Method for preparing biological activated carbon by hydrothermal carbonization of algae residue/algae sludge
A technology of biological activated carbon and hydrothermal carbonization, which is applied in the field of environmental protection and biological materials, can solve the problems of less research and industrialization, and achieve the effect of simple processing equipment, strong adjustable application scale, and avoid cumbersome operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Preparation of Biological Activated Carbon by Cultivating Cyanobacteria Mud in Laboratory
[0030] Include the following steps:
[0031] (1) Collect algae mud by centrifugation; 400ml algae culture solution (algae density: 1~5×10 7 algal cells per milliliter), centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant to collect the precipitate, and resuspend with 40ml deionized water.
[0032] (2) Put the algae mud (water content about 90%) into a 50ml hydrothermal reaction kettle (pressure less than 6MPa) and carbonize at a constant temperature of 160°C-220°C in an electric oven for 2-20 hours, then cool naturally to room temperature.
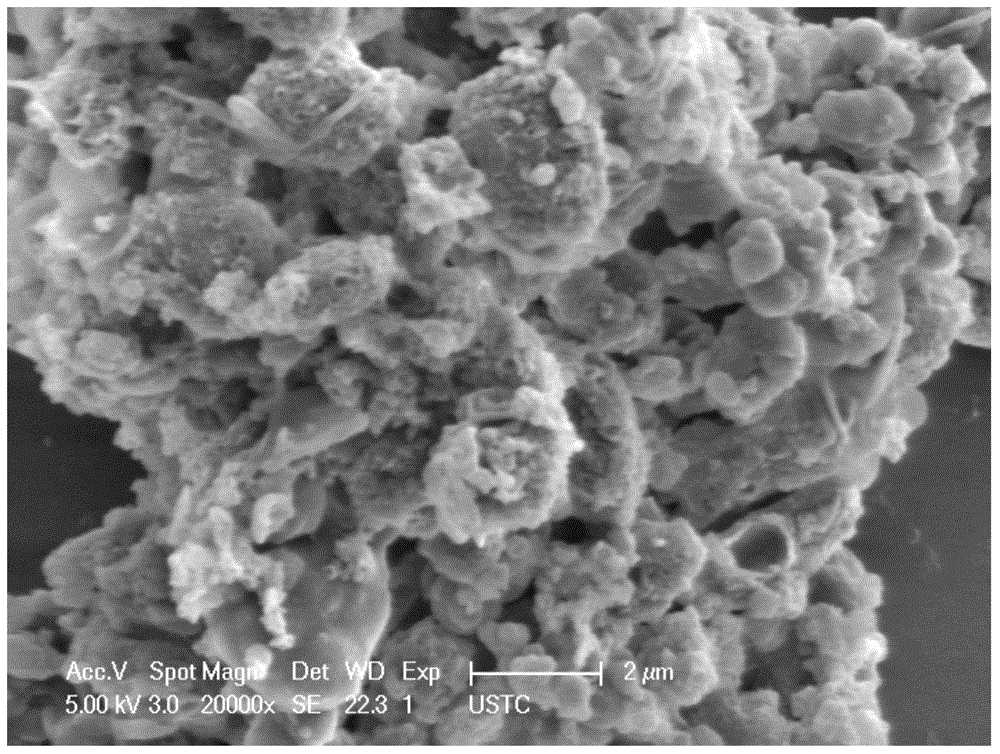
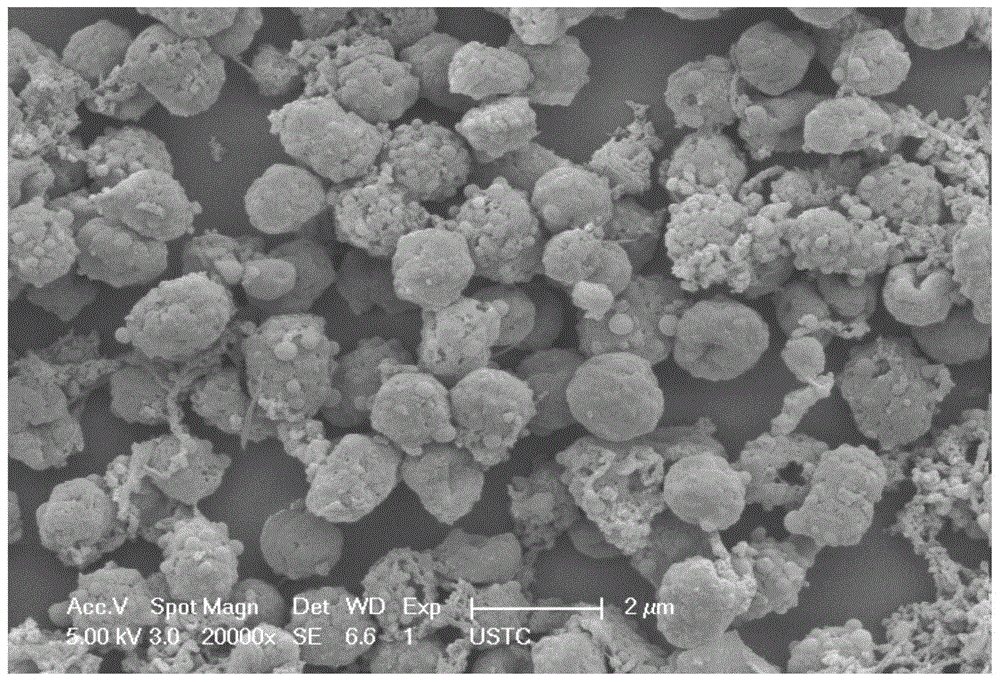
[0033] (3) Centrifuge the mixed solution in the hydrothermal reaction kettle (9000 rpm, 10 minutes), collect the precipitate, wash it with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times in turn, and then dry it at 50-60°C to obtain figure 1 The bioactivated carbon shown.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Direct use of algae residue / algae mud to prepare biological activated carbon
[0036] Include the following steps:
[0037] (1) Salvage the cyanobacteria algae residue / algae mud during the period of cyanobacteria outbreak.
