Large-caliber rotationally symmetric non-imaging free-form surface reflector and design method thereof
A curved mirror, rotationally symmetric technology, applied in the direction of condensing mirror, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the uniformity of the solar reflective surface light spot, difficult to obtain high-precision surface shape, etc., to achieve high precision and simplified processing technology. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
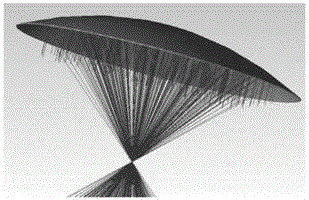
[0058] A large-aperture rotationally symmetrical non-imaging free-form surface reflector of the present invention and a design method thereof, the specific steps are:
[0059] 1. Design curve
[0060] Ray Equal Projection
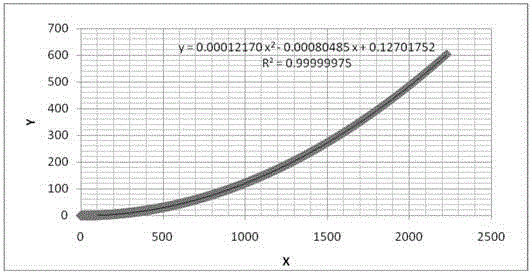
[0061] Suppose a beam of parallel light is incident on the reflective mirror surface, after being reflected by the reflective surface, the outgoing light is distributed on the receiving surface in equal proportions according to the projected radial length, as shown in the attached figure 1 shown. The incident light irradiates the Cn-1 and Cn points of the reflector, and the coordinates in the x direction are xn-1 and xn respectively. They are x'n-1 and x'n respectively, the mirror size is known to be L, and the spot size is D, according to the ratio distribution:
[0062] L D = C n - 1 R ...
Embodiment 2
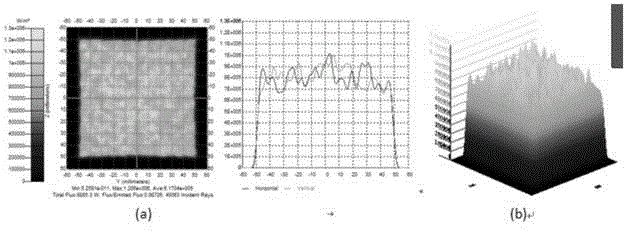
[0091] Import the free-form surface mirror obtained under the given conditions in Example 1 into the ray tracing software for optical simulation, simulate and calculate 1 million rays, and the irradiance diagram on the receiving surface is as follows Figure 5 As shown, (a) is a two-dimensional irradiance map, and (b) is a three-dimensional irradiance distribution map. It can be clearly seen from the figure that in the range of 100×100mm, the light irradiance distribution is quite uniform , the minimum irradiance is 68w / cm 2 , the average irradiance is 100w / cm 2 . The ratio of the minimum irradiance to the average irradiance in the interval is used as the criterion for judging the uniformity of the light spot. Therefore, the final uniformity of the design of the present invention is 80.9%. Regardless of the loss of reflective layer material, the optical efficiency of the receiving surface can reach 98.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0093] The acceptance angle analysis of the free-form reflector surface obtained under the given conditions in Example 1 shows that when the incident light is shifted, the light effect is also reduced. The relationship between the two is as follows Figure 6 shown. When the light effect is reduced to 90% of the light effect of 0°, the incident light angle at this time is the acceptance angle, and the designed acceptance angle is 0.41°. When the incident angle shifts, the light efficiency decreases, and the light intensity distribution on the receiving surface also changes accordingly. Figure 7 , Figure 8 , Figure 9 , Figure 10 Shown are the corresponding spot irradiance distribution diagrams when the incident angles are 0°, 0.2°, 0.4°, and 0.6°, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com