. and Figure 14 only means Figure 13 Axial section in .
[0090] The present embodiment 3 is different from the embodiment 1 in that the connection portion 47 between the frame 39 of the rotor 30 and the sheave 13 protrudes toward the stator core support portion 32a, and is connected to the stator core support portion 32a on the inner peripheral side of the stator core support portion 32a. Free ends on the opposite...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com