Nitrogen source compensation method for reducing major higher alcohol content of yellow wine
A compensation method and higher alcohol technology, applied in the field of nitrogen source compensation, can solve problems such as complex fermentation systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
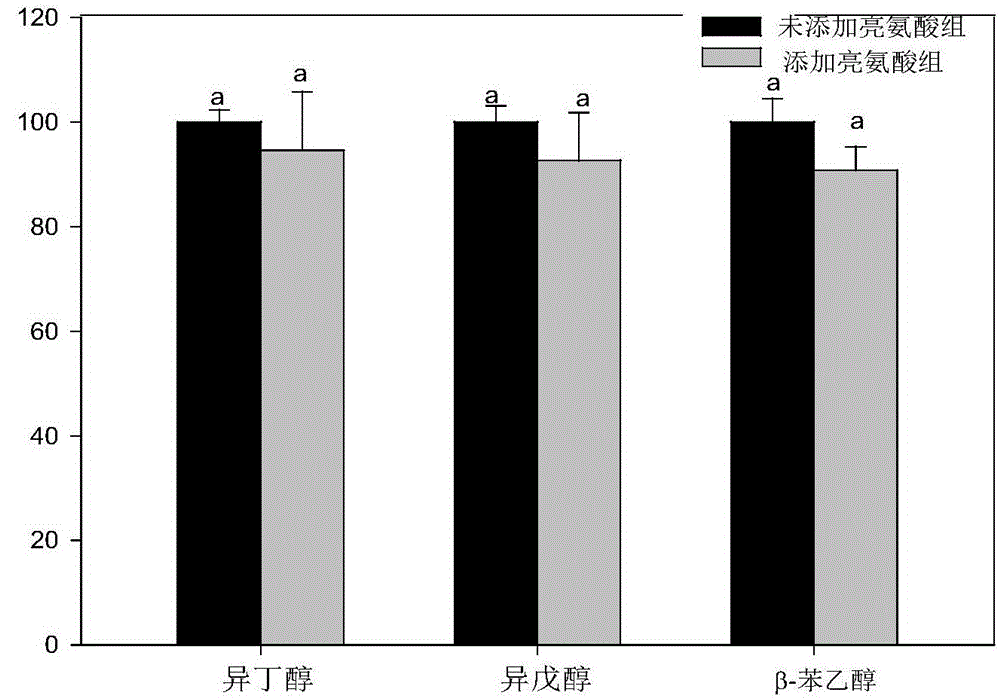
[0027] Example 1: Effect of leucine on the content of main higher alcohols in rice wine
[0028] (1) Rice soaking: soak the glutinous rice in water for no more than 24 hours;
[0029] (2) Steamed rice: Rinse the soaked glutinous rice and cook until soft and rotten without white heart;
[0030] (3) Put into the tank: After cooling the steamed glutinous rice, transfer it to the brewing tank, add water and mix according to the ratio of 1:3 to water.
[0031] (4) Nitrogen source compensation: add leucine to the brewing tank according to the addition amount of 150mg / L;
[0032] (5) Fermentation: add a certain amount of yeast culture liquid and wheat koji, mix well, pre-ferment at 28°C-30°C, and post-ferment at 16°C.
[0033] (6) Detection of higher alcohols: detection of higher alcohols in rice wine by headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with GC-MS;
[0034] (7) After the fermentation is over, check the alcohol content in rice wine with reference to the method for det...
Embodiment 2
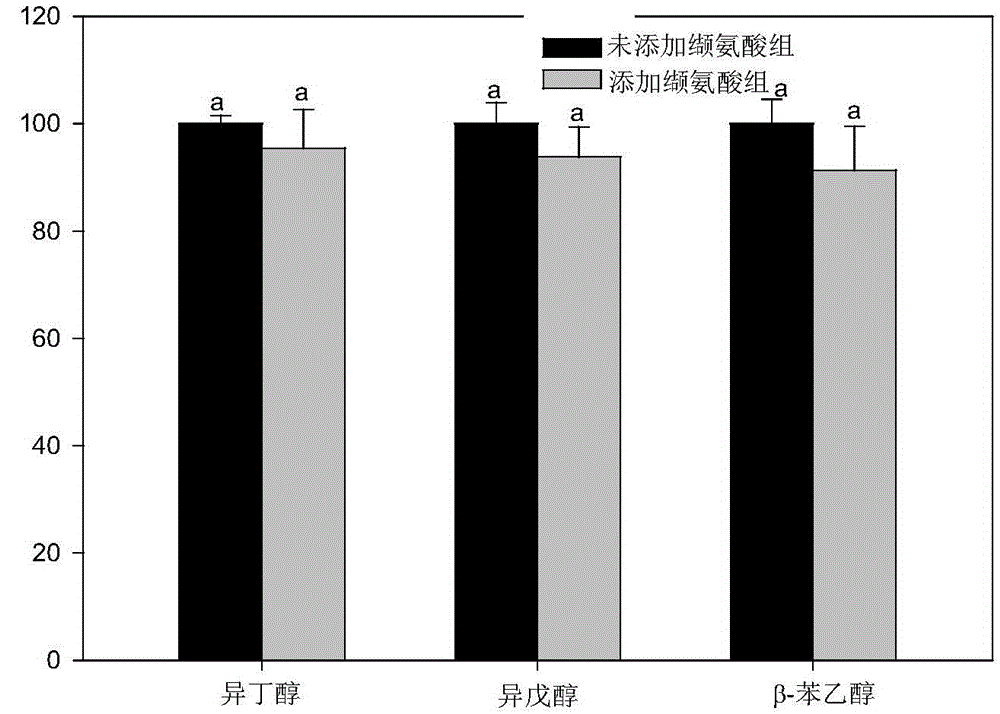
[0036] Embodiment 2: The influence of valine on the main higher alcohol content of yellow rice wine
[0037] (1) soaking rice: soaking glutinous rice in water;
[0038] (2) Steamed rice: Rinse the soaked glutinous rice and cook until soft and rotten without white heart;
[0039] (3) Put into the tank: After cooling the steamed glutinous rice, transfer it to the brewing tank, add water and mix well.
