Method for isolating tumor cell-derived exosomes from malignant pleural effusion
A technology for malignant pleural effusion and tumor cells, applied in tumor/cancer cells, cell dissociation methods, animal cells, etc., can solve the problems of restricting researchers' research, complicated and time-consuming steps, complex equipment requirements, etc., to overcome tumor specificity. Low performance, simple and effective cost, accurate and reliable method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Extraction of exosome derived from tumor cells in pleural effusion of lung cancer patients
[0040] ①With the patient’s informed and ethical consent, collect 2ml of preoperative pleural effusion specimens from tumor patients (pathological biopsy has confirmed lung cancer) in the first 10ml centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 4°C and 300g for 10 minutes , separated to remove the cells in the pleural effusion, and then to obtain the supernatant fluid.
[0041] ② Transfer the upper layer liquid obtained in ① into a second centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4°C and 10,000 g for 15 minutes, separate to remove organelles and other impurities, and obtain a supernatant.
[0042] ③ Transfer the supernatant into the third centrifuge tube, add the same amount of exosome extract (Total Exosome Isolation, Invitrogen) as the volume of the supernatant, mix, shake evenly, and incubate at 4°C overnight (6-16 hours average can), and then, centrifuge the incubated mixture at 4° C. ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: Extraction of tumor-derived exosome in pleural effusion of patients with esophageal cancer
[0072] The tumor-derived exosome in the pleural effusion of a patient with esophageal cancer was extracted by basically the same method as in Example 1. That is: ① The pleural effusion sample in the middle is a 5ml pleural effusion sample from a patient with esophageal cancer before operation, and other steps are exactly the same as in Example 1.
[0073] Similarly, the method in Example 1 was used to observe the product obtained in Example 2 with an electron microscope, and the morphology of exosomes consistent with the literature was also observed.
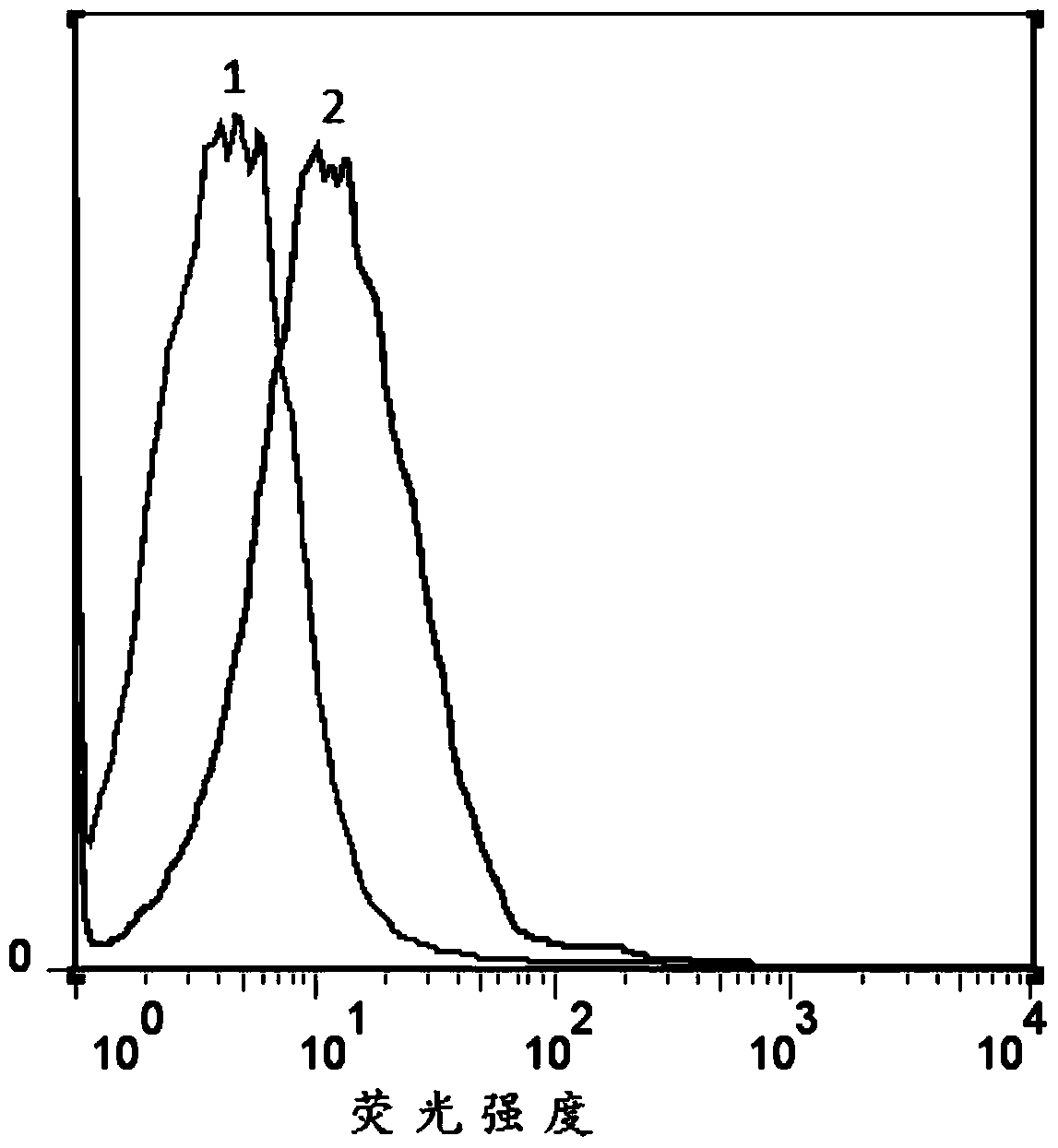
[0074] Further, immunofluorescence and flow cytometry were used to detect CD63 expression:
[0075] Resuspend the product obtained in Example 2 (i.e., tumor cell-derived exosome bound to magnetic beads) with 1 ml of 1×PBS to obtain a tumor exosome resuspension, that is, 1 ml of pleural effusion tumor-derived exosome re...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3: Extraction of tumor-derived exosomes in the pleural effusion of ovarian cancer patients
[0079] The tumor-derived exosome in the pleural effusion of a patient with ovarian cancer was extracted by basically the same method as in Example 1. That is: ① The pleural effusion sample in the middle is 2.5ml of the preoperative pleural effusion sample of an ovarian patient, and the other steps are exactly the same as those in Example 1.
