Treatment agent for synthetic fiber and its application
A synthetic fiber and synthetic fiber filament technology, which is applied in fiber treatment, fiber type, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of uneven adhesion of treatment agents, achieve excellent emulsion stability, less yarn breakage, and excellent product stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
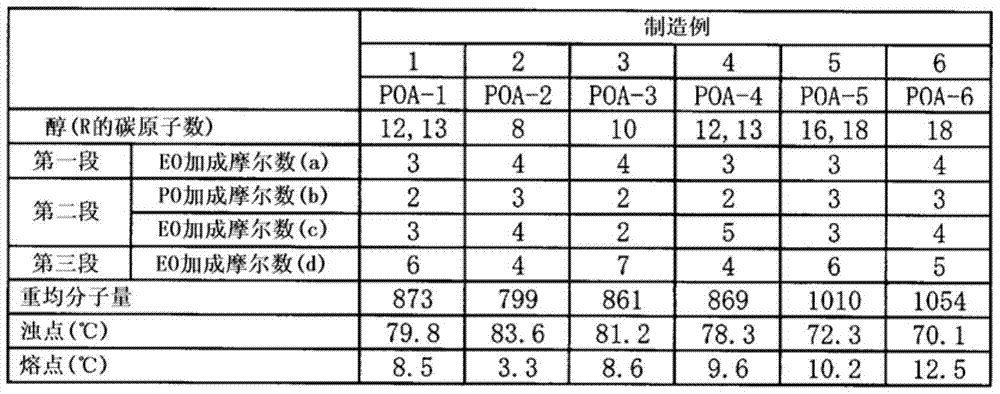
manufacture example 1
[0126] In a 2L autoclave (autoclave) capable of stirring and temperature regulation, with an alkylene oxide stuffing box, a nitrogen supply pipe, and a pressure regulating pump, put 193 g of C as alcohol. 12~13 Alcohol, 0.9 g potassium hydroxide as base catalyst. After replacing the inside of the autoclave with nitrogen, a dehydration operation was performed at 100 to 110° C. for 1 hour while stirring. Next, in order to achieve the desired molar ratio, at a gauge pressure of 0.0-0.4MPa and a reaction temperature of 140-150°C, 132g of ethylene oxide is put in as the first stage, and a mixture of 116g of propylene oxide and 132g of ethylene oxide is put in. As the second stage, 264 g of ethylene oxide was charged as the third stage, and the addition polymerization reaction was carried out for about 8 hours. Thereafter, the obtained polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether was neutralized and recovered with 1.4 g of lactic acid. Thus, polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether (POA-1) was obtained.
manufacture example 2~12 and manufacture comparative example 1~12
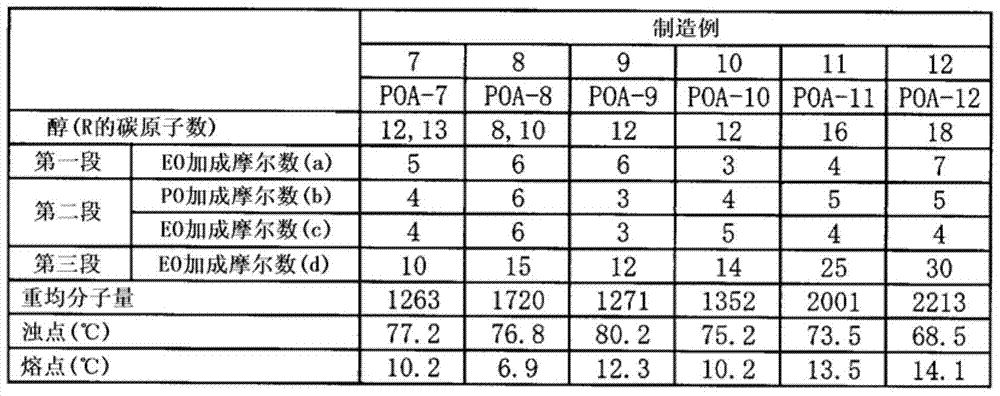
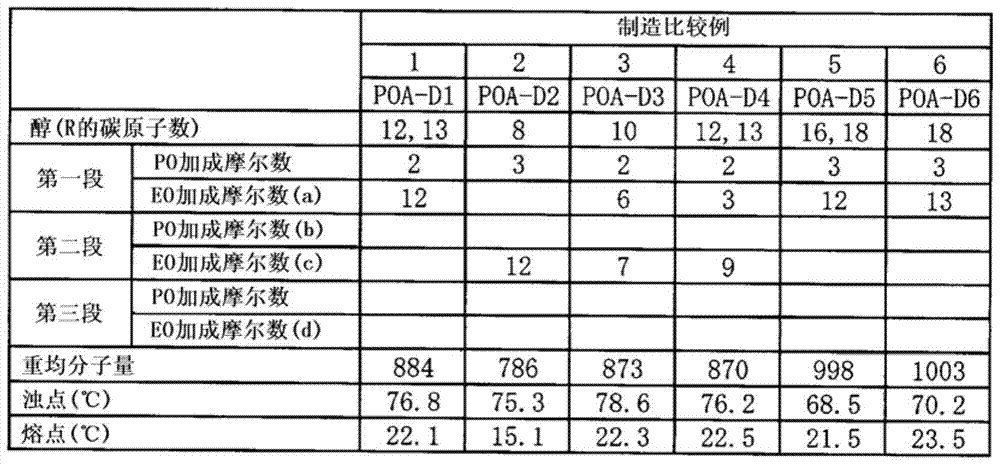
[0128] POA-2-12 and POA-D1-12 were obtained like manufacture example 1 except having changed the addition mole number of alcohol, ethylene oxide, and propylene oxide of each example described in Tables 1-4. The cloud point of a 1% by weight aqueous solution of polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether and the melting point of polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether were measured as follows.
[0129]
[0130] A 1% by weight aqueous solution of polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether was prepared. Next, the cloud point test solution was temporarily clouded by heating, and the temperature at which the cloudiness disappeared was defined as the cloud point.
[0131]
[0132] Take the polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether with a capillary tube of the specified size, make it close to the mercury bulb of the thermometer, raise the temperature slowly in the air bath, the sample melts, and take the temperature when it becomes opaque as the melting point .
[0133] Table 1
[0134]
[0135] Table 2
[0136]
[0137] tabl...
manufacture example 13
[0143] Except having changed the addition mole number of alcohol, ethylene oxide, and propylene oxide described in Table 5, it carried out similarly to manufacture example 1, and obtained polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether. The obtained polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether is esterified with fatty acid as follows.
[0144] Add 775g of polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether and 248g of lauric acid in the reaction container with stirring blade, heating device and dehydration pipe, and carry out esterification reaction at 180~210° C. for 8 hours. Thus, polyoxyalkylene alkyl ether ester (POAEE-13) was obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cloud point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| cloud point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com