A multi-level stacking logging identification method for deep coal measures and thin coal seams
An identification method and thin coal seam technology, applied in the direction of earthwork drilling, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve the problems of identifying coal seams, failing to meet the identification requirements of deep strata, and being unable to accurately identify and determine, so as to overcome misjudgment Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
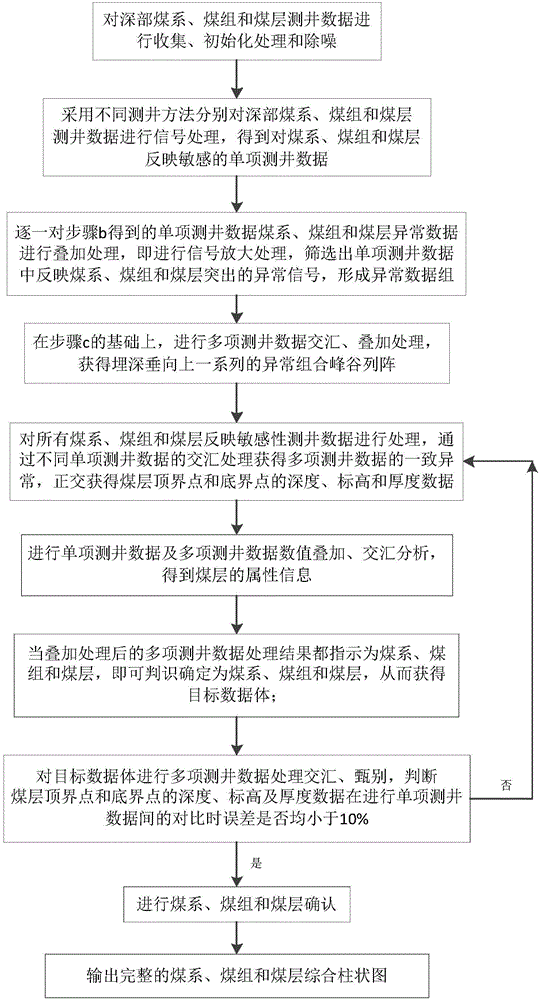
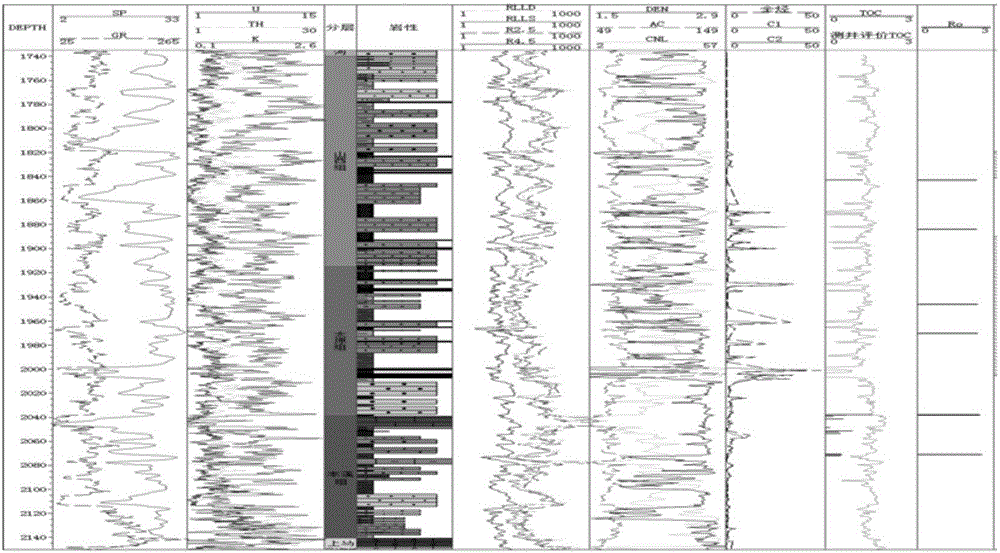
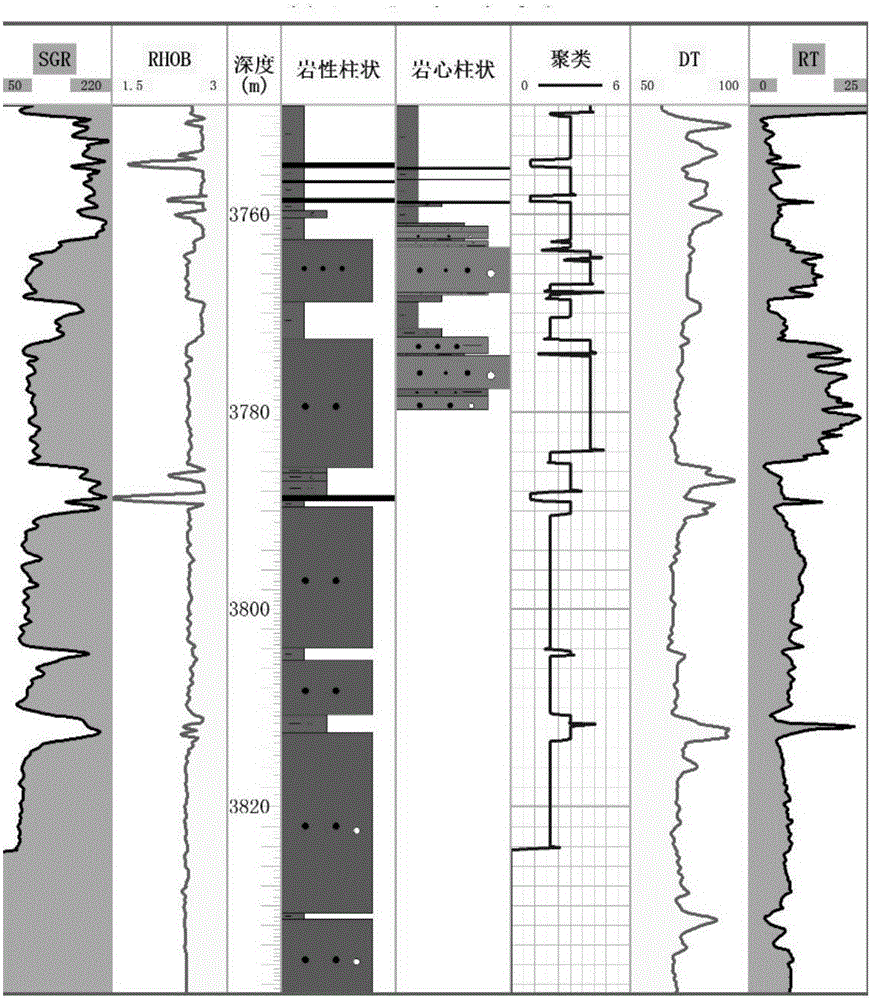
[0027] The basic idea of the present invention is: the thickness of the deep coal seam is small, all of which are extremely thin coal seams, generally less than 0.5m in thickness. However, the logging response of these thin coal seams is still relatively obvious, and some coal seams have relatively large logging anomalies. Since the logging interval is fixed, generally 0.15m, the theoretical resolution of the logging is 0.15m×2=0.3m. However, there are many influencing factors in actual work, and the logging resolution is generally greater than 0.5m. Since the coal seam is thin and less than the logging resolution, what it shows in the logging response is not the real coal seam characteristics, but contains a considerable part of the coal seam roof and floor lithology characteristics, which weakens the real coal seam measurement. The response degree of the well is blurred, and the boundary between the coal seam logging anomaly and the lithology of the roof and floor becomes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com