Immunogenic composition against aeromonas hydrophila
A technique of Aeromonas hydrophila, immunogenicity, applied in the direction of bacterial antigen components, methods of using bacteria, vaccines, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0269] Example 1: Isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila from Pangasius catfish
[0270] Aeromonas hydrophila causes a disease called septicemia, or Aeromonas mobilis sepsis, in pangasius catfish. This is one of the most common diseases in Vietnamese pangasius farming. Outbreaks of Aeromonas mobilis septicemia in the Mekong region when the season changes from wet to dry, and / or when fish are stressed due to, for example, handling, transport, high levels of nitrite or ammonia, or other types of environmental stressors more common.
[0271] The clinical sign of Aeromonas mobilis sepsis is hemolysin-induced hemorrhage. External signs commonly observed in infected fish are macrocephaly, exophthalmos, reddening of the fish surface, and bleeding from the anus and fins. Ulcerative skin lesions are also common in infected fish, with fin or tail necrosis (fin rot).
[0272] Internally, there will be an excess of clear or reddish fluid in clinical hydrops, but in most cases, the dominant...
Embodiment 2
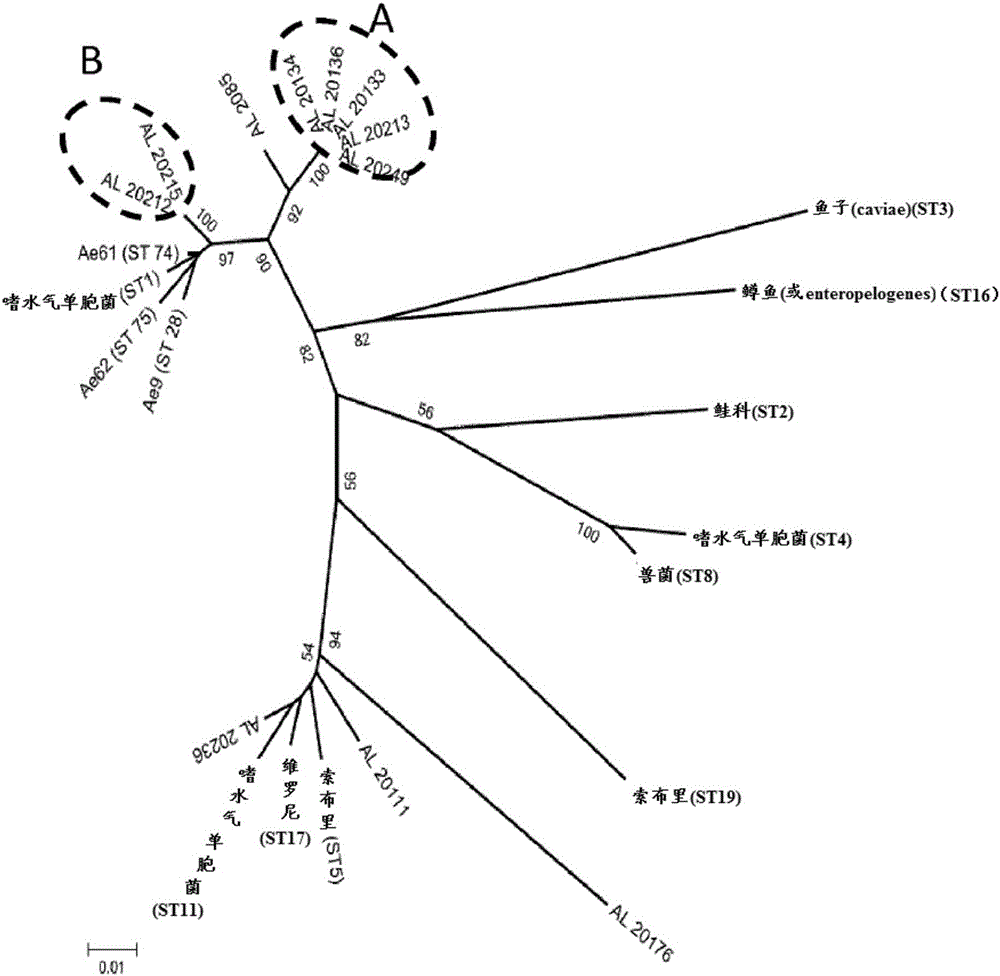
[0274] Example 2: Phylogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila
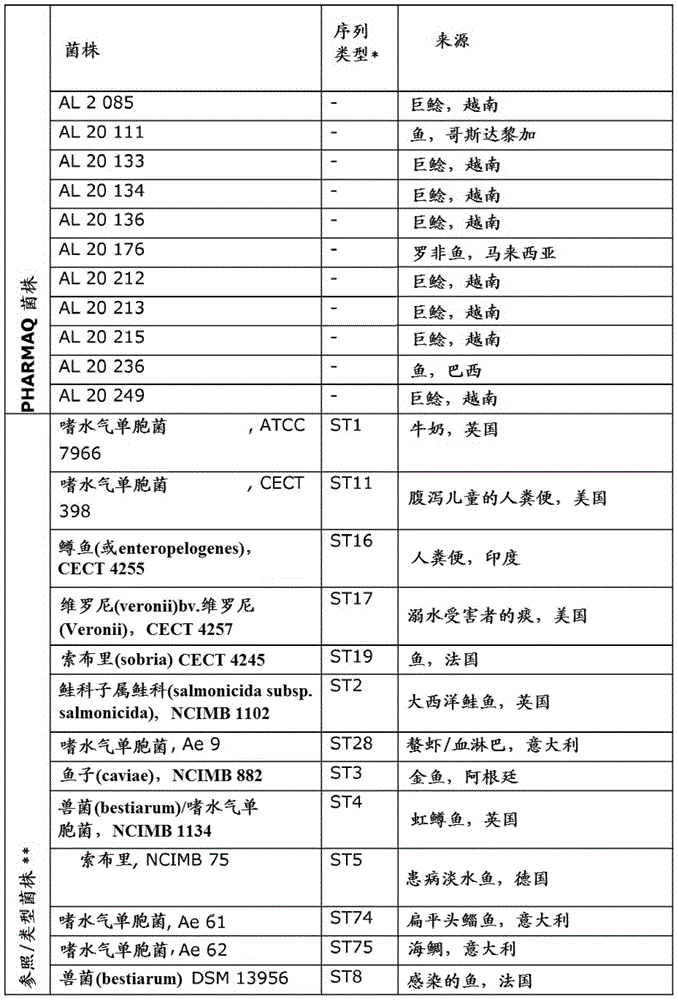
[0275] For the classification of Aeromonas hydrophila isolates obtained by the method described in Example 1, a simplified MLST-protocol was used, based on Martino et al., 2011 (incorporated herein by reference), using methionyl-tRNA Genetic information in the synthetase (metG) and citrate synthase I (gltA) genes for phylogenetic prediction.
