Slow characteristic based cell division recognition method and recognition device thereof
A cell division and identification method technology, applied in the field of slow feature-based cell division identification methods and identification devices, can solve the problems of reducing the cell division identification rate, strong noise in microscope images, high computational complexity, etc., and achieves easy identification and tracking. Effects of processing, reduced computational complexity, increased capability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] In order to make the feature extraction of cells more accurate, it can not only detect the edge of the image well, but also effectively reduce noise, see figure 1 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for identifying cell division based on slow features, the method comprising the following steps:
[0046] 101: Divide the cell image into a data set; randomly take half of the data in the positive and negative examples as the training set and the test set;
[0047] Wherein, before performing data set division on the cell image, the method further includes preprocessing the cell image to normalize the grayscale image.
[0048] 102: Use unsupervised slow feature analysis to extract cell data to obtain slow feature functions;
[0049] 103: Calculate the cumulative square offset feature of the slow feature of the cell, and obtain the arrangement of the slow feature change rate from small to large;
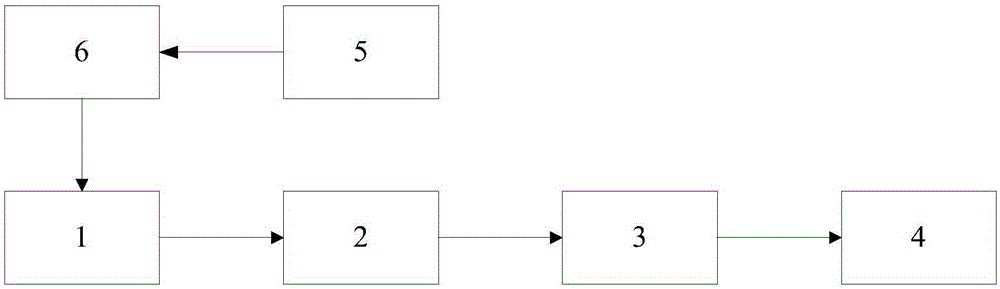
[0050] 104: Use the method of model learning to detect...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The scheme in embodiment 1 is described in detail below in conjunction with specific calculation formulas and examples, see the following description for details:
[0055] 201: Perform scale normalization preprocessing on all cell images;
[0056]Among them, each image sequence represents a cell division sequence, each image has a length W and a width H, and the sequence length is L. In order to simplify the problem, the embodiment of the present invention defaults that each sequence image to be split has been extracted, and the step of obtaining the split sequence through cell detection and tracking is no longer considered. So size normalization is to process each frame of image.
[0057] In the embodiment of the present invention, it is assumed that the size of the converted original cell image is s×s, and here s×s is uniformly set to 25×25 for illustration. There are no restrictions on the method of transformation.
[0058] 202: Divide the preprocessed cell image ...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Below in conjunction with specific Table 1 and Table 2, the scheme in Embodiment 1 and 2 is verified for feasibility, see the following description for details:
[0093] In this experiment, C2C12 mouse myoblasts commonly used in the prior art were used, and photographs were taken at five-minute intervals during the cell growth process by an optical microscope (Zeiss Axiovert T135V). The image sequence has a total of 1013 frames, and the resolution of each image is 1392*1040. Randomly select 1000 frames of cell images, and after preprocessing the original cell data, use manual labeling to classify the cell data, and randomly select half of the labeled positive and negative examples to form the training set and test set respectively set, where the length of each image sequence is 21 frames, and the image size of each frame is 25*25. This method is then used for slow feature learning. Information and parameter settings on cell types, cell culture environments, and data a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com