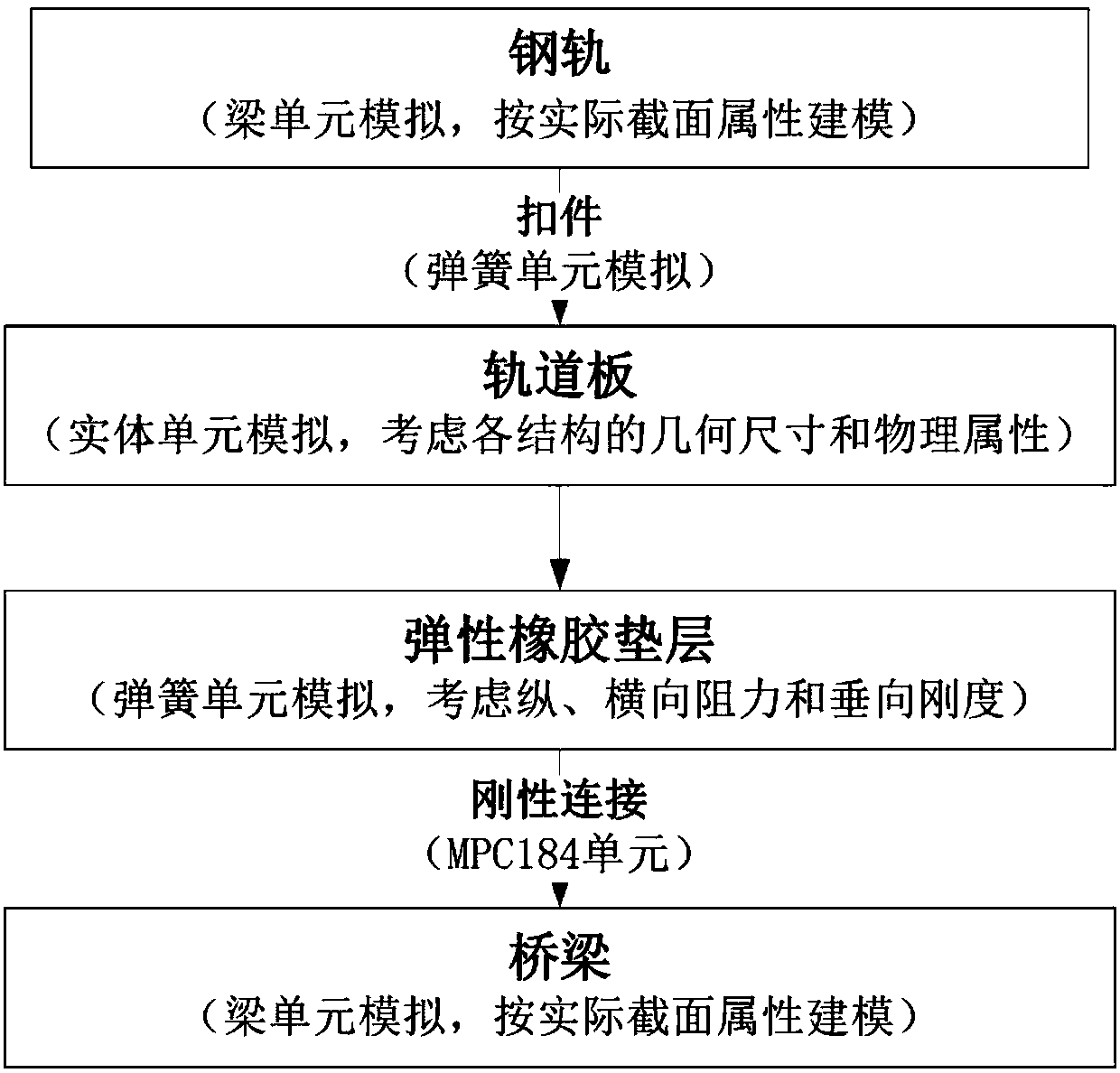
A Simplified Design Method for Ballastless Track Seamless Line of Extra Large Railway Bridge
A seamless line, ballastless track technology, applied in the direction of calculation, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult beam-rail interaction reaction, many model structural elements, unfavorable rapid check calculation, etc. Theoretical value and commercial promotion prospects, the effect of wide application and convenient modeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] In this example, in order to verify the correctness of the simplified model, a 62.5m single-span solid simply supported beam and a simplified simply supported beam were respectively established for comparative analysis. The calculation conditions are as follows: the temperature of the rail is raised by 40°C, and the temperature of the track slab is raised by 20°C , the temperature of the bridge rises by 25°C. Figure 8 is the rail longitudinal displacement diagram of the two calculation models under the action of temperature load, Figure 9 The rail longitudinal force diagrams of the two calculation models under the action of temperature load. Table 1 shows the size and calculation time of the two calculation models, and Table 2 lists the calculation results of the two calculation models under the same temperature load:
[0056] Table 1: Model size and computation time for two computational models
[0057]
solid model
simplified model
model siz...
Embodiment 2
[0062] In this example, in order to verify the correctness of the simplified model, a 62.5m single-span solid simply supported beam and a simplified simply supported beam were respectively established for comparative analysis. The calculation conditions are as follows: the vehicle load is calculated according to the ZK load, Apply a deflection force, the magnitude of the deflection force is 64kN / m / line, the loading diagram is as follows Figure 8 shown. Figure 10 are the rail longitudinal displacement diagrams of the two calculation models under the flexural load, Figure 11 The rail longitudinal force diagrams of two calculation models under the action of flexural load. Table 3 shows the size and calculation time of the two calculation models, and Table 4 lists the calculation results of the two calculation models under the same flexural load:
[0063] Table 3: Model size and computation time for two computational models
[0064]
solid model
simplified mo...
Embodiment 3
[0069] In this embodiment, a 62.5m single-span solid simply supported beam and a simplified simply supported beam are respectively established for comparative analysis, and the calculation conditions are as follows: the load is taken as ZK live load, and the braking rate is 0.164. Figure 13 The rail longitudinal displacement diagrams of the two calculation models under the braking load, Figure 14 The rail longitudinal force diagrams of the two calculation models under the braking load. Table 5 shows the size and calculation time of the two calculation models, and Table 6 lists the calculation results of the two calculation models under the same braking load:
[0070] Table 5: Model size and computation time for two computational models
[0071]
solid model
simplified model
model size
163MB
29.2MB
calculating time
149s
32s
[0072] Table 6: Calculation results of two calculation models under the same braking load
[0073] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com