Applications of Artepillin C and analogue thereof in preparing drugs used for preventing metabolic diseases
A technology of metabolic diseases, atoppirin, applied in the application field of medicine, can solve problems such as inability to improve
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0210] Example 1. Brazilian green propolis inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in diabetic mice
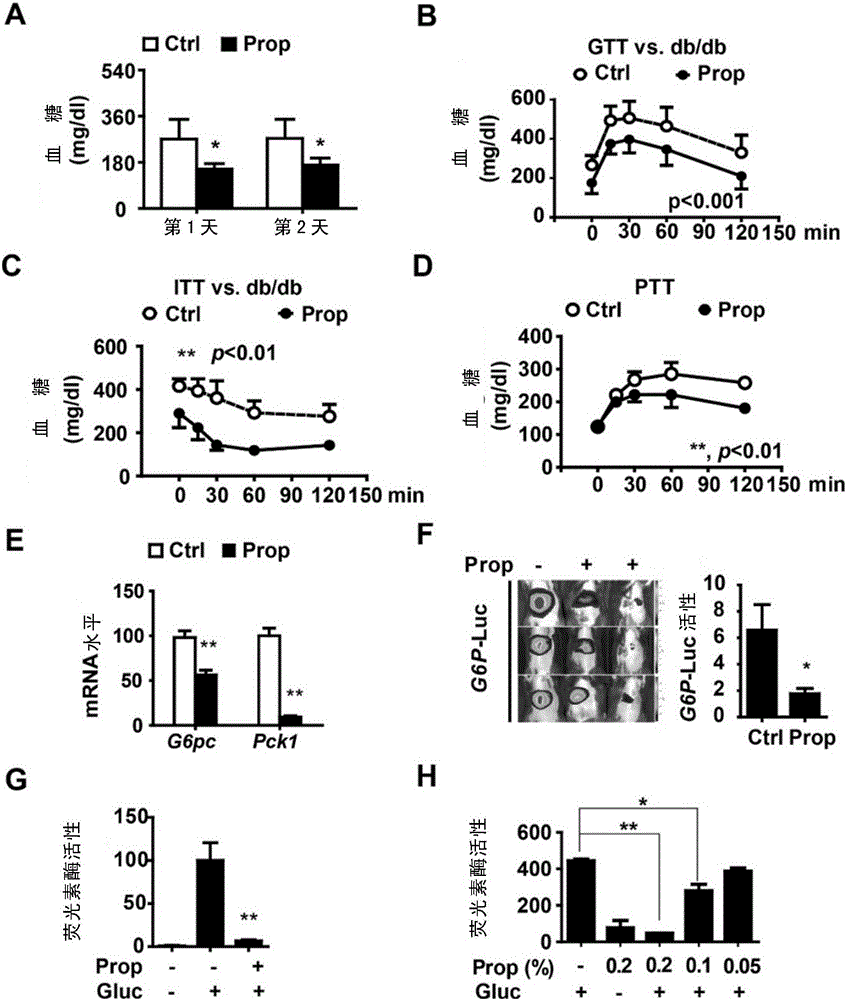
[0211] In order to study the hypoglycemic mechanism of propolis, the hypoglycemic activity of Brazilian green propolis was first tested in db / db diabetic mice. The results showed that short-term oral administration of Brazilian green propolis (250 mg / kg) for 1-2 days significantly reduced the fasting blood glucose ( figure 1 .A). Glucose tolerance in db / db diabetic mice after administration of Brazilian green propolis for 2 weeks ( figure 1 .B) and insulin sensitivity ( figure 1 .C) was significantly improved.
[0212] DIO (diet induced obesity, DIO) mice were administered with Brazilian green propolis for 2 weeks and then tested for pyruvate tolerance. The results showed that Brazilian green propolis significantly inhibited hepatic gluconeogenesis in high-fat-induced diabetic mice (DIO) ( figure 1 .D).
