A method of magnetic field strengthening Hangjin 2# soil loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron to remove pollutants in water
A technology of nanometer zero-valent iron and magnetic field enhancement, applied in the fields of magnetic/electric field water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of reduced reactivity and effectiveness of zero-valent iron Degrade pollutants, reduce the possibility of engineering applications and other issues, to achieve the effect of not easy particle agglomeration and self-oxidation, good ion exchange capacity and adsorption capacity, and improve resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
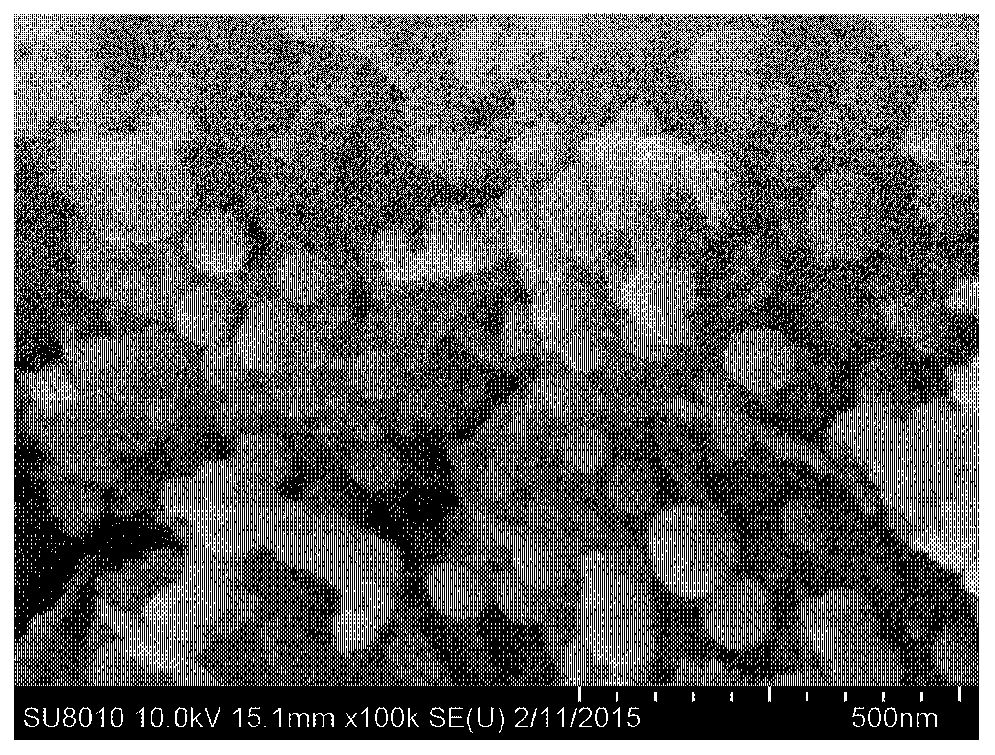
[0047] Preparation of composite magnetic material of Hangjin 2# soil loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron:
[0048] (1) 1.932g of FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in 50ml ethanol solution (40ml ethanol, 10ml water) to obtain a mixed solution.
[0049] (2) The mixed solution described in step (1) is put in the three-necked flask, and add 2.00g Hangjin soil through simply grinding through 200 mesh sieves, so that the mass ratio of nano zero-valent iron (NZVI) and Hangjin 2# soil is 1 :5.
[0050] (3) Pass nitrogen into the mixed solution described in step (2) and magnetically stir for 30 minutes to remove oxygen in the mixed solution.
[0051] (4) Dissolve 0.708 g of sodium borohydride in 100 ml of water, and transfer the sodium borohydride solution to a 250 ml pear-shaped flask.
[0052] (5) under the condition of continuous stirring and feeding nitrogen, the sodium borohydride solution described in step (4) is added in the three-necked flask described in step (3) at a rate o...
