A method for detecting the viability of cistanche seeds
A technology of viability and cistanche, which is applied in the field of detection of viability of Cistanche seeds, can solve the problems of complex detection conditions and operations, high cost of chemical reagents, long detection cycle, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1, the method for detecting the viability of Cistanche seeds
[0059] 1. Cistanche seed selection
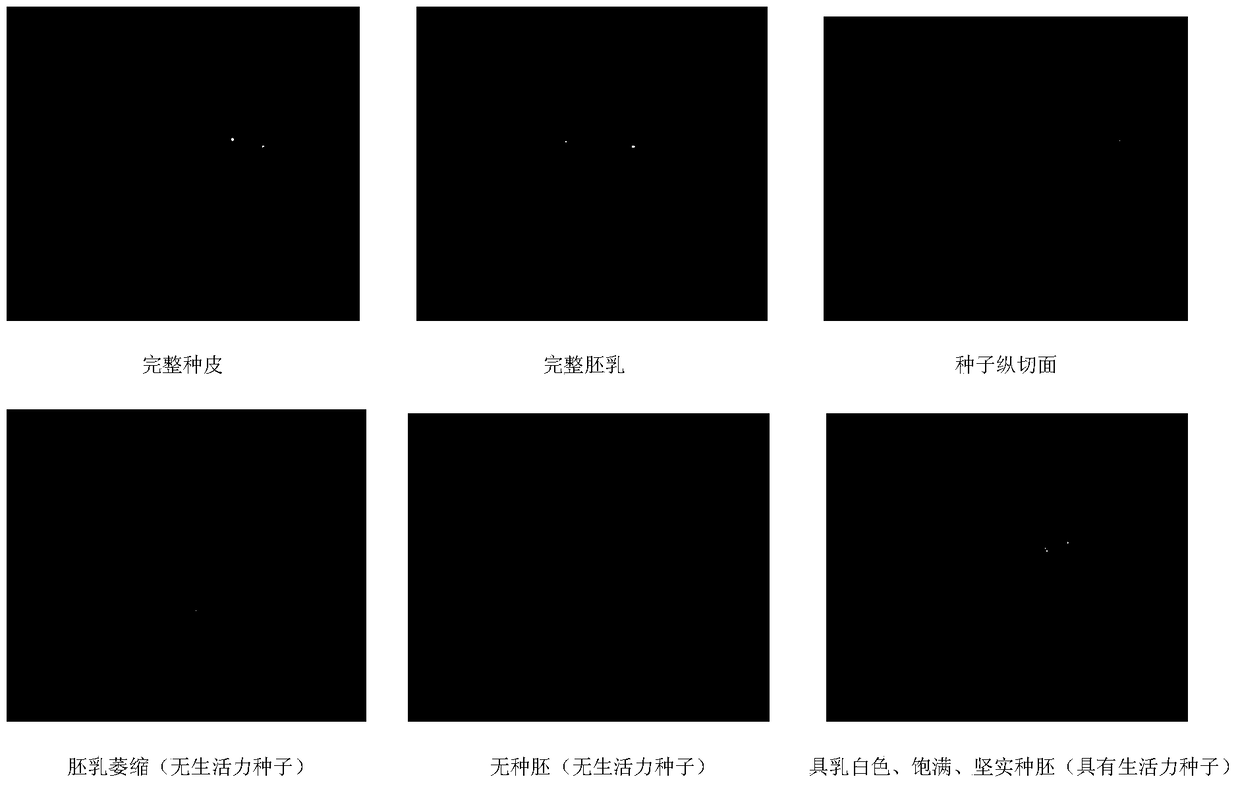
[0060] Cover the mature inflorescences of Cistanche deserticola that were normally strong in 2014 with three sections of white nylon mesh bags (the mesh size is greater than 70, to prevent the seeds from falling to the ground). After the seeds mature, collect the seeds from the inflorescences, mix the seeds with Evenly, pass it through soil sieves with apertures of 1.0, 0.8, 0.6, 0.4, and 0.2 mm in turn to obtain seeds with diameters of 0.8-1.0 mm, 0.6-0.8 mm, 0.4-0.6 mm, 0.2-0.4 mm, and 0-0.2 mm. mm seed at all levels. After absorbing water, the seeds of each diameter range were dissected under the dissecting microscope to observe the number of milky-white, plump, and solid embryos per 100 seeds of each level. Divide the number by 100 to obtain the percentage of seeds with viable embryos at each level. Seeds were repeated 4 times. The results of the determi...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2, the application of the method for detecting the viability of Cistanche seeds
[0087] 1. Select a group of seeds with a diameter of 0.4-1.0mm from a batch of Cistanche seeds
[0088] The 0-1.0mm seeds collected from the normal fruiting Cistanche infructome in 2014 are subjected to the following screening process:
[0089] 1) Pass a batch of Cistanche seeds through soil sieves with apertures of 1.0 and 0.4 mm to obtain seeds with a diameter of 0.4-1.0 mm;
[0090] 2) The seeds with a diameter of 0.4-1.0 mm are passed through soil sieves with an aperture of 1.0 and 0.5 mm to obtain seeds with a diameter of 0.5-1.0 mm;
[0091] 3) Pass the seeds with a diameter of 0.4-1.0 mm through soil sieves with apertures of 1.0 and 0.6 mm to obtain seeds with a diameter of 0.6-1.0 mm;
[0092] 4) Pass the seeds with a diameter of 0.6-1.0 mm through soil sieves with apertures of 1.0 and 0.8 mm to obtain seeds with a diameter of 0.8-1.0 mm.
[0093] Use a ten-thousandth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com