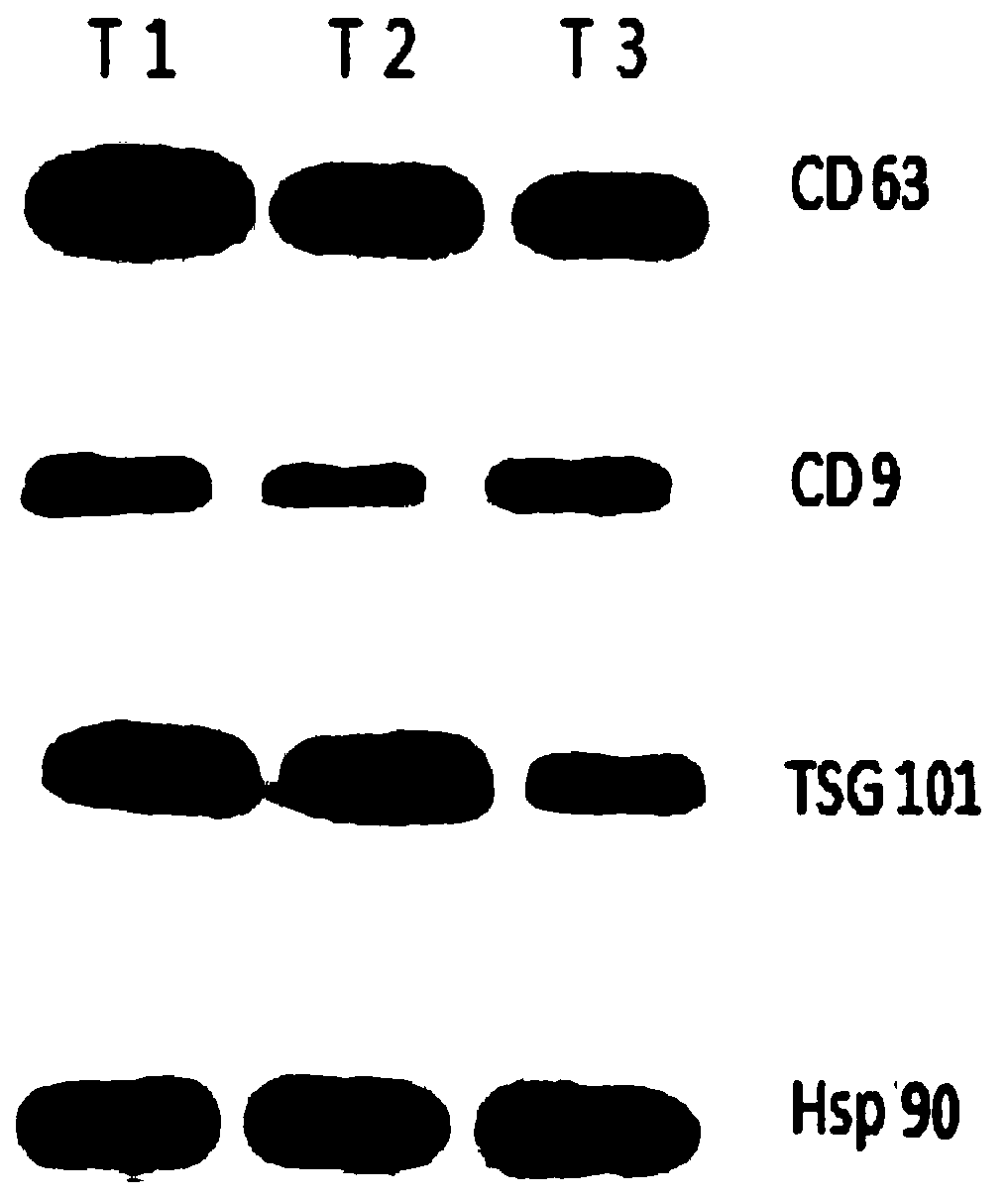
[0080] Using the product characterization method in Example 1, the product obtained in Example 3 was observed and tested. The results showed that: the product obtained in Example 3 had an exosome morphology that was consistent with that recorded in the literature, and the unique characteristics of exosomes were detected in the product. The expression of proteins CD9, CD63, Hsp90, Tsg101 and the strong expression of tumor antigen EpCAM protein prove that the product obtained in Example 3 is the exosome derived from tumor cells extrac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com