Embodiment 2
[0056] (1) Arrange a magnetic field around the reactor, the magnetic field used is a low-temperature superconducting magnetic field, and the magnetic field strength is about 40mT; in the complete mixing reactor, the initial concentration of methyl orange in printing and dyeing wastewater is 50mg / L, and the initial pH value is adjusted to 8.0.
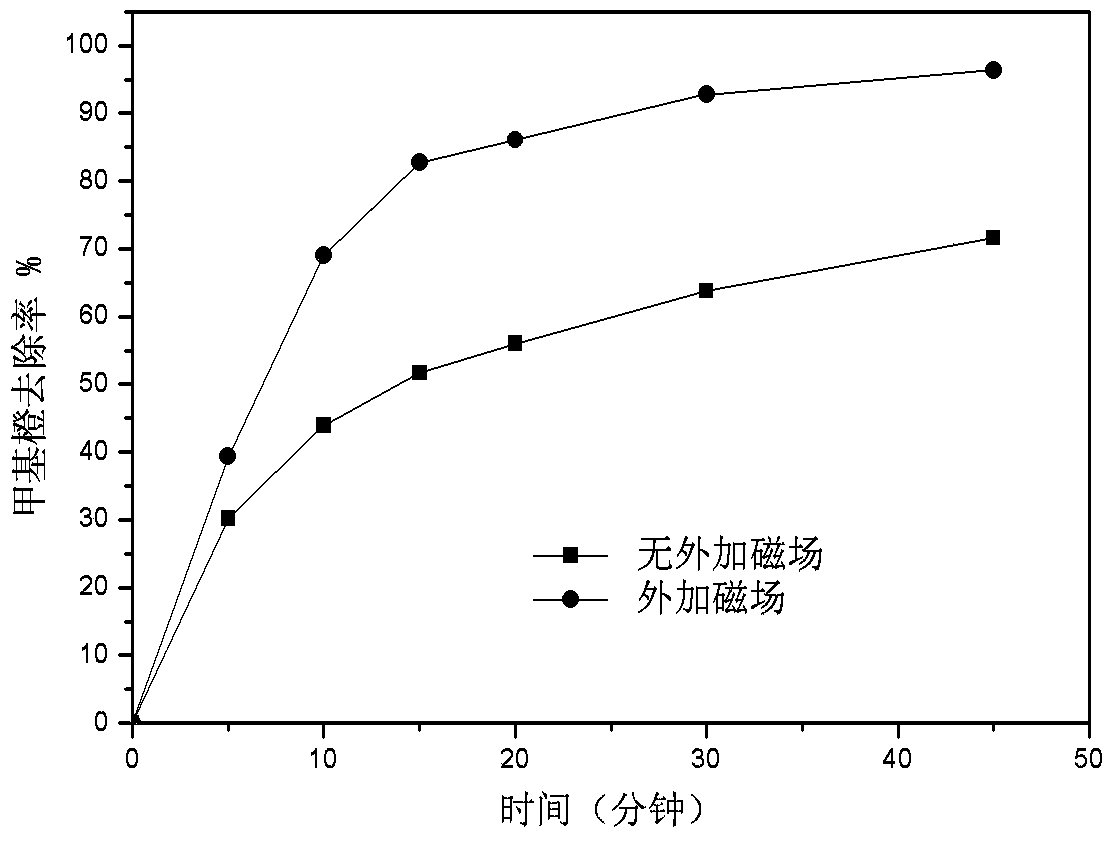
[0057] (2) In the above-mentioned methyl orange wastewater, first add the composite magnetic material of Hang Jin 2# loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron prepared by embodiment 1, the dosage of the composite magnetic material is 1g / L, and the condition that the external magnetic field exists Under the condition, the removal rate of methyl orange by the composite magnetic material can reach 92.8% within 30 minutes; while in the absence of a magnetic field, the removal rate of methyl orange is 63.76% in 30 minutes. The results are shown in figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the presence of an external magnetic field ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com