A display device and pixel circuit thereof
A technology of pixel circuit and voltage source, applied in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as uneven display
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
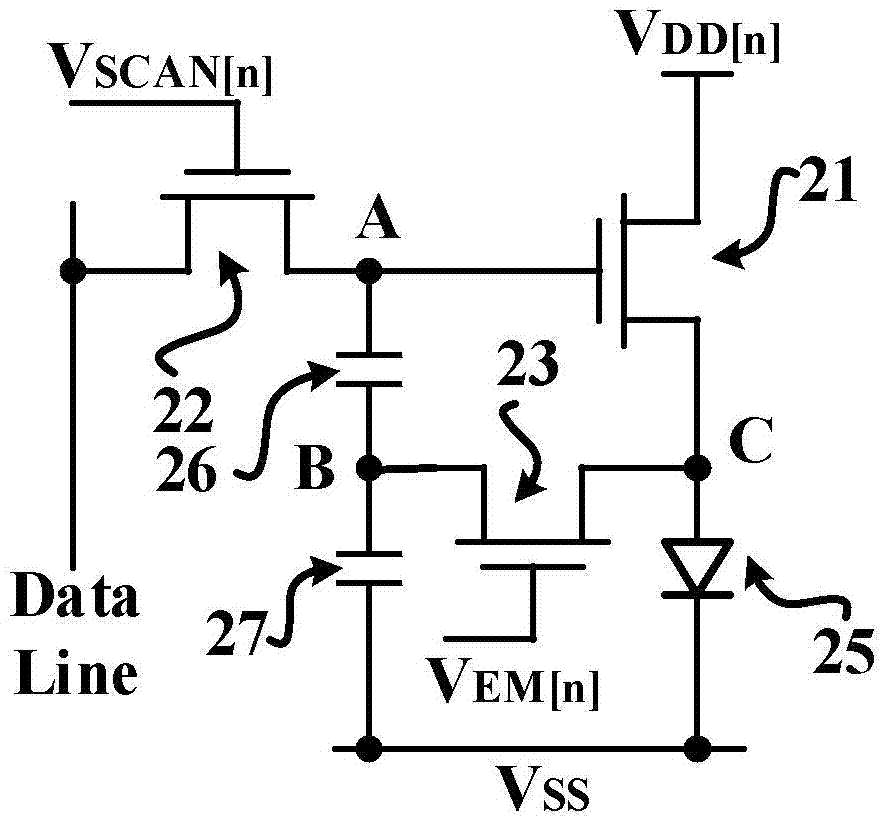
[0073] Please refer to figure 2 , this embodiment provides a pixel circuit, including a first transistor 21, a second transistor 22, a third transistor 23, a first capacitor 26, a second capacitor 27 and a light emitting device 25,
[0074] The first transistor 21 and the light emitting device 25 are serially connected to the first voltage source signal terminal V DD[n] and the second voltage source signal terminal V SS between. The control pole of the first transistor 21 is connected to the second pole of the second transistor 22, the first pole of the first transistor 21 is connected to the first voltage source signal terminal, and the second pole of the first transistor 21 is connected to the anode of the light emitting device 25 ;
[0075] The control electrode of the second transistor 22 is connected to the first scanning control signal terminal V SCAN[n] , used to receive the first scan control signal of the current row, the first pole of the second transistor 22 is...
