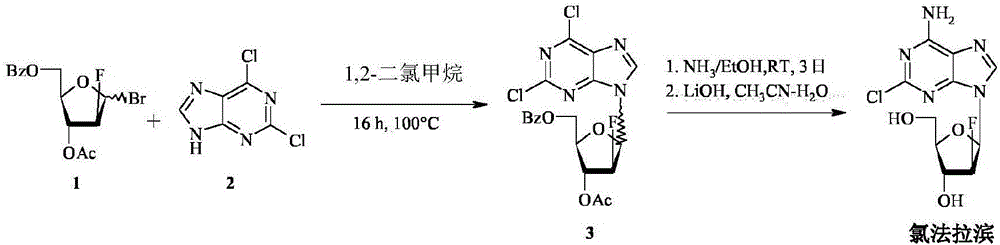
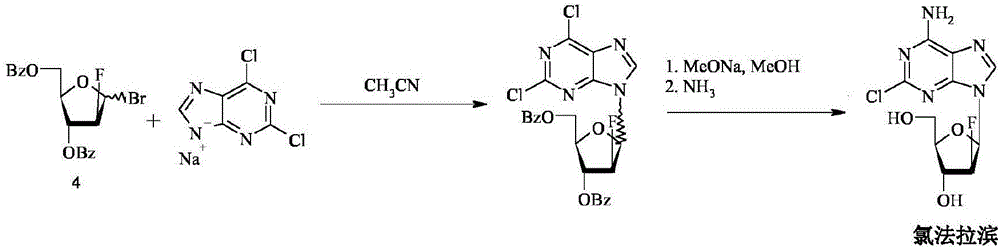
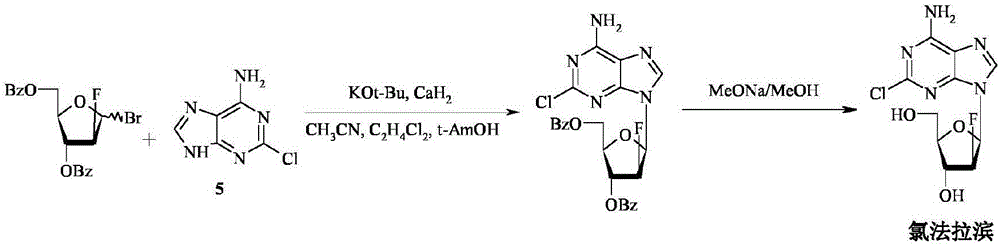
Method for the synthesis of clofarabine
A clofarabine and compound technology, applied in the field of α-N9 stereoisomers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1a
[0068] Example 1a: Preparation of 2-chloroadenosine(III) from 2-chloroadenine and uridine
[0069] At 58-61°C, mix 400g uridine and 150g KH with stirring 2 PO 4 Dissolved in a mixture of water (52L) and DMSO (1.8L). To the resulting solution was added a first batch (0.75 L) of a solution prepared from 2-chloroadenine (85 g), water (7 L) and KOH (120 g). The pH of the resulting mixture was adjusted to 7.1-7.2 with aqueous KOH. At 58-61°C, a solution of uridine phosphorylase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase was added with stirring. The remaining second batch of 2-chloroadenine solution was sequentially added to the reaction mixture with stirring at 58-61°C over a period of 3 hours, maintaining the pH in the range 7.1-7.2 with aqueous HCl. Then, the reaction mixture was stirred at 58-61 °C for 1 hour, and NaOH was added to adjust the pH to 11.
[0070] Purification of the resulting solution containing 2-chloroadenosine by preparative chromatography followed by isolation...
Embodiment 1b
[0071] Example 1b: Preparation of 2-chloroadenosine(III) from 2-chloroadenine and guanine
[0072] At 58-61°C, mix 229g guanine and 75g KH with stirring 2 PO 4 Dissolved in a mixture of water (52L) and DMSO (1.8L). To the resulting solution was added a first batch (0.75 L) of a solution prepared from 2-chloroadenine (42 g), water (7 L) and KOH (60 g). The pH of the resulting mixture was adjusted to 7.1-7.2 with aqueous KOH. The solution of purine nucleoside phosphorylase was added to the reaction mixture with stirring at 58-61°C. The remaining second batch of 2-chloroadenine solution was sequentially added to the reaction mixture with stirring at 58-61°C over a period of 3 hours, maintaining the pH in the range 7.1-7.2 with aqueous HCl. Then, the reaction mixture was stirred at 58-61 °C for 1 hour, and NaOH was added to adjust the pH to 11.
[0073] The resulting solution containing 2-chloroadenosine was purified by low pressure reverse phase column chromatography follo...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2: Benzoylation of 2-chloroadenosine
[0075] A solution of 2-chloroadenosine (750 g) in pyridine (7.5 L) was cooled to -5-0°C. Then, a solution of benzoyl chloride (720 g) in acetonitrile (1440 mL) was slowly added to the reaction mixture with stirring and cooling. Therefore, the internal temperature of the reaction mixture should not be higher than 5°C. The mixture was incubated for 30 min under the same conditions. Thereafter, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure at a temperature of 60°C. The residue was dissolved in CH 2 Cl 2 in, and sequentially with 1M H 2 SO 4 Aqueous solution, saturated NaHCO 3 Aqueous solution and water wash. The organic phase was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain 2-chloro-9-(2',5'-di-O-benzoyl-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-adenine and 2-chloro-9 -(3',5'-di-O-benzoyl-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-adenine mixture (together about 65% by HPLC), and 2',3', 5'-Tri-O-benzoyl-2-chloroadenosine (about 30% by HPLC).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com