Biliary tract exploration method and device based on superfine endoscope
A bile duct and channel technology, applied in endoscopy, laparoscopy, medical science and other directions, can solve the problems of guide wire displacement, difficulty in operation, inability to operate, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing gastric coiling, reducing pain, and maintaining good stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2, a method of biliary tract exploration based on an ultra-fine endoscope in this embodiment is suitable for cases where it is difficult to guide a guide wire into the common bile duct with an ultra-fine endoscope, and the steps are as follows:
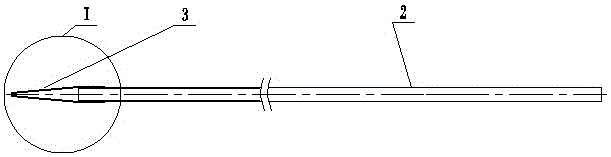
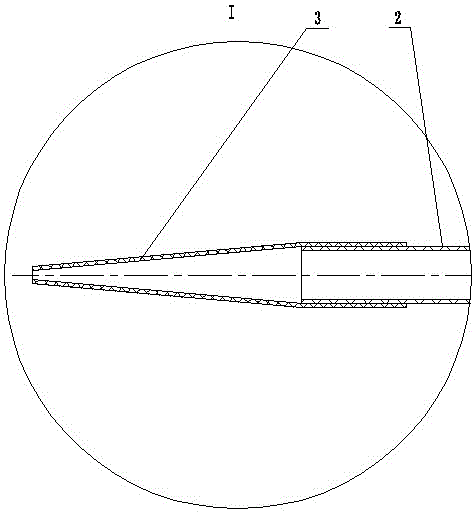
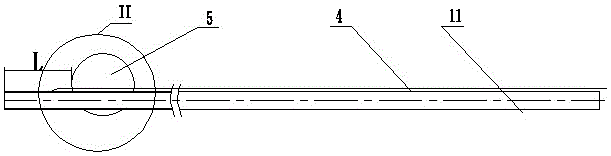
[0047] 1) After incision and dilation of the duodenal papilla by routine ERCP of the duodenoscope, the front end of the ultra-fine endoscope 2 is fixed to the transparent tapered guide head 3, and then the ultra-fine endoscope 2 is put on the outer tube within 4;
[0048] 2) Ultra-thin endoscope 2 with transparent tapered guide head 3 and sheathed with outer tube 4 enters the descending part of the duodenum through the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and stomach 8, and passes through the duodenal papilla. Play J-shaped reversal;
[0049] 3) When performing a J-shaped reversal, use the traction wire 11 to pull back the overtube 4, and after the ultra-fine endoscope 2 finds the opening of the duodenal papilla, the transpar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com