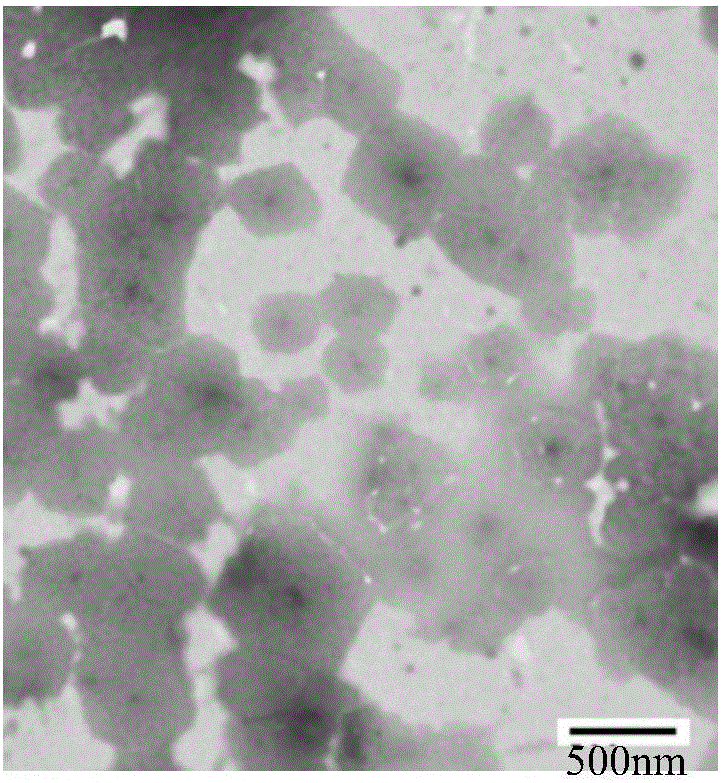
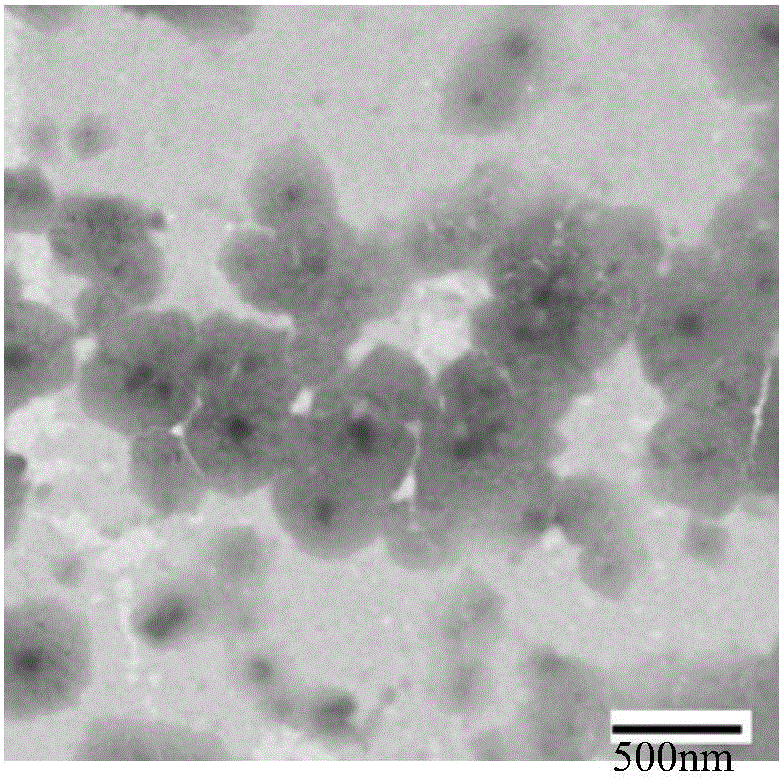
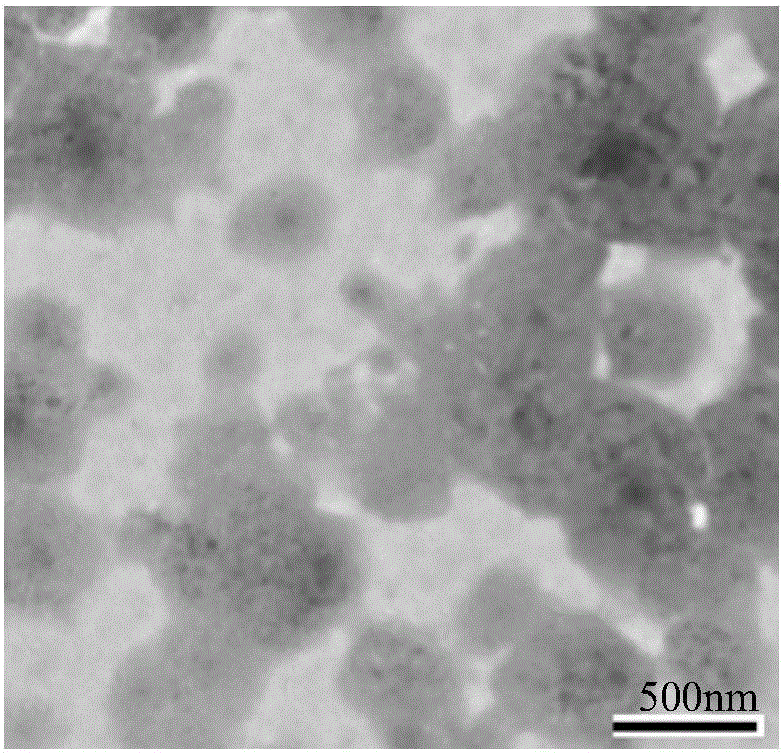
Method for separating extracellular microcapsules from cells, tissue culture supernatant or body fluid, specialized separating reagent, kit and application
A technology for separating cells and tissue culture, applied in tissue culture, culture process, animal cells, etc. It can solve the problems of the difference in the concentration of extracellular microcapsules, affect the use, and the sample volume is only 100-200mL, etc. Simple operation and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1. Isolation of extracellular microcapsules from the culture supernatant of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0038] 1. Materials
[0039] Cells: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, provided by Cell State (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd., were isolated and cultured according to conventional methods.
[0040] Main reagents: polyethylene glycol (PEG), purchased from Sigma, USA, product number 81260, with an average molecular weight of 6000. Sodium chloride was purchased from Sigma, USA. Tris and hydrochloric acid were of analytical grade and purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. Fetal bovine serum was purchased from Invitrogen. alpha-MEM medium was purchased from Invitrogen.
[0041] Preparation of main reagents:
[0042] (1) Prepare 500mM Tris HCl solution with a pH value of 8.0.
[0043] (2) Prepare 0.15M NaCl solution with Tris·HCl solution, Tris·HCl is 100mM.
[0044] (3) A 40% (W / V) polyethylene glycol (PEG) solution...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2. Isolation of extracellular microcapsules from the culture supernatant of human dendritic cells
[0061] 1. Materials