[0038] (2) Directly put 10g of algae residue / algae mud (water content is 90.5%) into the React in a 50ml hydrothermal reaction kettle (pressure less than 6MPa) in an electric oven at a constant temperature of 160°C to 220°C for 2 to 20 hours, then cool naturally to room temperature.
[0039] (3) Centrifuge the mixed liquid in the hydrothermal reaction kettle (9000 rpm, 10 minutes), collect the precipitate, wash it with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times in turn, and then dry it at 50-60°C to obtain the following: figure 2 The bioactivated carbon shown.
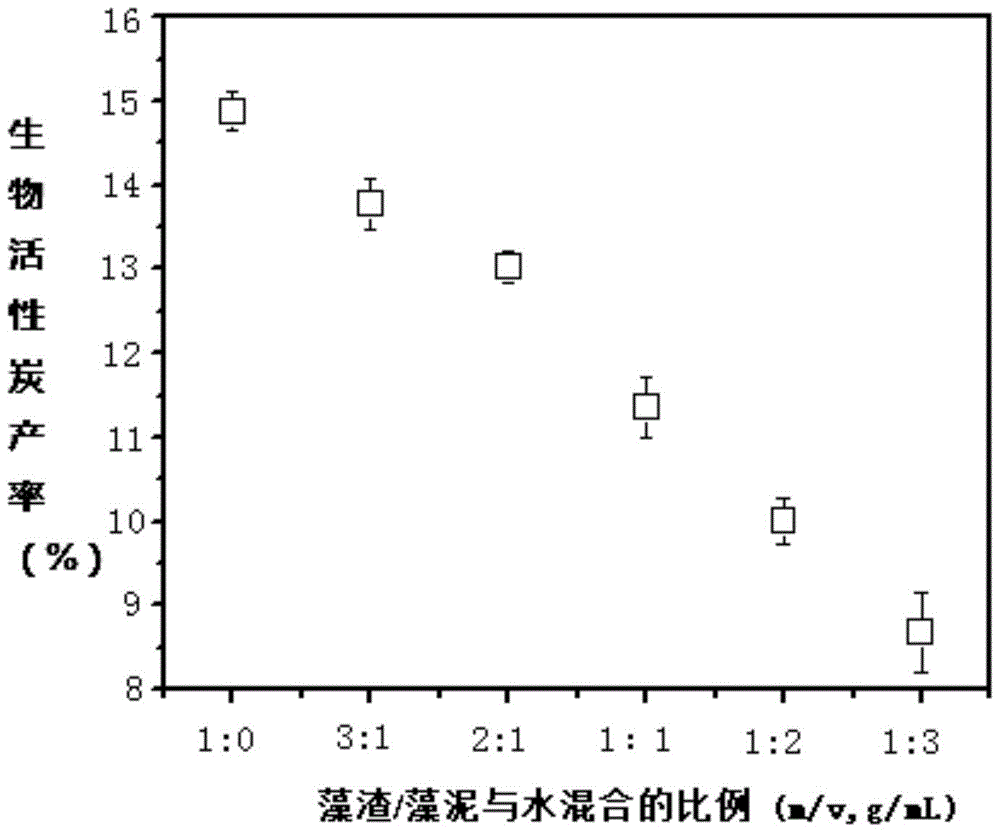
[0040] Such as image 3 As shown, with the increase of the amount of water added to the algae residue / algae mud, the conversion rate of bioactivated carbon gradually decreased (fr...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Preparation of bioactivated carbon from naturally dried cyanobacteria bloom residue
[0043] Include the following steps:
[0044] (1) When a cyanobacteria bloom breaks out, the naturally dried algae residue is manually salvaged and crushed into dry algae powder.
[0045] (2) 2g of dry algae powder is mixed with water at a mass volume ratio of 5% to 15%; 6g of dry algae powder is mixed with water at a mass volume ratio of 20% to 200%. Place in a 50ml hydrothermal reaction kettle (pressure less than 6MPa) in an electric oven at a temperature of 160°C to 220°C for 2 to 20 hours, then cool naturally to room temperature.
[0046] (3) Centrifuge the mixed liquid in the hydrothermal reaction kettle (9000 rpm, 10 minutes), collect the precipitate, wash it with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times in turn, and then dry it at 50-60°C to obtain biological activated carbon.
[0047] Such as Figure 4 As shown, with the increase of the amount of water added to the dr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com