[0213] After DIO mice were given Brazilian green propolis for 3 weeks...
Embodiment 2
[0216] Example 2. CREB / CRTC2 two-hybrid system detects the activity of Brazilian green propolis components.
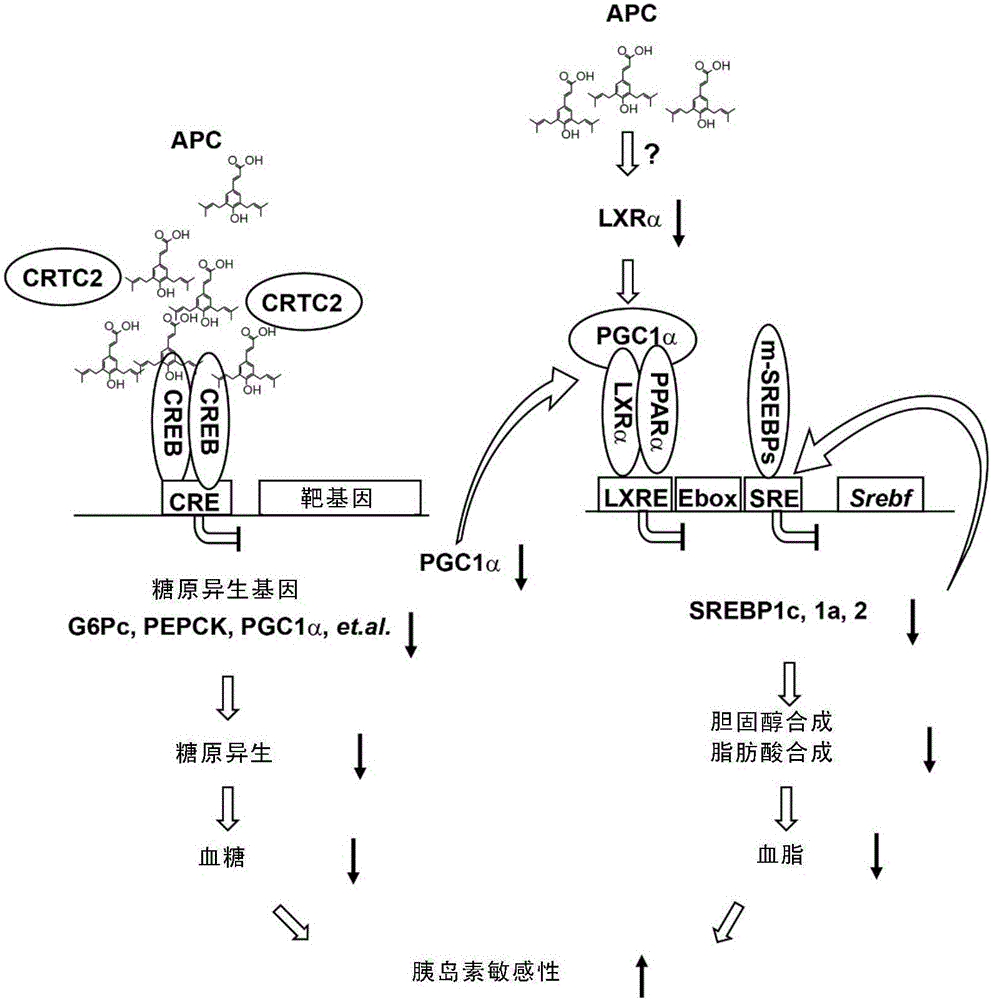
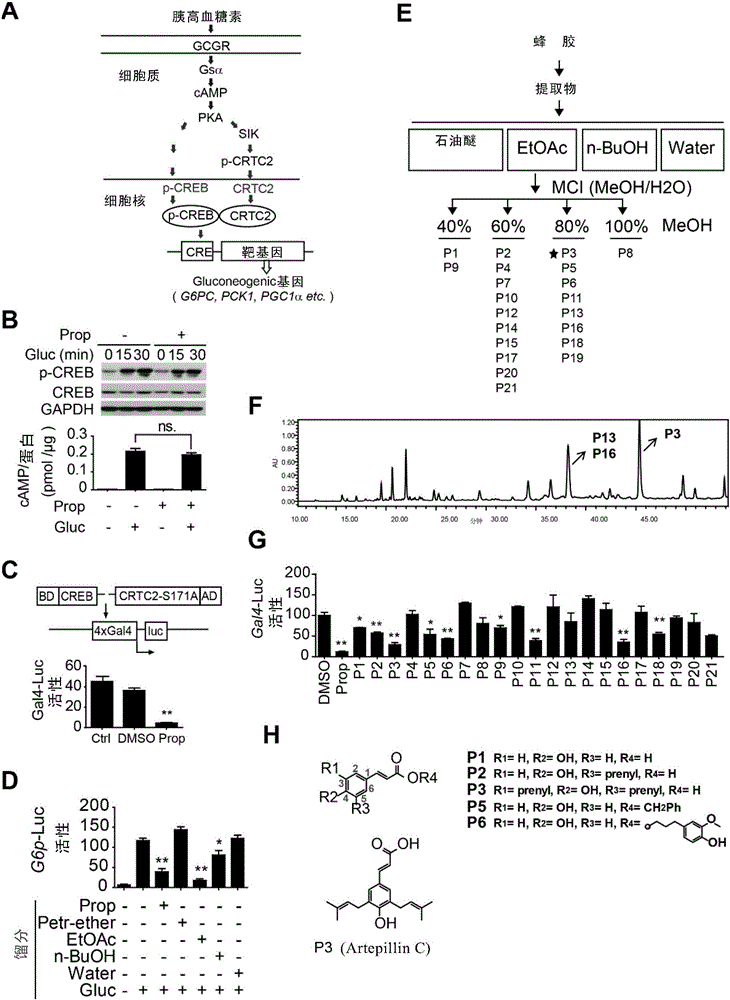
[0217] Glucagon-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis mainly depends on the GCGR-cAMP-PKA-CREB / CRTC2-CRE signaling pathway ( figure 2 .A).
[0218] Because Brazilian green propolis had no significant effect on the phosphorylation of cAMP and CREB stimulated by glucagon ( figure 2 .B), indicating that the inhibitory target of Brazilian green propolis on hepatic gluconeogenesis may be at the end of the glucagon signaling pathway. After being activated and dephosphorylated by glucagon, CRTC2 can effectively promote the transcription of genes related to hepatic gluconeogenesis through the combination of nuclear entry and CREB. Based on this principle, CREB was constructed: CRTC2-Ser171Ala mammalian two-hybrid system ( figure 2 .C) (this system uses mutant CRTC2-Ser171Ala to simulate the state of dephosphorylated and activated CRTC2), and the effect of propolis on CREB-CRTC...
Embodiment 3
[0222] Example 3. Artepillin C inhibits the protein interaction between CREB and CRTC2
[0223] In order to further study the molecular mechanism of Artepillin C inhibiting the mutual binding of CREB-CRTC2, the inventors detected the inhibitory activity of Artepillin C by immunoprecipitation. In HEK293T cell lysate overexpressing FLAG-mCRTC2, Artepillin C significantly inhibited the interaction between GST-hCREB beads and FLAG-mCRTC2 ( image 3 .A). Since hepatocytes can metabolize exogenous drugs and metabolic intermediates, it was further verified whether Artepillin C could maintain inhibitory activity in hepatocytes. Using primary hepatocytes as experimental materials, co-immunoprecipitation was used to detect the mutual binding of CREB and CRTC2, and this system was used to detect the inhibitory activity of Artepillin C in hepatocytes. The results showed that Artepillin C (10 μM) significantly inhibited the binding of CREB to CRTC2, and Artepillin C added again during im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com