Method for positioning low-frequency oscillation disturbance source of electric power system
A disturbance source location, low frequency oscillation technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve problems such as the location method of the disturbance source of the low frequency oscillation that is not seen, and achieve the effect of avoiding further expansion and avoiding failures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] like figure 1 As shown, the specific conditions of the power system low-frequency oscillation disturbance source location method described in this embodiment are as follows:
[0040] 1) With the help of the data recording function of the WAMS system, the real-time monitored active power signal and its S-transformed image are obtained, and the S-transformed image is used to judge whether the power grid has low-frequency oscillation, as follows:
[0041] The S-transform of active power signal x(t) is defined as:
[0042] S ( τ , f ) = ∫ - ∞ ∞ x ( t ) ( | f | 2 π e ...
Embodiment 2
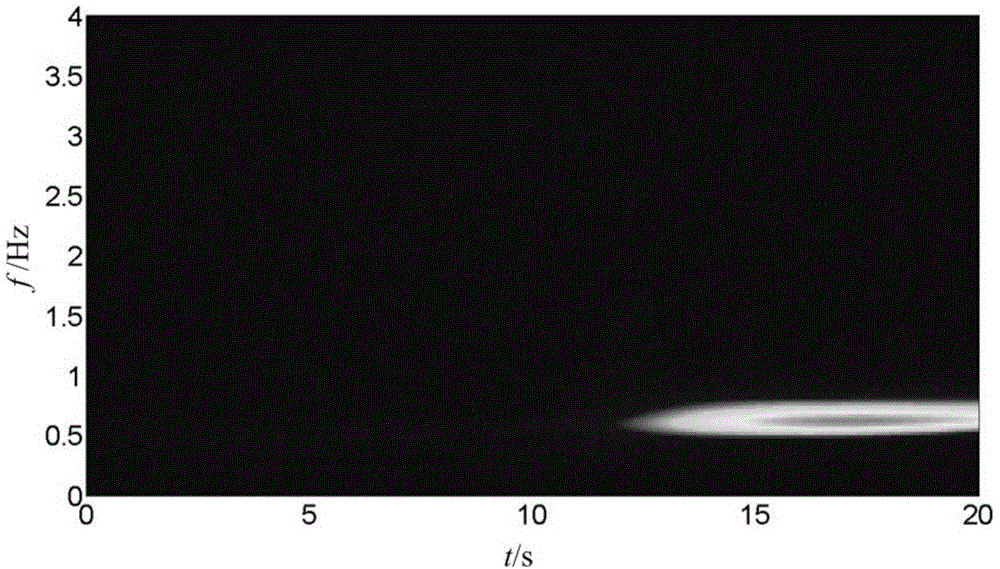
[0070] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment takes the active power data monitored by the PMU of a domestic provincial power grid on May 8, 2013 as an example, such as Figure 6 shown. Figure 7 is the S-transform image corresponding to the data. from Figure 6 It can be intuitively judged that low-frequency oscillation has occurred in the power grid, and there are currently three oscillation modes.
[0071] Extract the amplitude-frequency information of the S matrix, such as Figure 8 shown. The threshold δ is set to 2. It can be seen that there is a dominant oscillation mode with a frequency of 0.20 Hz at the current moment.
[0072] Extract the time and amplitude information corresponding to the dominant oscillation frequency, and perform differential processing, the result is as follows Figure 9 shown. From this, the starting time t of the low frequency oscillation can be determined k = 11.2s.
[0073] Finally, the disturbance source is locked ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com