Engineering organophosphorus hydrolase, nucleic acid, mutant and application of engineering organophosphorus hydrolase and mutant
An organophosphorus and hydrolase technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as poor performance of malathion, and achieve the effects of high organophosphorus hydrolysis activity and thermal stability, good practical application value, and good thermal stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Site-directed Saturation Mutagenesis of Organophosphate Hydrolases
[0056] In this example, the method of active site cassette mutation (CASTing) is used to transform organophosphate hydrolase, and the plasmid pET28a-PoOPH preserved by the inventor is selected. M2 , Carry out CASTing mutations to transform protein active pocket amino acids. According to the protein structure information, select Val55, Leu57, Leu62, Thr87, Val89, Phe111, Leu115, Trp172, Met188, Ile250, Trp263, Phe265 for site-directed saturation mutation.
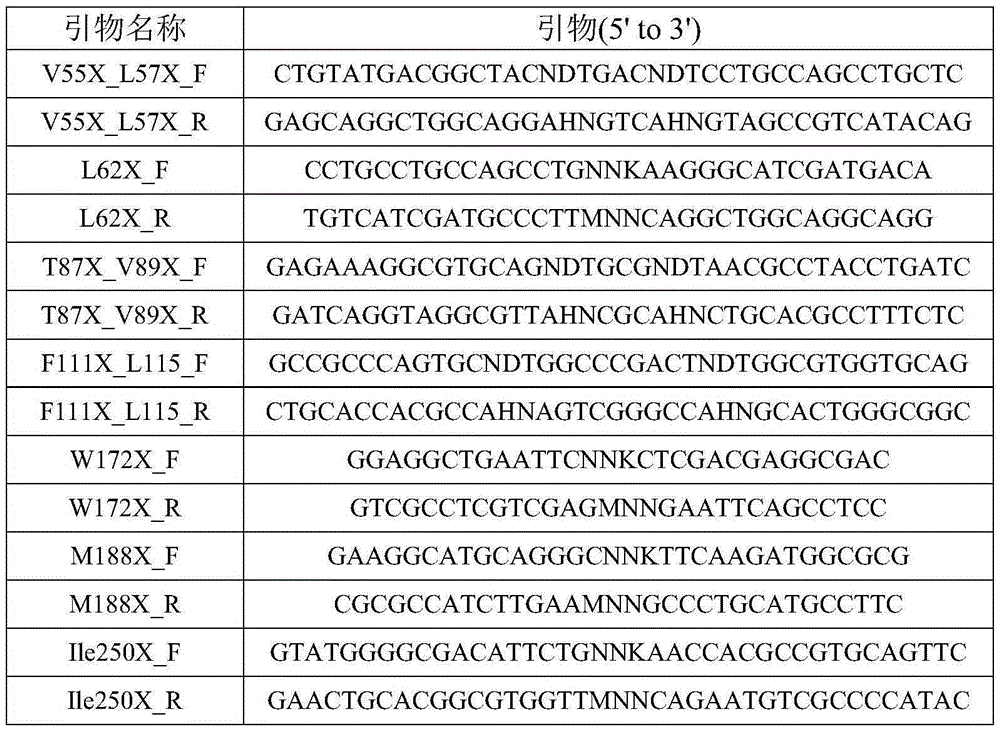
[0057] Design primers for site-directed saturation mutagenesis, as shown in Table 1.
[0058] Table 1. List of primers for site-directed saturation mutagenesis
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] Among them, N represents any one of the four bases A, C, G, and T, M represents any one of the two bases T and G, and K represents any one of the two bases A and C , D represents any one of the three bases A, G, and T, and H represents any one of the three b...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Site-directed Saturation Mutagenesis of Organophosphate Hydrolases
[0074] The present embodiment adopts error-prone PCR (epPCR) technology to the mutant PoOPH that CASTing obtains M5 Carry out random mutation of the whole sequence to transform organophosphate hydrolase.
[0075] Design gene cloning primers as follows:
[0076] PoOPH-F: 5'-GAATTC GAGCTC ATGCGTCTTTTTCTCG-3'
[0077] PoOPH-R: 5'-CCC AAGCTT GGCGGTCGCTACGGA-3'
[0078] Wherein, the underlined part of the upstream primer PoOPH-F is the SacI restriction site, and the underlined part of the downstream primer PoOPH-R is the HindIII restriction site.
[0079] with PoOPH M5 Gene sequence of pET28a-PoOPH M5 The plasmid was used as a template for PCR amplification. The PCR system is: template 25ng, upstream and downstream primers (10pmol / μl) 1μl each, 2×TaqMix 12.5μl, 150μM nCl 2 , ddH 2 O to make up to 25 μl. The PCR amplification program is: (1) 95°C for 2min; (2) 94°C for 30sec; (3) 55°C for 30sec; ...
Embodiment 3
[0087] DNA Recombination Transformation of Organophosphate Hydrolase
[0088] Using DNA rearrangement technology, the dominant mutants obtained in the error-prone PCR mutation library are randomly combined to merge beneficial mutations. All the dominant mutant genes obtained in the above-mentioned error-prone PCR mutation library were mixed as a template for gene cloning, and the cloning primers were the same as error-prone PCR. The PCR reaction system is: mixed recombinant plasmid template 25ng, 10×Buffer 2.5μl, dNTPs (2mM) 2.5μl, a pair of cloning primers (10pmol / μl) 0.75μl each, KOD-plus-enzyme 0.5U, distilled water to make up to 25μl. The PCR amplification program is: (1) 2 min at 94°C; (2) 10 sec at 98°C; (3) 30 sec at 55°C; (4) 1 min at 68°C; steps (2) to (4) are performed for 25 cycles. Use an agarose gel DNA recovery kit to recover the only target band, concentrate the resulting mixed mutant gene to 200ng / μl, and use DNaseI to perform random cutting. The enzyme cuttin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com