Rotating electrical machine
A technology for rotating electric machines and wire groups, applied to the shape/style/structure of winding conductors, which can solve problems such as increased winding resistance, longer wire length, and lower efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0056] The rotating electrical machine 1 according to Embodiment 1 will be described.
[0057] The rotating electrical machine 1 has a stator and a rotor. The rotor rotates relative to the stator, and the rotational power is transmitted to a mechanical device (not shown) via a shaft (not shown) fixed to the rotor to operate the mechanical device. The rotating electrical machine 1 is, for example, a permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine or an induction type rotating electrical machine. In the rotary electric machine 1, for example, the winding configuration in the stator 3 has been improved.
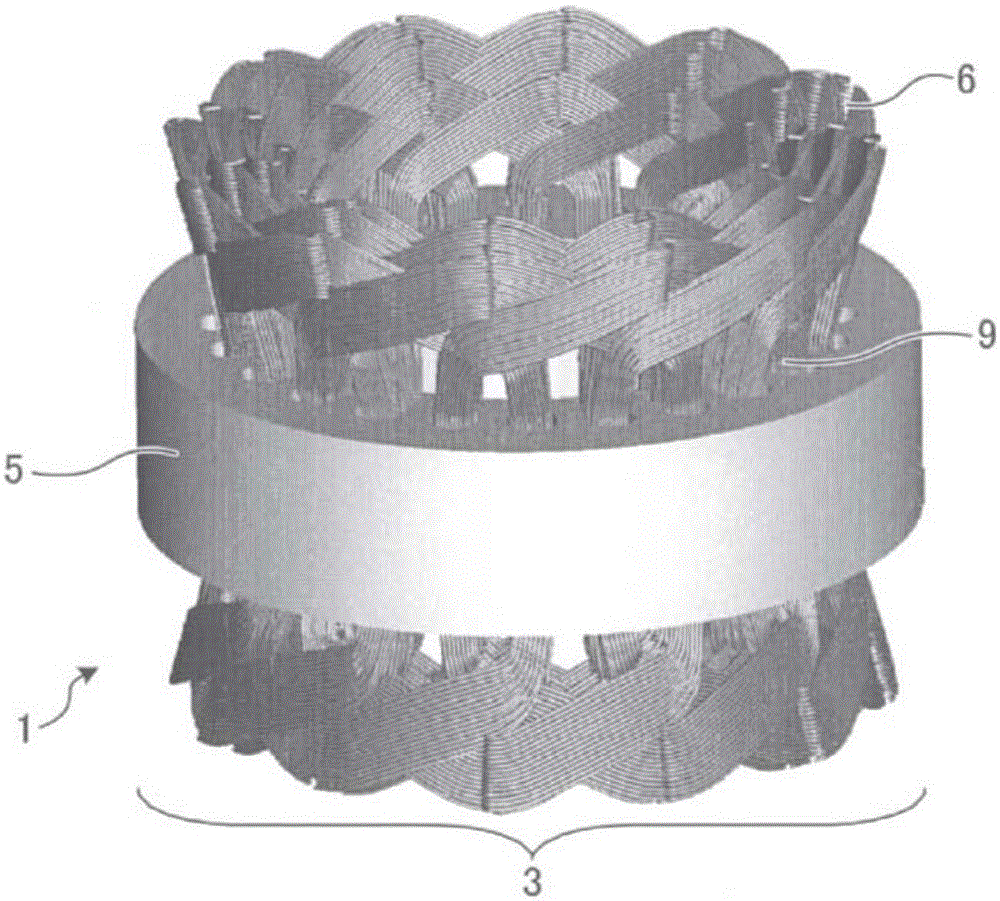
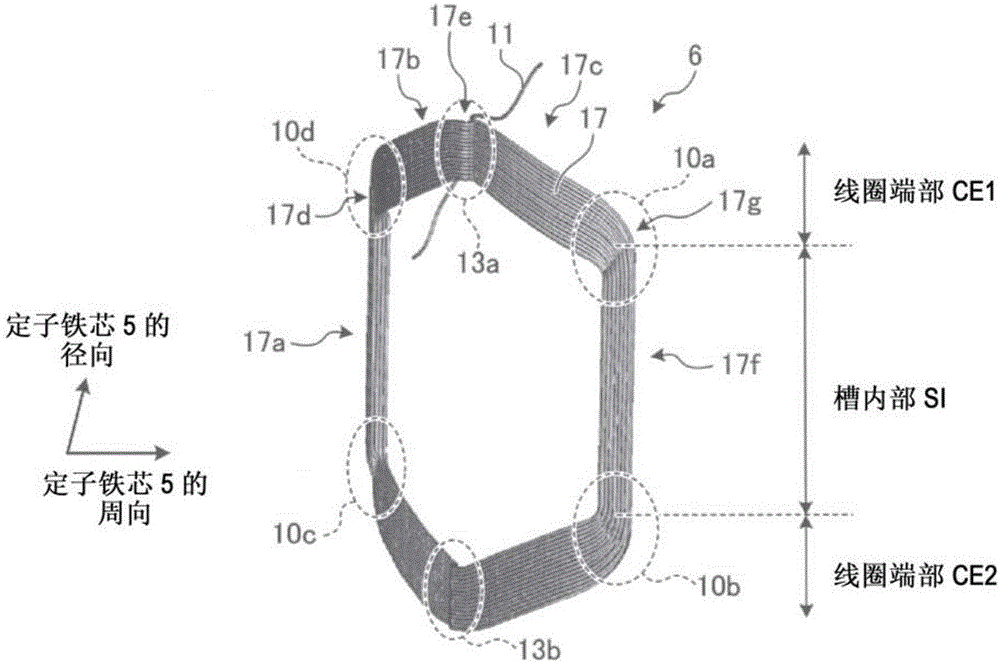
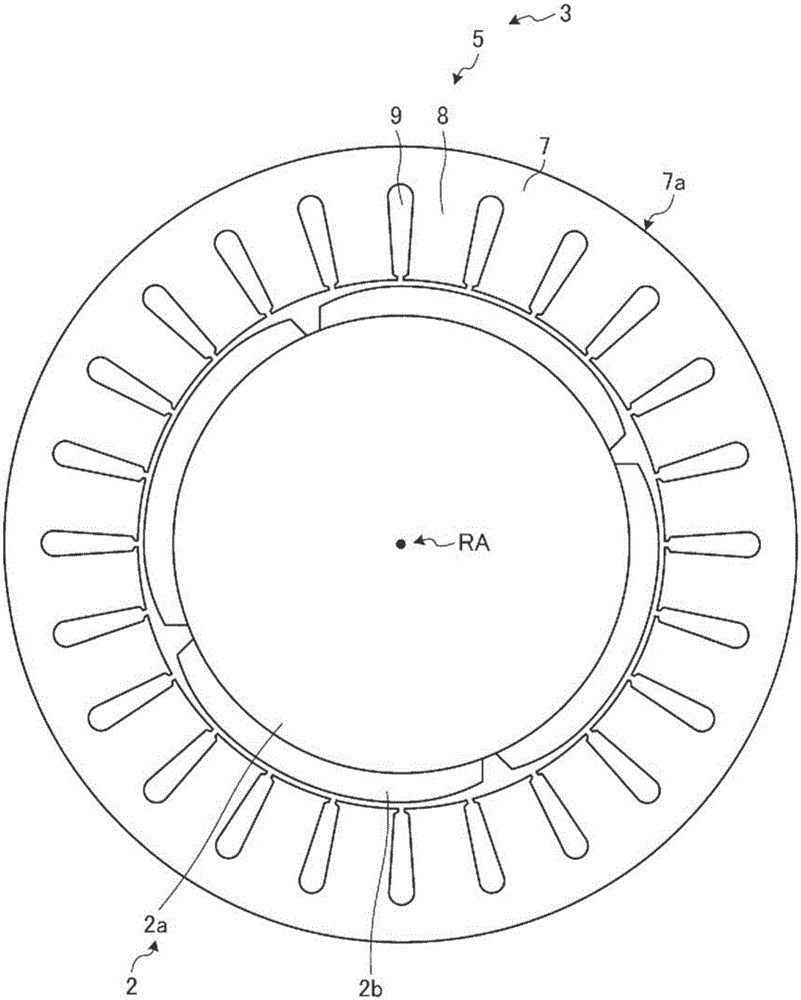
[0058] Specifically, the rotating electrical machine 1 has Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 structure shown. figure 1 It is a perspective view showing the configuration of a stator core and a stator winding in the rotating electric machine 1 . figure 2 It is a perspective view showing the structure of the coil in a stator winding. image 3 It is a figure which shows the structure at ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0132] Hereinafter, rotating electrical machine 200 according to Embodiment 2 will be described. Hereinafter, the description will focus on the differences from Embodiment 1. FIG.