Embodiment 2
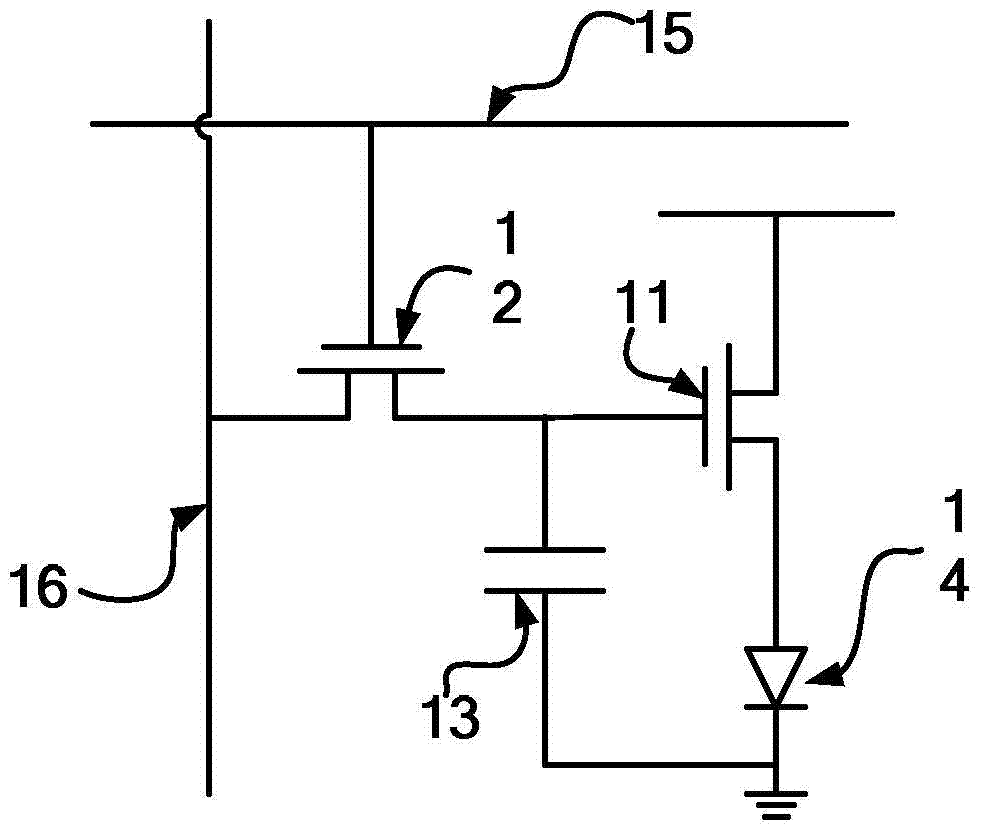
[0096] Such as Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment provides another pixel circuit, and its main difference from Embodiment 1 is that a fourth transistor 24 is added, and the fourth transistor 24 controls the second pixel circuit in the circuit under the control of the third scanning signal. Node B and the third node C are initialized; at this time, the first voltage source signal terminal V DD The input is no longer a pulse signal, but a constant high level, and the initialization is completed by the fourth transistor 24 .
[0097] The control electrode of the fourth transistor 24 is connected to the third scanning control signal terminal V R[n] , the first pole is connected to the anode of the light emitting device 25, and the second pole is connected to the third voltage source signal terminal V CM , for responding to the third scan control signal, to initialize the voltages of the second node B and the third node C to a certain low level in the initialization phase.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Please refer to Figure 6 , this embodiment provides another pixel circuit, its main difference from Embodiment 2 is that a fifth transistor 28 is added, and the control electrode of the fifth transistor 28 is connected to the fourth scanning signal terminal V SN[n] , the first pole is connected to the fourth voltage source signal terminal for inputting a constant reference voltage V REF , the second electrode is connected to the control electrode of the first transistor 21 . Under the control of the fourth scanning signal, the fifth transistor 28 provides a constant reference voltage V REF The benefit of doing this is that the row programming time can be greatly reduced, making the pixel circuit more suitable for large-area, high-resolution, high-frame-rate displays.
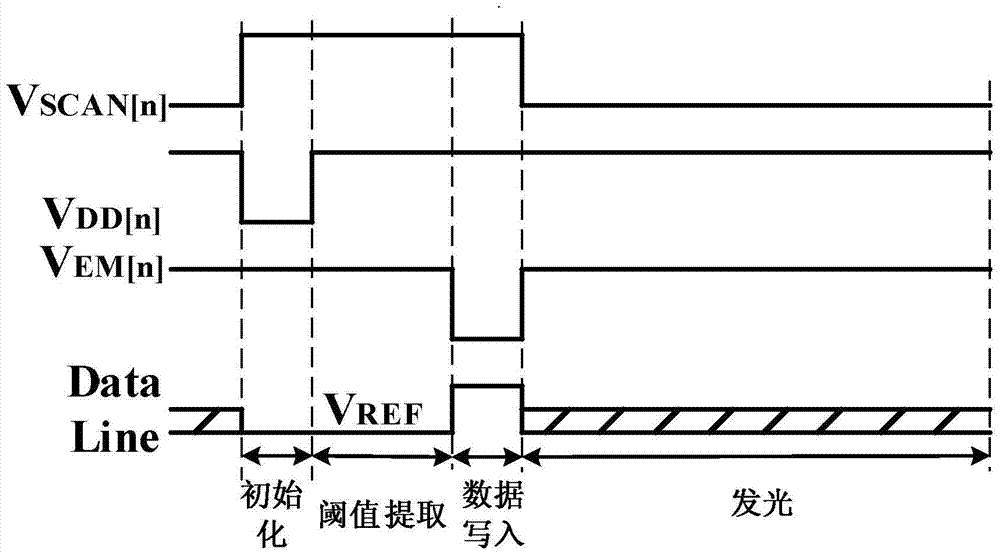
[0103] The driving signal waveform diagram of the pixel circuit in this embodiment is as follows Figure 7 As shown, a frame time T is also divided into four phases: an initialization phase, a thresho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com