A positioning-guided orthopedic reduction forceps
A technology of positioning guide and reset forceps, which is applied in fixers, medical science, surgical forceps, etc., can solve the problems of loss of accurate guidance, large surgical trauma, prolonged operation time, etc., achieve reliable clamping and precise guidance, reduce incision and Trauma, the effect of reducing the chance of infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
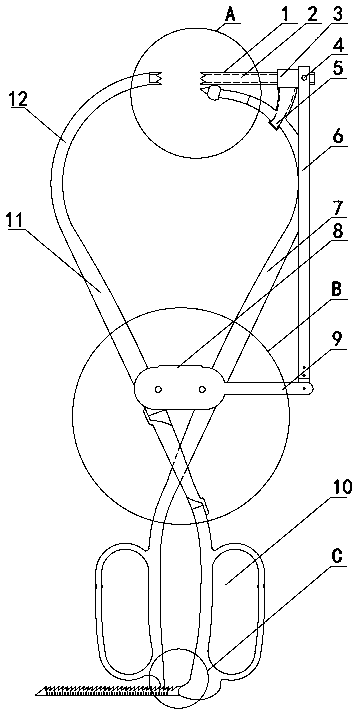
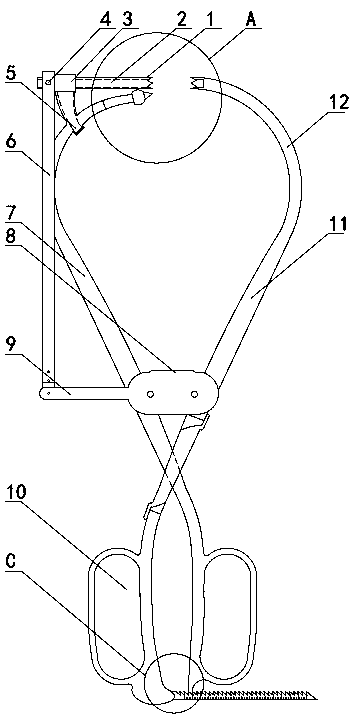
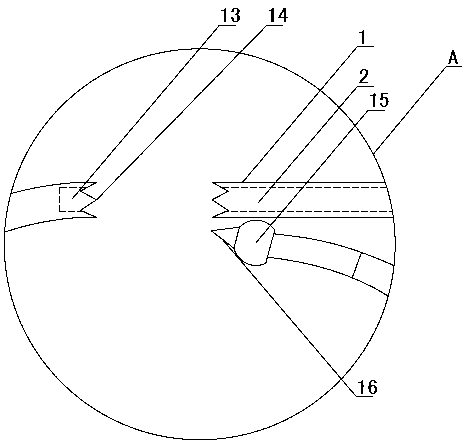
[0032] Such as Figure 1~2 As shown, a positioning-guided orthopedic reduction forceps includes a left forceps arm 11 and a right forceps arm 7. The left forceps arm 11 and the right forceps arm 7 are arranged alternately and can be fixed by a fixed stopper 8. The left forceps arm 11 The intersection point with the right tong arm 7 is located at the bottom of the fixed limiter 8 . At the lower ends of the left tong arm 11 and the right tong arm 7, respectively, a left and right corresponding finger cuffs 10 are arranged, which is convenient for the surgeon to carry out the clamping operation. The upper ends of the left tong arm 11 and the right tong arm 7 are respectively provided with a first clamping tip and a second clamping tip through an arc-shaped connecting section 12, and the first clamping tip and the second clamping tip are arranged opposite to each other left and right. The arc-shaped connection section 12 connected to the upper ends of the left pincer arm 11 and t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: in embodiment 2, the end of the first clamping tip maintains the cone tip guide end, and the end of the second clamping tip cancels the cone tip guide end, which is designed as The inclined surface 32 with only one tip forms a tapered sleeve with only one tip, and the other designs are the same as in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the end of the guide sleeve 1 can also be designed as an inclined surface 32 with only one tip, and the design of the tapered guide end remains at the end of the second clamping tip.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that in embodiment 3, the design of the conical point guide end of multiple tips is canceled at the end of the right clamp arm 7, and the design is the same inclination as the second clamping tip surface 32, and a guide groove 13 matching with the channel 2 is provided at the center of the inclined surface 32.
[0052] In this positioning-guided orthopedic reduction forceps, the arrangement of the first clamping tip and the second clamping tip can be any combination of the above embodiments.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com