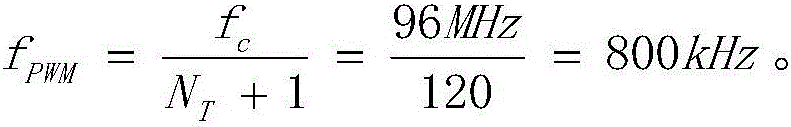Measurement circuit and measuring method of LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer)
A technology of measuring circuit and sampling circuit, which is applied in measuring devices, electromagnetic measuring devices, electric/magnetic position measurement, etc., can solve the problems of easy introduction of errors and drift, poor compensation accuracy, poor calibration accuracy, etc., and achieve zero-point residual voltage compensation , Avoid component tolerances and reduce measurement errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The present invention provides an LVDT measurement circuit, which includes:
[0050] The sine pulse width modulator 10 is used for outputting a rectangular wave signal with adjustable pulse width and frequency; the pulse width of the rectangular wave signal is adjusted sinusoidally;
[0051] The signal conditioning circuit 20, whose input terminal is connected to the sine pulse width modulator 10, is used to sequentially filter and amplify the rectangular wave signal to output a sine wave signal with adjustable amplitude and frequency;
[0052] Linear differential transformer 30, the primary coil 31 is connected to the signal conditioning circuit output terminal 20 to receive a sine wave signal as an LVDT excitation signal, and the secondary coil 32 outputs an LVDT differential signal;
[0053] The first sampling circuit 40, whose input terminal is connected to the primary coil 31, is used to sample the LVDT excitation signal;
[0054] The second sampling circuit 50, whose input ...
Embodiment 2
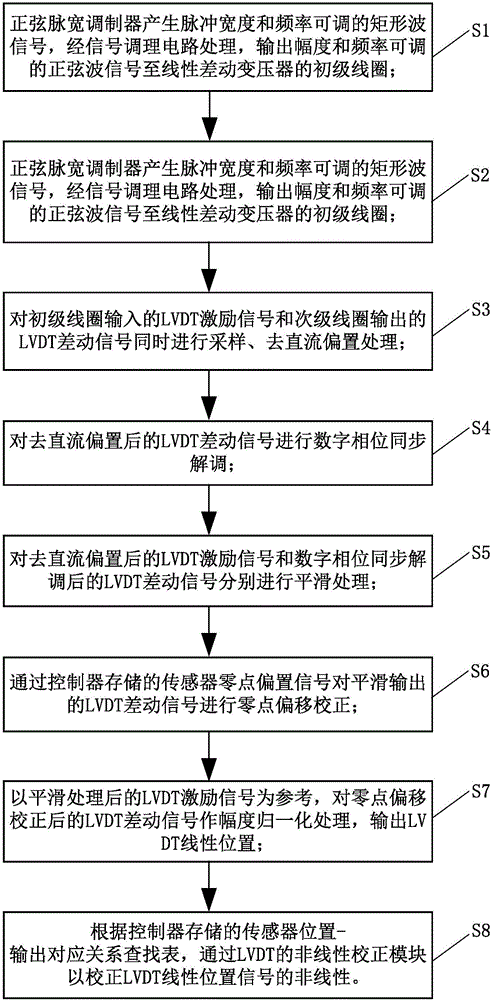
[0064] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a measurement method based on an LVDT measurement circuit, which includes the following steps:
[0065] S1, a sine pulse width modulator generates a rectangular wave signal with adjustable pulse width and frequency, processed by a signal conditioning circuit, and outputs a sine wave signal with adjustable amplitude and frequency to the primary coil of a linear differential transformer;
[0066] S2, the sine pulse width modulator generates a rectangular wave signal with adjustable pulse width and frequency, processed by the signal conditioning circuit, and outputs a sine wave signal with adjustable amplitude and frequency to the primary coil of the linear differential transformer;
[0067] S3: Simultaneously sample the LVDT excitation signal input by the primary coil and the LVDT differential signal output by the secondary coil and process the DC bias removal;
[0068] S4: Perform digital phase synchronization demodulation on...
Embodiment 3
[0082] On the basis of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, this embodiment provides specific embodiments of the LVDT measurement circuit and the measurement method thereof.
[0083] Taking the MHR500LVDT sensor as an example, the LVDT measurement circuit uses a sine wave excitation frequency of 2.5kHz and an effective value of 3V, and the controller 60 uses the NXP microcontroller LPC1768. The LPC1768 integrates a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation, pulse width modulation) module, which can be used to generate an SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation, sinusoidal pulse width modulation) signal, which is equivalent to the sinusoidal pulse width modulator 10 of the present invention. The clock frequency of the PWM module is set to 96MHz, and the PWM period register is N T Set to 119, so the frequency f of the PWM signal PWM for:
[0084] f P W M = f c N T + 1 = 96 M H z 120 = 800 k H z .
[0085] Use the general-purpose timer inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com