Biomarkers of miR-34 activity
A technology of biomarkers and markers, applied in the field of cancer therapy, can solve problems such as no effect and little effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0118] Example 1 - Materials and methods
[0119] Cell culture, oligonucleotides and proliferation assays. Syngeneic cancer cells derived from MCF10A breast cancer and SW48, HCT116, DLD-1 and RKO colorectal cancer cell lines were obtained from Horizon Discovery Ltd (Cambridge, UK). See Table 3. Synthetic miRNA mimics and siRNA were purchased from Life Technologies (Ambion, Austin, TX). To stimulate the TP53 pathway, cells were pretreated with 10 μM etoposide for 28 h, and RNA was harvested for qRT-PCR analysis. Determine the use of each cell line using siRNA against EG5, a spindle protein required for proliferation 2000 (Invitrogen) or RNAiMAX TM (Invitrogen) for optimal transfection conditions. Reverse transfections were performed in duplicate or triplicate. In short, to contain 20 μl per well of 2000 (SW48, MCF10A, DLD-1, HCT116) or RNAiMAX (RKO) Add 5 μl of a solution of oligonucleotides in RNase-free water. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 20 m...
Embodiment 3
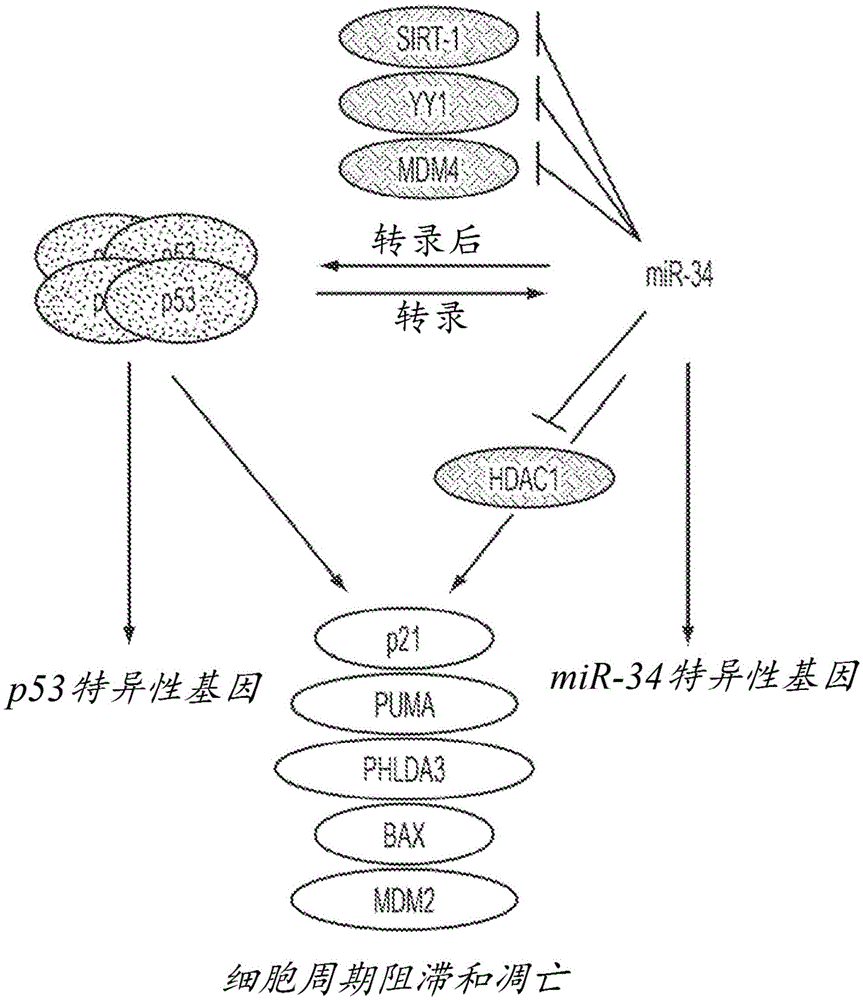
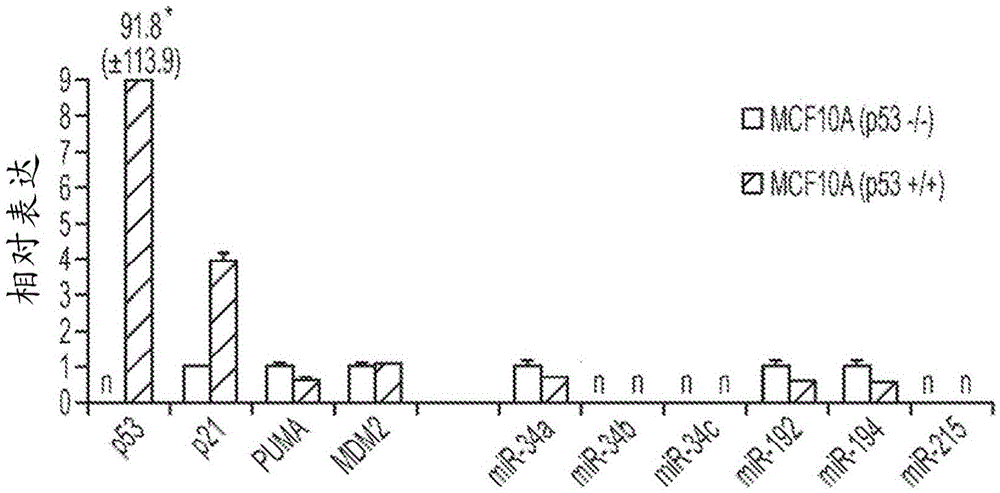
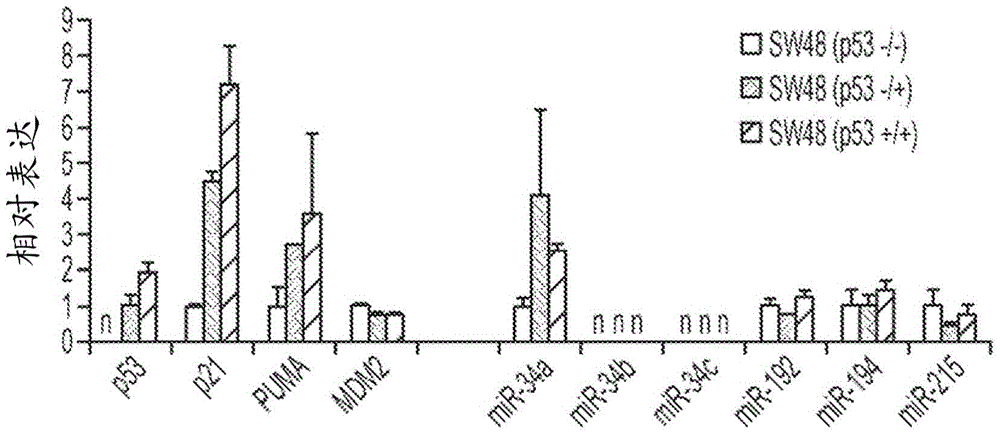
[0138] Example 3 - miR-34a but not miR-215 induces TP53-regulated genes in the absence of TP53
[0139] To understand the miR-34-induced phenotype in TP53-positive and TP53-deficient cells, the expression levels of genes related to the TP53 / miR-34 axis were determined. A possible explanation for the TP53-independent effect is that these cells do not express endogenous