A method for evaluating the microscopic pore structure of tight reservoirs and classifying them
A technology for microscopic pores and tight reservoirs, which is applied in the fields of petroleum exploration and geological research, and can solve problems such as difficulty in observing micron-nanoscale pores, inability to measure 14nm pore size, poor permeability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
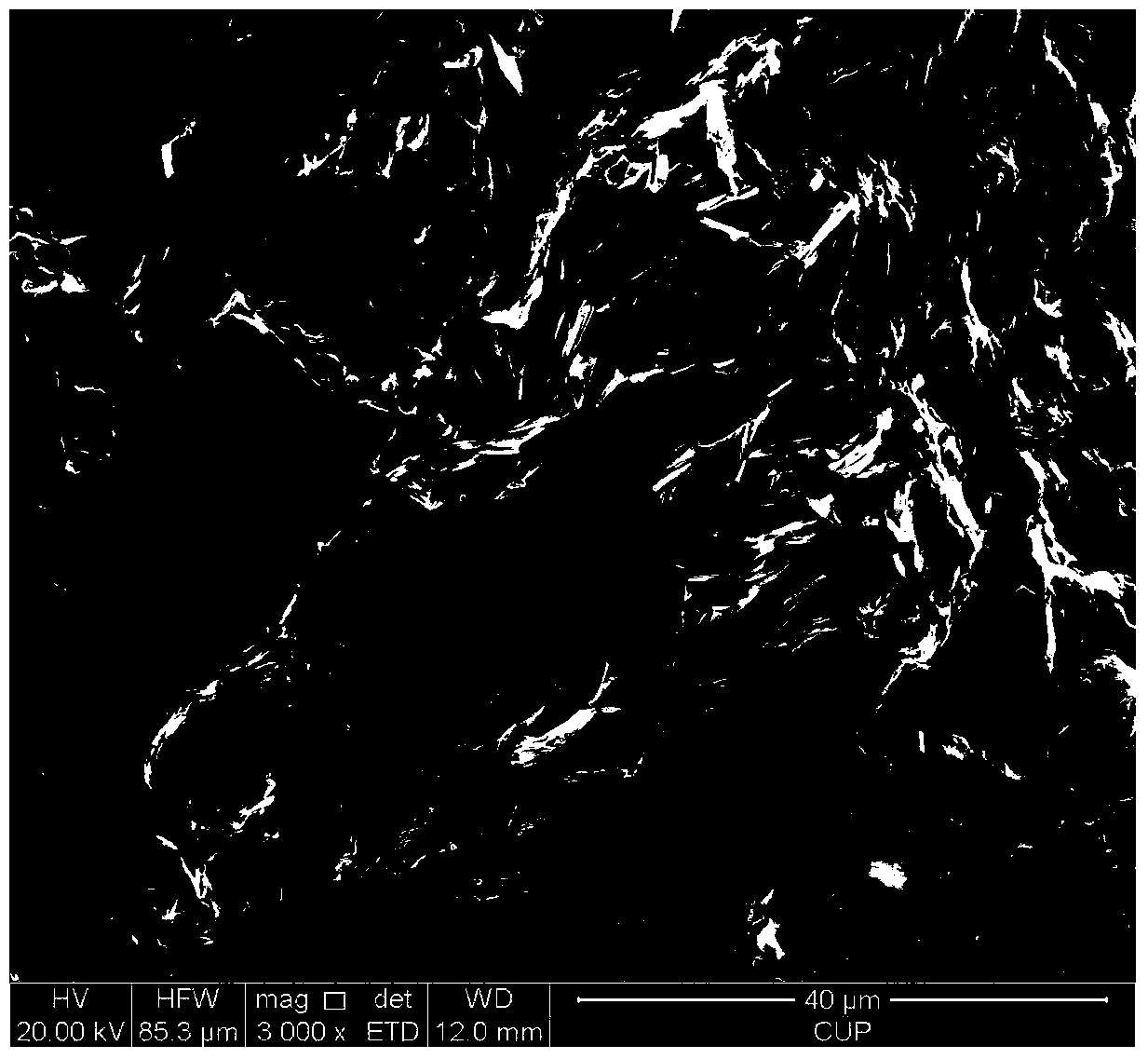
[0074] The Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin in western my country is a set of coal-measure strata dominated by sand and mudstone deposited on the Middle and Lower Triassic carbonate rocks, of which the Xu1, Xu3 and Xu5 members are dominated by mudstone Shale, Xu 2, Xu 4 and Xu 6 are dominated by gray, off-white fine-medium sandstone. The long-term exploration practice in western Sichuan has targeted the low-permeability sandstone reservoirs of the Xu 2 and Xu 4 Members. However, through unconventional oil and gas evaluation work, it has been found that the Xu 5 Member also has great gas potential. The fifth member of the Xu Member is buried at a depth of 3500-5000m, and its lithological combination is dominated by thin sand-mud interbeds, of which fine sandstone is about 20%, siltstone is about 25%, and mud shale is about 55%. The average reservoir porosity is 3.21%, and the average permeability is 0.0329×10 -3 μm 2 . Reservoir pores are mainly in the micron-nano scale...
