Controllable annular spring and detachable pot cover lifting handle with the same
An annular spring, detachable technology, applied in the field of detachable pot lid handle, can solve the problem of uncontrollable snap ring spring, and achieve the effects of convenient use, stable connection and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
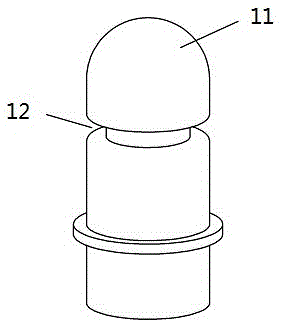
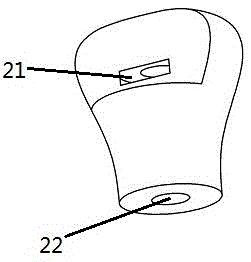
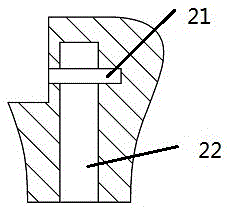
[0017] Example 1, figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a cylindrical pin, which is cylindrical as a whole, 11. Arc-shaped head, 12. Groove, and the other end can be connected to the lid by common welding, threads, etc. figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the female buckle body, 21. The spring placement space, 22. The cylindrical male buckle accommodation space. image 3 It is a sectional view of the female buckle body.
[0018] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of an ellipse spring, 41. ellipse major axis point, 42 ellipse minor axis point, when the long axis of both ends of the ellipse spring is squeezed, it will force 42. ellipse minor axis point to expand outward. Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of an elliptical spring with a force-applying part, 51. The force-applying part, when the elliptical spring is loaded into the 21. spring placement space, the force applied by the 51. force-applying part will make the elliptical spring subject to 21. The spring is placed...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Embodiment 2, the controllable spring is the main point of the present invention, so the following description will focus on how the spring is controllable, and will not repeat others. Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of a semi-circular and semi-elliptical spring. 71. The upper part of the semicircle and the lower part of 72. The ellipse, when the long axis point of the lower part of the ellipse is squeezed by force, the inner diameter of the spring is expanded. Tighter and has better stability than oval springs.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3, Figure 8 Schematic diagram of a ring spring under force at both ends. 81. Forced parts at both ends, 82. Ring spring, when 81. Forced parts at both ends give 82. Ring spring a tangential force, 82. The inner diameter of the ring spring expands, which can control the opening and closing of the spring.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com