SIRT1 or MDM4. However, as demonstrated by qRT-PCR, TP53 + / + and TP53 - / - The cells both carried detectable levels of SIRT1 and MDM4 mRNA, suggesting that the TP53-independent phenotype was not due to the absence of these gene products (Figure 8). In contrast, both mRNAs were reduced in cells transfected with miR-34, according to experimental data showing that SIRT1 and MDM4 are directly targeted by this miRNA (Yamakuchi et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(36):13421-6 (2008); Mandke et al., PLoS One7(8):e42034 (2012)). Similarly, the miR-34a target MET and the miR-215 target BCL2 were specifically downregulate...
Embodiment 4
[0140] Example 4 - HDAC1 is a direct target of miR-34a
[0141] p21 CIP1 / WAF1 A plausible explanation for the TP53-independent upregulation is the potential involvement of other TP53 family members TP63 and TP73. These two proteins exert distinct roles from TP53; however, they also control a set of genes that overlap with those of TP53. Endogenous mRNA levels of TP63 and TP73 were determined in TP53 wild-type and TP53-deficient cells that had been transfected with miR-34a. However, none of these cells showed detectable levels of TP63 or TP73, suggesting the involvement of these gene products is unlikely (data not shown).
[0142] Next, the regulatory mechanism independent of TP53 and the controllable p21 CIP1 / WAF1 A nuclear regulator of expression. One candidate of interest is HDAC1 because it has a putative miR-34a binding site in its 3'UTR ( Figure 10 ), down-regulated in cells transfected with miR-34a ( Figure 11 ), and has been associated with p21 in the absence of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com