Embodiment 2
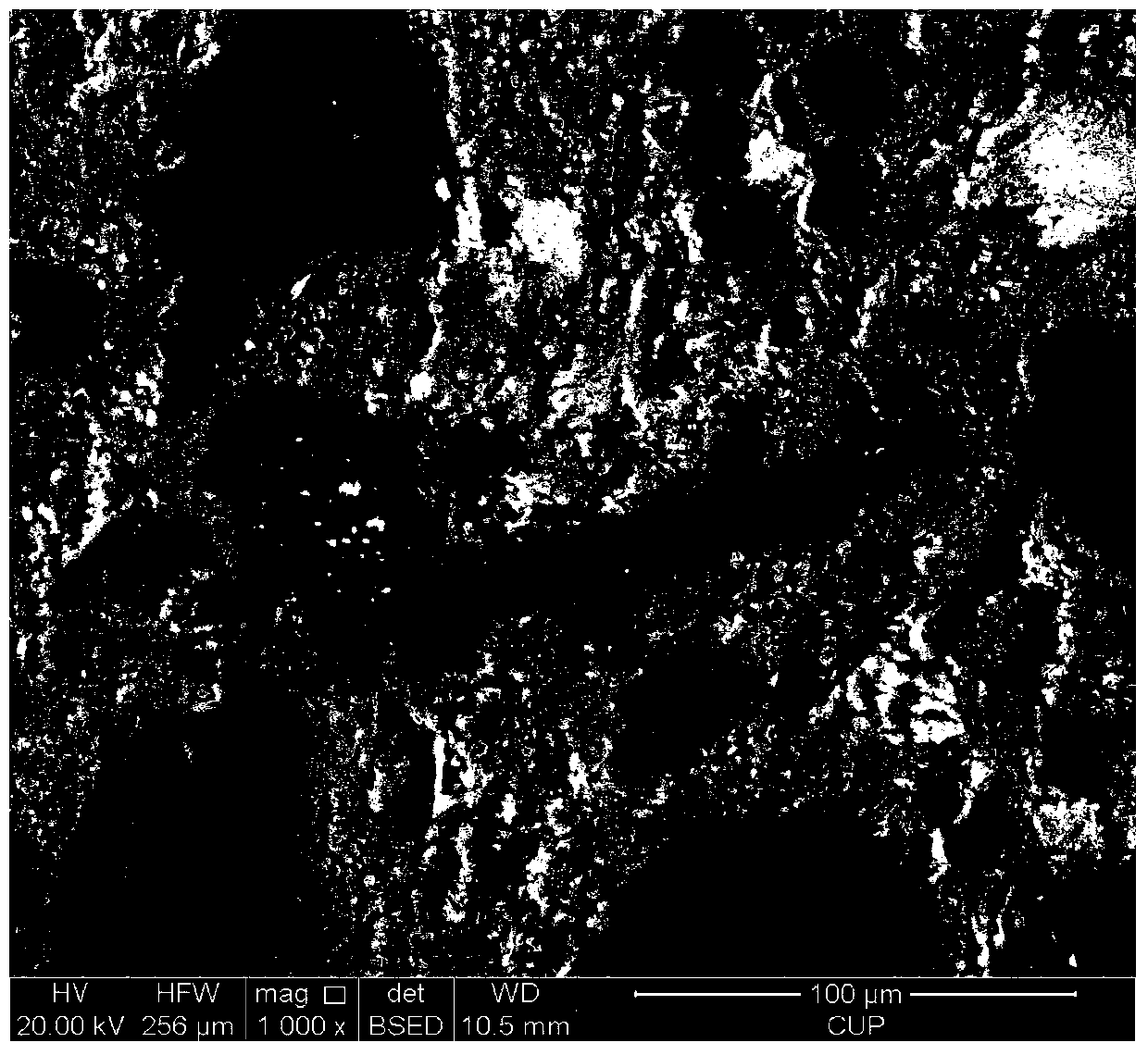
[0100] In the northern part of the Tarim Basin in western China, a set of channel facies sandstone mainly composed of fluvial facies and delta facies develops in a stable distribution. The porosity of the sandstone is 1-8%, and the permeability is mainly 0.01-0.1×10 -3 μm 2 , belonging to tight reservoirs. The main problems in reservoir research are as follows: (1) There are many types of reservoir cementation, and some small cements are small and difficult to identify; (2) Pores are small, with well-developed micropores and nanopores. It is difficult to identify it; (3) The particles are in close contact and the radius of the pore roar is extremely low. When the maximum mercury injection pressure is low, it is difficult to fully reflect the structural characteristics of the pore roar. In this regard, this embodiment provides a microscopic pore structure evaluation and reservoir classification method for the above-mentioned tight reservoirs, such as figure 1 As shown, it inc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com