[0276] PCR was performed using primers described in Martino et al., 2011, which is incorporated herein by reference. Use Vector The software assembles, quality-checks, and trims the DNA sequences. External reference sequences were obtained from http: / / pubmlst.orq / aeromonas and include all Aeromonas hydrophila strains from Martino et al., 2011, as well as some other Aeromonas species for reference purposes (full strains See table below for information). Sequence alignment and phylogenetic prediction were performed in MEGA5 as described in Tamura et al., 2011, which is incorpora...
Embodiment 3
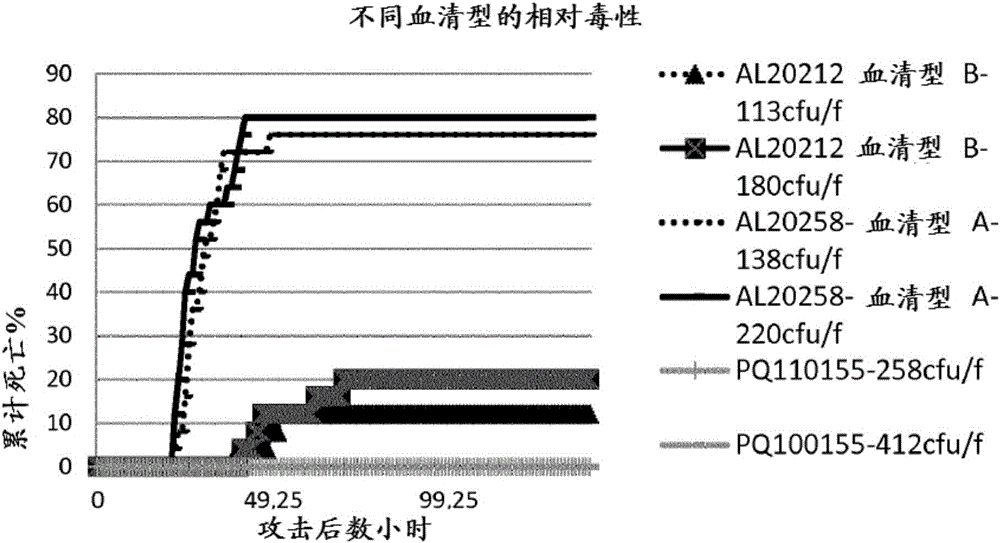
[0283] Example 3a Toxicity of different Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from fish
[0284] Aeromonas hydrophila biotype A (AL20258), biotype B (AL20212) and PQ110155 (not biotype A or B) were isolated as described in Example 1 and propagated in TSB for 24 hours. Fish weighing 18 g (batin) reared in fresh water at 28°C were injected with 0.1 ml of two different concentrations of bacterial suspension (less than 500 cfu / fish). Observations for mortality continued after challenge. Aeromonas hydrophila biotypes A and B caused rapid death, whereas PQ110155 was avirulent. Fish injected with biotype A produced higher mortality compared with biotype B as the challenge dose was used. Dead fish all showed symptoms of Aeromonas sepsis.
[0285] This experiment demonstrates that Aeromonas hydrophila biotypes A and B are virulent to pangasius and are the primary pathogens of pangasius.
[0286] Example 3b Toxicity of different Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from fish
[0287...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com