A method for rapid propagation of lupine "gallery" leaves combined with out-of-bottle rooting technology
An exogenous root and lupine technology, applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, plant regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of low seed setting rate, difficulty in ensuring time and quantity, difficulty in inheriting good characters, etc., and achieve short differentiation time, The effect of efficient preservation of genetic traits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] In this example, cytokinin ZT is not added to the callus induction and differentiation medium, and the callus induction culture is not cultured in the dark as a control, including the following steps:
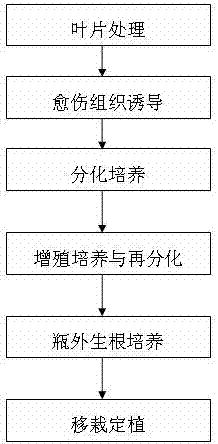
[0024] 1. Leaf treatment: Cut off the young leaves 2 / 3 away from the tip, rinse with running water for 30 minutes, and cut them into 1cm-wide slices through the main vein. On the ultra-clean workbench, first disinfect with 75% alcohol for 10 seconds, rinse with sterile water twice; then use 10% NaOCl magnetic stirring for 5 minutes, rinse with sterile water for 5 times; then disinfect with 0.1% mercuric chloride solution for 3 minutes, Rinse 5 times with sterile water; finally blot the leaf surface moisture with sterile filter paper. Cut off the leaf edge, cut into 3mm×3mm blocks in the form of crosscutting the main vein, and make 2 to 3 incisions on the main vein.
[0025] 2. Callus induction: Inoculate the treated leaves on the medium MS+6-BA 0.5mg / L+ZT1.0mg / L+PVP 5.0...
Embodiment 2
[0034] In this example, different concentrations of 6-BA and NAA were added to the proliferation and redifferentiation medium as a control, including the following steps:
[0035] 1. Leaf treatment: Cut off the young leaves 2 / 3 away from the tip, rinse with running water for 30 minutes, and cut them into 1cm-wide slices through the main vein. On the ultra-clean workbench, first disinfect with 75% alcohol for 10 seconds, rinse with sterile water twice; then use 10% NaOCl magnetic stirring for 5 minutes, rinse with sterile water for 5 times; then disinfect with 0.1% mercuric chloride solution for 3 minutes, Rinse 5 times with sterile water; finally blot the leaf surface moisture with sterile filter paper. Cut off the leaf edge, cut into 3mm×3mm blocks in the form of crosscutting the main vein, and make 2 to 3 incisions on the main vein.
[0036] 2. Callus induction: Inoculate the treated leaves on the medium MS+6-BA 0.5mg / L+ZT1.0mg / L+PVP 5.0mg / L+VC 1.0mg / L with the back side do...
Embodiment 3
[0044] In this example, the concentration of rooting liquid and the soaking time are different during rooting culture outside the bottle, and the ratio of nutrient soil when transplanting and planting is different as a comparison, including the following steps:
[0045] 1. Leaf treatment: Cut off the young leaves 2 / 3 away from the tip, rinse with running water for 30 minutes, and cut them into 1cm-wide slices through the main vein. On the ultra-clean workbench, first disinfect with 75% alcohol for 10 seconds, rinse with sterile water twice; then use 10% NaOCl magnetic stirring for 5 minutes, rinse with sterile water for 5 times; then disinfect with 0.1% mercuric chloride solution for 3 minutes, Rinse 5 times with sterile water; finally blot the leaf surface moisture with sterile filter paper. Cut off the leaf edge, cut into 3mm×3mm blocks in the form of crosscutting the main vein, and make 2 to 3 incisions on the main vein.
[0046] 2. Callus induction: Inoculate the treated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com