[0040] (4) Nitrogen source compensation: add valine to the brewing tank according to the addition amount of 150mg / L;
[0041] (5) Fermentation: add a certain amount of yeast culture liquid and wheat koji, mix well, pre-ferment at 28°C-30°C, and post-ferment at 16°C.
[0042] (6) Detection of higher alcohols: detection of higher alcohols in rice wine by headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with GC-MS;
[0043] (7) After the fermentation is over, check the alcohol content in rice wine with reference to the method for detecting the alcohol content of wine in the national...
Embodiment 3
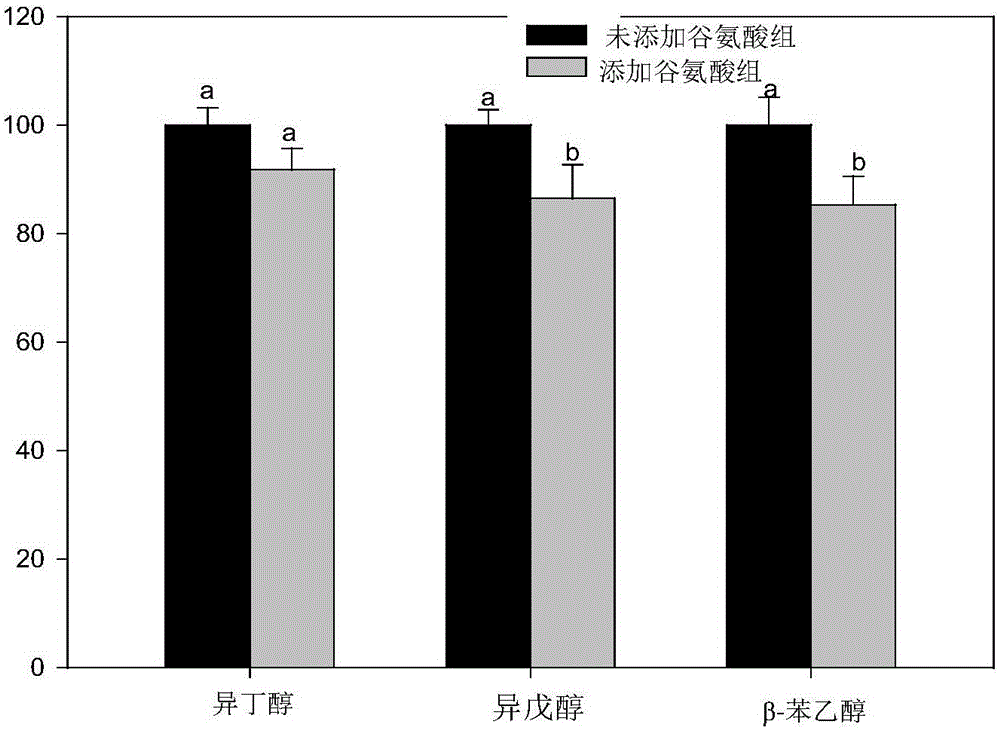
[0045] Example 3: Effect of glutamic acid on the main higher alcohol content of yellow rice wine
[0046] (1) Rice soaking: soak the glutinous rice in water for no more than 24 hours;
[0047] (2) Steamed rice: Rinse the soaked glutinous rice and cook until soft and rotten without white heart;
[0048] (3) Put into the tank: After cooling the steamed glutinous rice, transfer it to the brewing tank, add water and mix according to the ratio of 1:3 to water.
[0049] (4) Nitrogen source compensation: add glutamic acid to the brewing tank according to the addition amount of 150mg / L;
[0050] (5) Fermentation: add a certain amount of yeast culture liquid and wheat koji, mix well, pre-ferment at 28°C-30°C, and post-ferment at 16°C.
[0051] (6) Detection of higher alcohols: detection of higher alcohols in rice wine by headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with GC-MS;
[0052] (7) After the fermentation is over, check the alcohol content in rice wine with reference to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com