[0133] In Embodiment 1, a coil is exemplarily described in which the conductive wires 11 arranged in two layers in the radial direction in the slot interior SI are changed to one layer in the radial direction at the coil ends CE1 and CE2. In Embodiment 2, a coil is exemplarily described in which the conductive wires 21 arranged in three layers in the radial direction in the slot interior SI are changed to one layer in the radial direction at the coil ends CE1 and CE2.
[0134] Specifically, in the stator winding 206 of the stator 203 of the rotary electric machine 200, as Figure 9 ~ Figure 11 As shown, the structure of each coil 217 forming the winding of each phase is different from Embodiment 1 in the following points. Figure 9 It is a figure which looked at the state which inserted the coil ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0156] Hereinafter, rotating electric machine 300 according to Embodiment 3 will be described. Hereinafter, description will focus on parts different from those in Embodiment 2. FIG.
[0157] In Embodiment 2, the coil 217 is exemplarily described in which the arrangement of the conducting wires 21 in three layers in the slot interior SI is changed to one layer in the coil ends CE1 and CE2, but as seen Figure 13 It can also be seen that the conductive wires 21 at the coil ends CE1 and CE2 pass through the area corresponding to the first layer or the third layer inside the slot SI, and the area corresponding to the second layer inside the slot is not used at the coil ends.
[0158] Therefore, in Embodiment 3, the method of making a conducting wire also pass through the area|region corresponding to the 2nd layer of the slot interior SI in coil end part CE1, CE2 is demonstrated.
[0159] Specifically, in the stator winding 306 of the stator 303 of the rotary electric machine 300...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com