A graph data storage and query method for large-scale social networks
A social network and data storage technology, applied in the direction of memory address/allocation/relocation, etc., can solve the problem that the server program cannot proxy data requests from different maps, cannot effectively support graph computing, and the graph database is difficult to access and update graph data, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0063] Example 1 data access instance
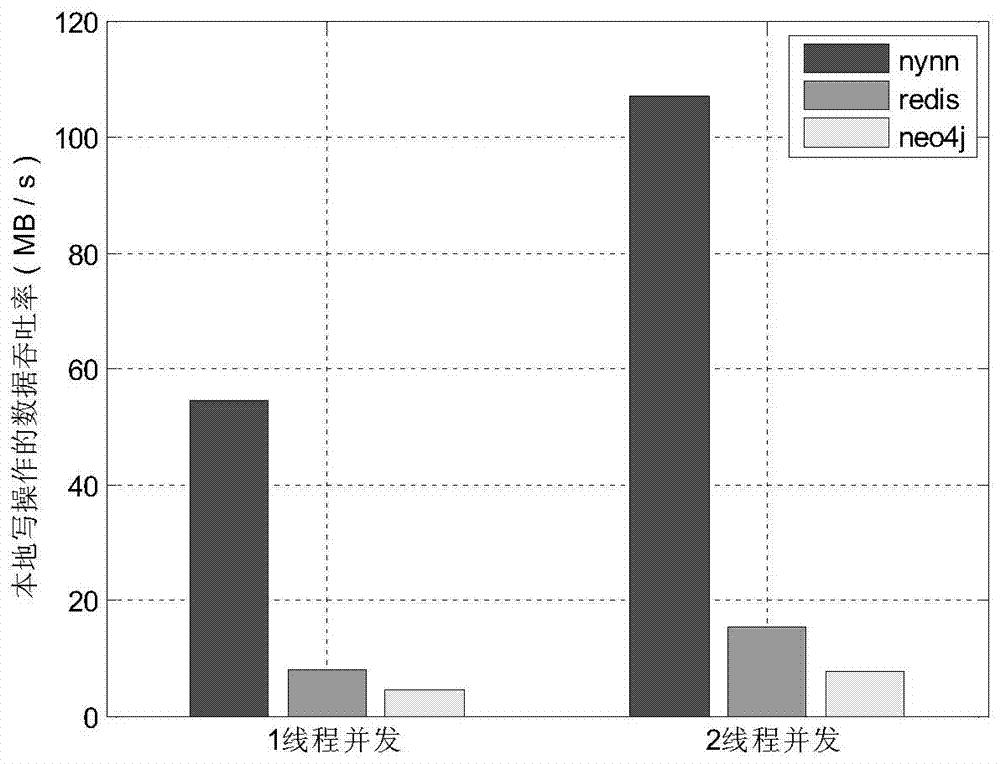
[0064] The present invention has tested the writing performance of the present invention and comparative system Redis and Neo4j under different concurrency, and the writing performance has taken the average value under ten data sets, wherein in the test image 3 Among them, the present invention is represented by NYNN.
[0065] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that the local writing performance of the present invention is obviously better than Redis and Neo4j, and the design of metadata, the data transmission format and the mechanism of data writing affect the writing performance. First of all, the division of graph data in the present invention adopts continuous equal-width vertex intervals, and the metadata can be cached locally through the first data write request, and then the metadata cached locally can be used for data addressing, which reduces the addressing IO overhead. When writing data, write it to the local memory-mapped f...
example 2
[0074] Instance 2 data update instance
[0075] This paper tests the data updating performance of the present invention and comparative systems Redis and Neo4j, and the performance takes the average value under ten data sets.
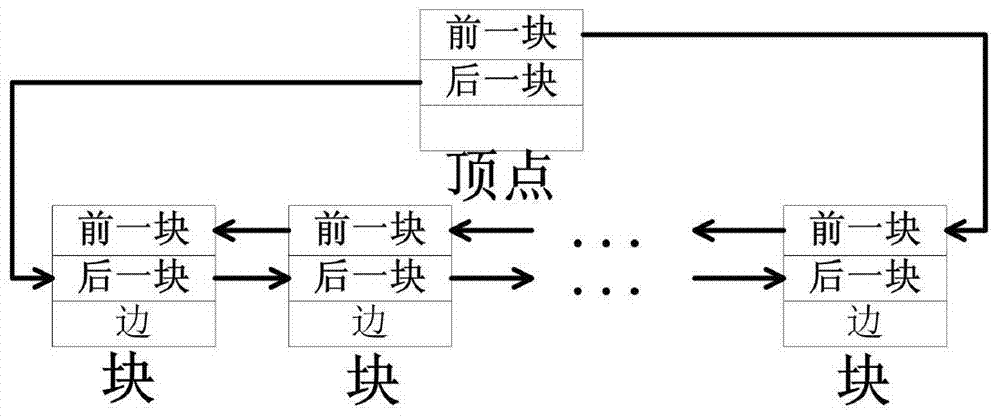
[0076] Such as Figure 8 As shown, for the incremental update of data, the present invention adopts a chained distribution method, which can eliminate the problem of frequent data movement caused by data insertion and deletion. However, Redis and Neo4j adopt the method of sequential allocation. As the data is updated, the data needs to be moved and relocated. During this process, new query processing cannot be performed.
example 3
[0077] Example 3 Data Remote Access Example
[0078] This paper tests the performance difference of the present invention with and without prefetch mechanism. The present invention provides multiple data prefetch mechanisms, which is convenient for the upper layer application to select the best data prefetch mode based on its own application background. This experiment uses BFS prefetching. The algorithm used in the experiment is to count the total number of edges in the graph data set. The idea of the algorithm is: divide the vertices of the graph into n slices, and each slice specifies a thread for processing. All threads Parallel access to graph data in the present invention. The thread puts the vertices to be visited in the access request into the queue, then processes the vertices at the head of the queue, visits the neighborhood of the vertices, and counts the number of vertices and edges. If the end point of the current edge is located in the shard to which the thre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com