[0062] Cells: Human dendritic cells, provided by Cell State (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd., were isolated and cultured according to conventional methods.
[0063] Main reagents: polyethylene glycol (PEG), purchased from Sigma, USA, product number 1546605, average molecular weight 8000. Sodium chloride was purchased from Sigma, USA. IL-4, GM-CSF and LPS were purchased from Peprotech. AIM-V serum-free medium is a product of Invitrogen.
[0064] Preparation of main reagents:
[0065] (1) Prepare 2M NaCl solution with deionized water.
[0066] (2) Use 2M NaCl solution to prepare 30% (W / V) polyethylene glycol (PEG) solution.
[0067] 2. Method
[0068] 1) Cultivate human dendritic cells by conventional methods, the medium is AIM-V serum-free medium, and the culture conditions are 37°C, 5% CO 2 , 95% humidity, add IL-4 (final concentrati...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3. Isolation of extracellular microcapsules from human peripheral blood
[0077] 1. Materials
[0078] Cells: Human peripheral blood, derived from healthy donors. Human plasma was harvested according to conventional methods and anticoagulated with heparin.
[0079] Main reagents: polyethylene glycol (PEG), purchased from Sigma, USA, product number 1546569, with an average molecular weight of 4000. Sodium chloride was purchased from Sigma, USA.
[0080] Preparation of main reagents:
[0081] (1) Prepare 2M NaCl solution with deionized water.
[0082] (2) Prepare 48% (W / V) polyethylene glycol (PEG) solution with 2M NaCl solution.
[0083] 2. Method
[0084] 1) Prepare human plasma by conventional methods, the specific method is: centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes. Transfer the plasma to a 50 mL centrifuge tube.
[0085] 2) Add 10 mL of 48% (W / V) PEG solution to 30 mL of human plasma, the final concentration of PEG is 12% (W / V), and mix well.
[0086] 3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com