Entity classification method for data space
A data-oriented and classification-oriented technology, applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer components, etc., can solve problems such as classification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
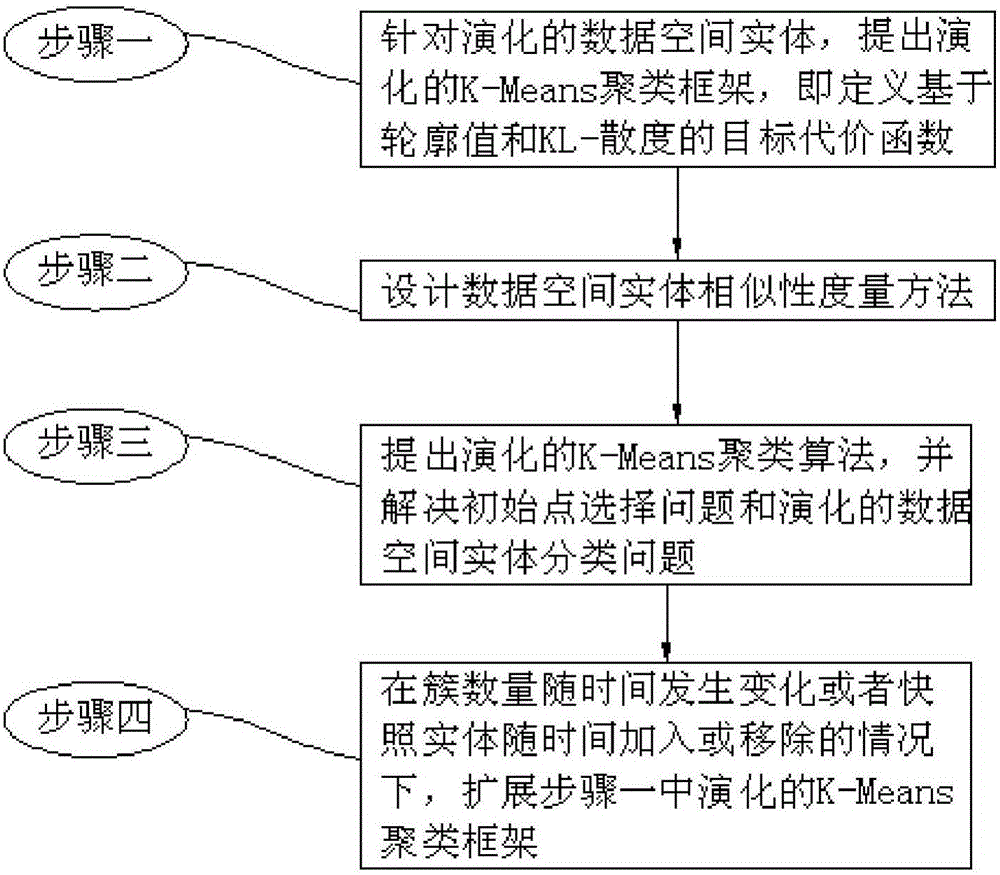
[0023] The data space-oriented entity classification method of this embodiment combines figure 1 As shown in the flowchart, the method is realized through the following steps:
[0024] Step 1. For the evolved data space entity, propose an evolutionary K-Means clustering framework, that is, define an objective cost function based on contour values and KL-divergence;
[0025] Step 2, designing a method for measuring the similarity of entities in data space;
[0026] Step 3. Propose an evolutionary K-Means clustering algorithm, and solve the initial point selection problem and the evolutionary data space entity classification problem;
[0027] Step 4. Expand the K-Means clustering framework evolved in Step 1 when the number of clusters changes over time or snapshot entities are added or removed over time.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Different from the specific embodiment 1, the data space-oriented entity classification method of this embodiment of the present embodiment proposes an evolutionary K-Means clustering framework as described in step 1, that is, defines the The process of the objective cost function is,
[0029] Step 11. Define the total objective cost function by linear combination:
[0030] The cost function consists of two parts: the snapshot cost of the current time step and the historical cost of the historical time step, respectively denoted as Cost snapshot and Cost temporal ;; The former is only used to measure the snapshot quality of the current clustering result about the current entity information, which reflects the clustering algorithm's metrics. Obviously, the higher the snapshot cost, the lower the snapshot quality; while the latter is based on the current clustering The degree of fitting between the structure and the historical cluster structure is used to measure the ti...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0066] The difference from the specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that in the data space-oriented entity classification method of this embodiment, the process of designing the data space entity similarity measurement method described in step 2 is as follows:
[0067] On the one hand, the snapshot entity itself contains rich information, such as structured attribute information and unstructured content information; on the other hand, in the data space environment, entities reappear over time, and this historical occurrence pattern information is very important for judging Whether two entities are similar also plays a role. For this reason, the data space entity is the snapshot entity, and the similarity of the snapshot entity is measured according to the entity's own information and the entity's historical occurrence mode information, that is, the similarity function of the snapshot entity is determined by the self-similarity Composed of two parts, sex and historical similarity, the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com